Abstract
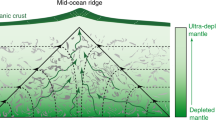
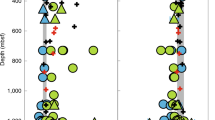
Degassing of the Earth's mantle through magmatism results in the irreversible loss of helium to space, and high 3He/4He ratios observed in oceanic basalts have been considered the main evidence for a ‘primordial’ undegassed deep mantle reservoir. Here we present a new global data compilation of ocean island basalts, representing upwelling ‘plumes’ from the deep mantle, and show that island groups with the highest primordial signal (high 3He/4He ratios) have striking chemical and isotopic similarities to mid-ocean-ridge basalts. We interpret this as indicating a common history of mantle trace element depletion through magmatism. The high 3He/4He in plumes may thus reflect incomplete degassing of the deep Earth during continent and ocean crust formation. We infer that differences between plumes and the upper-mantle source of ocean-ridge basalts reflect isolation of plume sources from the convecting mantle for ∼1–2 Gyr. An undegassed, primordial reservoir in the mantle would therefore not be required, thus reconciling a long-standing contradiction in mantle dynamics.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lupton, J. E. & Craig, H. Excess 3He in oceanic basalts; evidence for terrestrial primordial helium. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 26, 133–139 (1975)
Kurz, M. D., Jenkins, W. J. & Hart, S. R. Helium isotopic systematics of oceanic islands and mantle heterogeneity. Nature 297, 43–47 (1982)
Hart, S. R., Hauri, E. H., Oschmann, L. A. & Whitehead, J. A. Mantle plumes and entrainment: Isotopic evidence. Science 256, 517–520 (1992)
Farley, K. A., Natland, J. H. & Craig, H. Binary mixing of enriched and undegassed (primitive?) mantle components (He, Sr, Nd, Pb) in Samoan lavas. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 111, 183–199 (1992)
O'Nions, R. K., Evensen, N. M. & Hamilton, P. J. Geochemical modeling of mantle differentiation and crustal growth. J. Geophys. Res. 84, 6091–6101 (1979)
Allègre, C. J., Staudacher, T. & Sarda, P. Rare gas systematics: formation of the atmosphere, evolution and structure of the earth's mantle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 81, 127–150 (1987)
Graham, D. W. in Noble Gases in Geochemistry and Cosmochemistry (eds Porcelli, D., Ballentine, C. J. & Wieler, R.) 247–317 (Mineralogical Society of America, Washington DC, 2002)
Kurz, M. D., Jenkins, W. J., Hart, S. R. & Clague, D. Helium isotopic variations in volcanic rocks from Loihi Seamount and the Island of Hawaii. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 66, 388–406 (1983)
Graham, D. W., Humphris, S. E., Jenkins, W. J. & Kurz, M. D. Helium isotope geochemistry of some volcanic rocks from Saint Helena. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 110, 121–131 (1992)
Hanyu, T. & Kaneoka, I. The uniform and low 3He/4He ratios of HIMU basalts as evidence for their origin as recycled materials. Nature 390, 273–276 (1997)
Moreira, M. & Kurz, M. D. Subducted oceanic lithosphere and the origin of the ‘high mu’ basalt helium isotopic signature. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 189, 49–57 (2001)
Stuart, F. M., Lass-Evans, S., Fitton, J. G. & Ellam, R. M. High 3He/4He ratios in picritic basalts from Baffin Island and the role of a mixed reservoir in mantle plumes. Nature 424, 57–59 (2003)
Hofmann, A. W., Jochum, K. P., Seufert, M. & White, W. M. Nb and Pb in oceanic basalts: new constraints on mantle evolution. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 79, 33–45 (1986)
Zindler, A. & Hart, S. R. Helium: problematic primordial signals. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 79, 1–8 (1986)
Hofmann, A. W. Mantle geochemistry: the message from oceanic volcanism. Nature 385, 219–229 (1997)
Coltice, N. & Ricard, Y. Geochemical observations and one layer mantle convection. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 174, 125–137 (1999)
Creager, K. C. & Jordan, T. H. Slab penetration into the lower mantle. J. Geophys. Res. 89, 3031–3049 (1984)
Dziewonski, A. M. & Woodhouse, J. H. Global images of the Earth's interior. Science 236, 37–48 (1987)
Grand, S. P. & van der Hilst, R. D. Global seismic tomography: A snapshot of convection in the Earth. GSA Today 7, 1–7 (1997)
van der Hilst, R. D. & Karason, H. Compositional heterogeneity in the bottom 1000 kilometers of Earth's mantle: Toward a hybrid convection model. Science 283, 1885–1888 (1999)
Abedini, A. A. & Hurwitz, S. A global dataset of noble gas concentrations and their isotopic ratios in volcanic areas. Eos Trans. AGU 85, abstract V51B–0524 (2004)
O'Nions, R. K. & Oxburgh, E. R. Heat and helium in the Earth. Nature 306, 429–431 (1983)
Mukhopadhyay, S., Lassiter, J. C., Farley, K. A. & Bogue, S. W. Geochemistry of Kauai shield-stage lavas: Implications for the chemical evolution of the Hawaiian plume. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 4, doi:10.1029/2002GC000342 (2003)
Farley, K. A. Rapid cycling of subducted sediments into the Samoan mantle plume. Geology 23, 531–534 (1995)
Hofmann, A. W. & White, W. M. Mantle plumes from ancient oceanic crust. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 57, 421–436 (1982)
Craig, H., Clarke, W. B. & Beg, M. A. Excess 3He in deep water on the East Pacific Rise. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 26, 125–132 (1975)
Hauri, E. H., Lassiter, J. C. & DePaolo, D. J. Osmium isotope systematics of drilled lavas from Mauna Loa, Hawaii. J. Geophys. Res. 101, 11793–11806 (1996)
Kellogg, L. H. & Wasserburg, G. J. The role of plumes in mantle helium flux. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 99, 276–289 (1990)
Porcelli, D. & Wasserburg, G. J. Mass transfer of helium, neon, argon, and xenon through a steady-state upper mantle. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 59, 4921–4937 (1995)
Anderson, D. L. A model to explain the various paradoxes associated with mantle noble gas geochemistry. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 9087–9092 (1998)
Albarède, F. Time-dependent models of U–Th–He and K–Ar evolution and the layering of mantle convection. Chem. Geol. 145, 413–429 (1998)
Montelli, R. et al. Finite-frequency tomography reveals a variety of plumes in the mantle. Science 303, 338–343 (2004)
Morgan, J. P. & Morgan, J. W. Two-stage melting and the geochemical evolution of the mantle: a recipe for mantle plum-pudding. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 170, 215–239 (1999)
Ballentine, C. J., van Keken, P. E., Porcelli, D. & Hauri, E. H. Numerical models, geochemistry and the zero-paradox noble-gas mantle. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 360, 2611–2631 (2002)
Allègre, C. J., Hofmann, A. W. & O'Nions, R. K. The argon constraints on mantle structure. Geophys. Res. Lett. 23, 3555–3557 (1996)
Davies, G. F. Geophysically constrained mantle mass flows and the 40Ar budget: A degassed lower mantle? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 166, 149–162 (1999)
Lassiter, J. C. Role of recycled oceanic crust in the potassium and argon budget of the Earth: Toward a resolution of the ‘missing argon’ problem. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 5, doi:10.1029/2004GC000711 (2004)
Wood, B. J. & Blundy, J. D. The effect of cation charge on crystal-melt partitioning of trace elements. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 188, 59–71 (2001)
Parman, S. W., Kurz, M. D., Hart, S. R. & Grove, T. L. Solubility of helium in olivine at 1 atmosphere. Eos Trans. AGU 85, abstract U41A–0725 (2004)
Staudacher, T. & Allègre, C. J. Terrestrial xenology. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 60, 389–406 (1982)
Goldstein, S. L., O'Nions, R. K. & Hamilton, P. J. A Sm-Nd isotopic study of atmospheric dusts and particulates from major river systems. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 70, 221–236 (1984)
Farley, K. A., Maierreimer, E., Schlosser, P. & Broecker, W. S. Constraints on mantle He-3 fluxes and deep-sea circulation from an oceanic general circulation model. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 100, 3829–3839 (1995)
Hart, S. R. A large scale isotope anomaly in the southern hemisphere mantle. Nature 309, 753–757 (1984)
Salters, V. J. M. & Stracke, A. Composition of the depleted mantle. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 5, doi:10.1029/2003GC000597 (2004)
Sun, S.-S. & McDonough, W. F. in Magmatism in the Ocean Basins (eds Saunders, A. D. & Norry, M. J.) 313–345 (Blackwell Scientific, Oxford/Boston, 1989)
Harper, C. L. & Jacobsen, S. B. Noble gases and Earth's accretion. Science 273, 1814–1818 (1996)
Porcelli, D. & Ballentine, C. J. in Noble Gases in Geochemistry and Cosmochemistry (eds Porcelli, D., Ballentine, C. J. & Wieler, R.) 411–480 (Mineralogical Society of America, Washington DC, 2002)
Tolstikhin, I. & Hofmann, A. W. Early crust on top of the Earth's core. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 148, 109–130 (2004)
Lehnert, K., Su, Y., Langmuir, C., Sarbas, B. & Nohl, U. A global geochemical database structure for rocks. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 1, doi:10.1029/1999GC000026 (2000)
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Abedini for sharing her noble gas database; W. White and D. Graham for comments that helped to improve the manuscript; A.W. Hofmann and A. Class for discussions. This study was supported by National Science Foundation grants. This is LDEO Contribution number 6791.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Reprints and permissions information is available at npg.nature.com/reprintsandpermissions. The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Methods
Details of global data compilation and data filters, grouping of ocean island into helium isotope groups. Details of model calculation of the incomplete degassing model for the Earth' mantle, as well as calculation of plume source formation ages. Discussion of consistency of neon isotopes with the incomplete degassing model. This file also contains additional references. (DOC 82 kb)
Supplementary Figure S1
Neon-helium isotope relationships in OIB and MORB. This figure shows that neon data are consistent with range of helium isotope ratios reflecting variable production rates of radiogenic 4He in plume sources with variable Th+U. (DOC 165 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Class, C., Goldstein, S. Evolution of helium isotopes in the Earth's mantle. Nature 436, 1107–1112 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03930
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03930
This article is cited by
-
Earth’s mantle composition revealed by mantle plumes
Nature Reviews Earth & Environment (2023)
-
Helium in diamonds unravels over a billion years of craton metasomatism
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Formation of Venus, Earth and Mars: Constrained by Isotopes
Space Science Reviews (2021)
-
Distinct formation history for deep-mantle domains reflected in geochemical differences
Nature Geoscience (2020)
-
Chemical structure of the Earth’s mantle defined by fast diffusion elements like helium
Acta Geochimica (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.