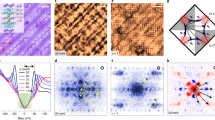
Abstract
The phase diagram of hole-doped copper oxides shows four different electronic phases existing at zero temperature. Familiar among these are the Mott insulator, high-transition-temperature superconductor and metallic phases. A fourth phase, of unknown identity, occurs at light doping along the zero-temperature bound of the ‘pseudogap’ regime1. This regime is rich in peculiar electronic phenomena1, prompting numerous proposals that it contains some form of hidden electronic order. Here we present low-temperature electronic structure imaging studies of a lightly hole-doped copper oxide: Ca2-xNaxCuO2Cl2. Tunnelling spectroscopy (at energies |E| > 100 meV) reveals electron extraction probabilities greatly exceeding those for injection, as anticipated for a doped Mott insulator. However, for |E| < 100 meV, the spectrum exhibits a V-shaped energy gap centred on E = 0. States within this gap undergo intense spatial modulations, with the spatial correlations of a four CuO2-unit-cell square ‘checkerboard’, independent of energy. Intricate atomic-scale electronic structure variations also exist within the checkerboard. These data are consistent with an unanticipated crystalline electronic state, possibly the hidden electronic order, existing in the zero-temperature pseudogap regime of Ca2-xNaxCuO2Cl2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Timusk, T. & Statt, B. The pseudogap in high-temperature superconductors: an experimental survey. Rep. Prog. Phys. 62, 61–122 (1999)
Hoffman, J. E. et al. A four unit cell periodic pattern of quasi-particle states surrounding vortex cores in Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ . Science 295, 466–469 (2002)
Vershinin, M. et al. Local ordering in the pseudogap state of the high-Tc superconductor Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ . Science 303, 1995–1998 (2004)
McElroy, K. et al. Destruction of antinodal state coherence via ‘checkerboard’ charge ordering in strongly underdoped superconducting Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ. Preprint at 〈http://arXiv.org/cond-mat/0406491〉 (2004).
Howald, C., Fournier, P. & Kapitulnik, A. Inherent inhomogeneities in tunneling spectra of Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8-x crystals in the superconducting state. Phys. Rev. B 64, 100504 (2001)
Cren, T., Roditchev, D., Sacks, W. & Klein, J. Nanometer scale mapping of the density of states in an inhomogeneous superconductor. Europhys. Lett. 54, 84–90 (2001)
McElroy, K. et al. Relating atomic-scale electronic phenomena to wave-like quasiparticle states in superconducting Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ . Nature 422, 592–596 (2003)
Ronning, F. et al. Photoemission evidence for a remnant Fermi surface and a d-wave-like dispersion in insulating Ca2CuO2Cl2 . Science 282, 2067–2072 (1998)
Ronning, F. et al. Evolution of a metal to insulator transition in Ca2-xNaxCuO2Cl2 as seen by angle-resolved photoemission. Phys. Rev. B 67, 165101 (2003)
Hiroi, Z., Kobayashi, N. & Takano, M. Probable hole-doped superconductivity without apical oxygens in (Ca, Na)2CuO2Cl2 . Nature 371, 139–141 (1994)
Kohsaka, Y. et al. Growth of Na-doped Ca2CuO2Cl2 single crystals under high pressures of several GPa. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 12275–12278 (2002)
Kohsaka, Y. et al. Imaging nano-scale electronic inhomogeneity in lightly doped Mott insulator Ca2-xNaxCuO2Cl2 . Phys. Rev. Lett. (2004) (in the press); preprint at 〈http://arXiv.org/cond-mat/0406089〉
Wei, J. Y. T. et al. Quasiparticle tunneling spectra of the high-Tc mercury cuprates: Implications of the d-wave two-dimensional van Hove scenario. Phys. Rev. B 57, 3650–3662 (1998)
Fu, H. C., Davis, J. C. & Lee, D.-H. On the charge ordering observed by recent STM experiments. Preprint at 〈http://arXiv.org/cond-mat/0403001〉 (2004)
Varma, C. M. Non-Fermi-liquid states and pairing instability of a general model of copper oxide metals. Phys. Rev. B 55, 14554–14580 (1997)
Chakravarty, S., Laughlin, R. B., Morr, D. K. & Nayak, C. Hidden order in the cuprates. Phys. Rev. B 63, 094503 (2001)
Lee, P. A. Pseudogap and competing states in underdoped cuprates. Preprint at 〈http://arXiv.org/cond-mat/0307508〉 (2003).
Zaanen, J. & Gunnarsson, O. Charged magnetic domain lines and the magnetism of high-Tc oxides. Phys. Rev. B 40, 7391–7394 (1989)
Machida, K. Magnetism in La2CuO4 based compounds. Physica C 158, 192–196 (1989)
White, S. R. & Scalapino, D. J. Phase separation and stripe formation in the two-dimensional t-J model: A comparison of numerical results. Phys. Rev. B 61, 6320–6326 (2000)
Emery, V. J., Kivelson, S. A. & Tranquada, J. M. Stripe phases in high-temperature superconductors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 8814–8817 (1999)
Sachdev, S. Quantum criticality: Competing ground states in low dimensions. Science 288, 475–480 (2000)
Bosch, M., van Saarloos, W. & Zaanen, J. Shifting Bragg peaks of cuprate stripes as possible indications for fractionally charged kinks. Phys. Rev. B 63, 092501 (2001)
Kivelson, S. A., Fradkin, E. & Emery, V. J. Electronic liquid-crystal phases of a doped Mott insulator. Nature 393, 550–553 (1998)
Vojta, M. Superconducting charge-ordered states in cuprates. Phys. Rev. B 66, 104505 (2002)
Podolsky, D., Demler, E., Damle, K. & Halperin, B. I. Translational symmetry breaking in the superconducting state of the cuprates: Analysis of the quasiparticle density of states. Phys. Rev. B 67, 094514 (2003)
Chen, H.-D., Vafek, O., Yazdani, A. & Zhang, S.-C. Pair density wave in the pseudogap state of high temperature superconductors. Preprint at 〈http://arXiv.org/cond-mat/0402323〉 (2004).
Chen, H.-D., Hu, J.-P., Capponi, S., Arrigoni, E. & Zhang, S.-C. Antiferromagnetism and hole pair checkerboard in the vortex state of high Tc superconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 137004 (2002)
Tešanović, Z. Charge modulation, spin response, and dual Hofstadter butterfly in high-Tc cuprates. Preprint at 〈http://arXiv.org/cond-mat/0405235〉 (2004).
Anderson, P. W. A suggested 4 × 4 structure in underdoped cuprate superconductors: a Wigner supersolid. Preprint at 〈http://arXiv.org/cond-mat/0406038〉 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge and thank P. Coleman, E. Demler, M. Franz, J. E. Hoffman, P. A. Lee, K. Machida, K. McElroy, D. Pines, S. Sachdev, T. Senthil, T. Timusk, M. Vojta and J. Zaanen for discussions and communications. This work was supported by the ONR, NSF, MEXT, JST and NEDO. C.L. acknowledges support from a NSERC Postdoctoral Fellowship and Y.K. from a JPSJ Research Fellowship for Young Scientists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Figure 1
Doping dependence of the spectra from x = 0.08 to 0.12. (PDF 84 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
Topography and associated Fourier transform showing the existence of 1/4 and 3/4 signal in topographic signal. (PDF 282 kb)
Supplementary Figure 3
Raw spectra and averages from the white and red points of Fig. 3b from the main text. (PDF 100 kb)
Supplementary Figure 4
Doping dependence of the low temperature resistivity from x = 0.06 to 0.10. (PDF 101 kb)
Supplementary Figure 5
Low energy spectra along a line cut showing heterogeneous features possibly related to superconductivity in x = 0.12 sample. (PDF 278 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanaguri, T., Lupien, C., Kohsaka, Y. et al. A ‘checkerboard’ electronic crystal state in lightly hole-doped Ca2-xNaxCuO2Cl2. Nature 430, 1001–1005 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02861
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02861
This article is cited by
-
Robust charge-density-wave correlations in the electron-doped single-band Hubbard model
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Low-energy gap emerging from confined nematic states in extremely underdoped cuprate superconductors
npj Quantum Materials (2023)
-
Magnetic-field-sensitive charge density waves in the superconductor UTe2
Nature (2023)
-
Critical nematic correlations throughout the superconducting doping range in Bi2−zPbzSr2−yLayCuO6+x
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Charge order driven by multiple-Q spin fluctuations in heavily electron-doped iron selenide superconductors
Nature Communications (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.