Abstract
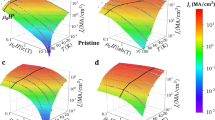
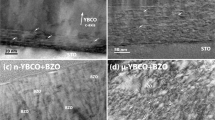
Following the discovery of type-II high-temperature superconductors in 1986 (refs 1, 2), work has proceeded to develop these materials for power applications. One of the problems, however, has been that magnetic flux is not completely expelled, but rather is contained within magnetic fluxons, whose motion prevents larger supercurrents. It is known that the critical current of these materials can be enhanced by incorporating a high density of extended defects to act as pinning centres for the fluxons3,4. YBa2Cu3O7 (YBCO or 123) is the most promising material for such applications at higher temperatures (liquid nitrogen)3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13. Pinning is optimized when the size of the defects approaches the superconducting coherence length (∼ 2–4 nm for YBCO at temperatures ≤77 K) and when the areal number density of defects is of the order of (H/2) × 1011 cm-2, where H is the applied magnetic field in tesla3,4. Such a high density has been difficult to achieve by material-processing methods that maintain a nanosize defect, except through irradiation5. Here we report a method for achieving a dispersion of ∼8-nm-sized nanoparticles in YBCO with a high number density, which increases the critical current (at 77 K) by a factor of two to three for high magnetic fields.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bednorz, J. G. & Muller, K. A. Possible high Tc superconductivity in the Ba-La-Cu-O system. Z. Phys. B 64, 189–193 (1986)
Wu, M. K. et al. Superconductivity at 93 K in a new mixed-phase Y-Ba-Cu-O compound system at ambient pressure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 908–910 (1987)
Larbalestier, D., Gurevich, A., Matthew Feldmann, D. & Polyanskii, A. High-Tc superconducting materials for electric power applications. Nature 414, 368–377 (2001)
Matsushita, T. Flux pinning in superconducting 123 materials. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 13, 730–737 (2000)
Civale, L. et al. Vortex confinement by columnar defects in YBa2Cu3O7 crystals: enhanced pinning at high fields and temperatures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 648–651 (1991)
Selvamanickam, V. et al. Fabrication of 100 A class, 1 m long coated conductor tapes by metal organic chemical vapor deposition and pulsed laser deposition. Physica C 392–396, 859–862 (2003)
Verebelyi, D. T. et al. Uniform performance of continuously processed MOD-YBCO-coated conductors using a textured Ni-W substrate. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 16, L19–L22 (2003)
Groves, J. R. et al. Recent progress in continuously processed IBAD MgO template meters for HTS applications. Physica C 382, 43–47 (2002)
Goyal, A. et al. Recent progress in the fabrication of high-Jc tapes by epitaxial deposition of YBCO on RABiTS. Physica C 357–360, 903–913 (2001)
Balachandran, U. et al. Development of coated conductors by inclined substrate deposition. Physica C 392–396, 806–814 (2003)
Kakimoto, K., Iijima, Y. & Saitoh, T. Fabrication of long-Y123 coated conductors by a combination of IBAD and PLD. Physica C 392–396, 783–789 (2003)
Yamasaki, H., Nakagawa, Y., Sawa, A., Obara, H. & Develos, K. Flux pinning effects of twin boundaries studied with unidirectionally twinned YBCO films. Physica C 372–376, 1885–1889 (2002)
Feenstra, R., Christen, D. K., Klabunde, C. E. & Budai, J. D. Role of oxygen vacancies in the flux-pinning mechanism, and hole-doping lattice disorder in high-current-density YBa2Cu3O7-x films. Phys. Rev. B 45, 7555–7558 (1993 1992)
Larbalestier, D. C. & Maley, M. P. Conductors from superconductors: conventional low-temperature and new high-temperature superconducting conductors. MRS Bull. 18, 50–56 (Aug. 1993)
Dam, B. et al. Origin of high critical currents in YBa2Cu3O7-x superconducting thin films. Nature 399, 439–442 (1999)
Pan, V. M. et al. Nature of magnetic field and angular dependencies of the critical current density in epitaxial HTS YBa2Cu3O7-x films. Physica C 388–389, 431–432 (2003)
Reichelt, K. Nucleation and growth of thin films. Vacuum 38, 1083–1099 (1988)
Redl, F. X., Murray, K.-S., Cho, C. B. & O'Brien, S. Three-dimensional binary superlattices of magnetic nanocrystals and semiconductor quantum dots. Nature 423, 968–971 (2003)
Springholz, G., Holy, V., Pinczolits, M. & Bauer, G. Self-organized growth of three-dimensional quantum-dot crystals with FCC-like stacking and a tunable lattice constant. Science 282, 734–737 (1998)
Liu, P., Zhang, Y. W. & Lu, C. Self-organized growth of three-dimensional quantum-dot superlattices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 3910–3912 (2002)
Haugan, T. et al. Island-growth of Y2BaCuO5 nanoparticles in (211∼1.5 nm/123∼10 nm)xN composite multilayer structures to enhance flux pinning of YBa2Cu3O7-δ films. J. Mater. Res. 18, 2618–2623 (2003)
Gross, R. E. & Campbell, A. M. Numerical calculation of elastic pinning parameters by point pins. Physica C 260, 188–196 (1996)
Haugan, T., Barnes, P. N., Brunke, L., Maartense, I. & Murphy, J. Effect of O2 partial pressure on YBa2Cu3O7-δ thin film growth by pulsed laser deposition. Physica C 297, 47–57 (2003)
Zhu, Y., Cai, Z. X., Budhani, R. C., Suenaga, M. & Welch, D. O. Structures and effects of radiation damage in cuprate superconductors irradiated with several-hundred-MeV heavy ions. Phys. Rev. B 48, 6436–6450 (1993)
Acknowledgements
The Air Force Office of Scientific Research supported this work. We thank J. Murphy, L. Brunke, J. Evans and T. Campbell for experimental assistance, and S. Apt of UES Inc. at the Wright-Patterson AFB Materials Directorate for assistance with SEM and TEM. We also thank R. Feenstra and A. A. Gapud at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) for providing Jc(H) data for a reference 123 film.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haugan, T., Barnes, P., Wheeler, R. et al. Addition of nanoparticle dispersions to enhance flux pinning of the YBa2Cu3O7-x superconductor. Nature 430, 867–870 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02792
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02792
This article is cited by
-
Impact of high growth rates on the microstructure and vortex pinning of high-temperature superconducting coated conductors
Nature Reviews Physics (2023)
-
Insulating nanoparticle induced pinning in YBCO superconductor: crossover from collective to strong pinning regimes
Applied Physics A (2023)
-
Interfacial Shearing and Transverse Normal Stress in a Superconducting Coated Conductor Strip with Combined Transport Current and Magnetic Field
Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism (2023)
-
Effectiveness of Two Pinning Profiles in Controlling Magnetic Critical Current Density in YBCO + YCMO Composites
Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism (2023)
-
Enhanced critical current density and pinning properties in KNbO3 nanoparticles added YBCO superconductor
Applied Physics A (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.