Abstract
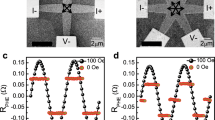
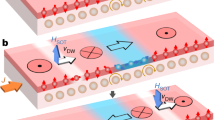
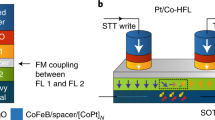
Magnetic information storage relies on external magnetic fields to encode logical bits through magnetization reversal. But because the magnetic fields needed to operate ultradense storage devices are too high to generate, magnetization reversal by electrical currents is attracting much interest as a promising alternative encoding method. Indeed, spin-polarized currents can reverse the magnetization direction of nanometre-sized metallic structures through torque1,2,3,4; however, the high current densities of 107–108 A cm-2 that are at present required exceed the threshold values tolerated by the metal interconnects of integrated circuits5,6. Encoding magnetic information in metallic systems has also been achieved by manipulating the domain walls at the boundary between regions with different magnetization directions7,8,9,10,11,12,13, but the approach again requires high current densities of about 107 A cm-2. Here we demonstrate that, in a ferromagnetic semiconductor structure, magnetization reversal through domain-wall switching can be induced in the absence of a magnetic field using current pulses with densities below 105 A cm-2. The slow switching speed and low ferromagnetic transition temperature of our current system are impractical. But provided these problems can be addressed, magnetic reversal through electric pulses with reduced current densities could provide a route to magnetic information storage applications.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Slonczewski, J. Current-driven excitation of magnetic multilayer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 159, L1–L7 (1996)
Berger, L. Emission of spin waves by a magnetic multilayer traversed by a current. Phys. Rev. B 54, 9353–9358 (1996)
Tsoi, M. et al. Excitation of a magnetic multilayer by an electric current. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 4281–4284 (1998) erratum (81), 493 (1998)
Albert, F. J., Katine, J. A., Buhrman, R. A. & Ralph, D. C. Spin-polarized current switching of a Co thin film nanomagnet. Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 3809–3811 (2000)
Sze, S. M. (ed.) VLSI Technology 412 (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1988)
Michael, N. L., Kim, C. U., Gillespie, P. & Augur, R. in Proc. Advanced Metallization Conf., 29–30 Oct. 2002, Tokyo (ed. Zaima, S.)) 42–43 (Office Sofiel, Tokyo, 2002)
Berger, L. Exchange interaction between ferromagnetic domain wall and electric current in very thin metallic films. J. Appl. Phys. 55, 1954–1956 (1984)
Freitas, P. P. & Berger, L. Observation of s-d exchange force between domain wall and electric current in very thin permalloy films. J. Appl. Phys. 57, 1266–1269 (1985)
Gan, L., Chung, S. H., Aschenbach, K. H., Dreyer, M. & Gomez, R. D. Pulsed-current-induced domain wall propagation in permalloy patterns observed using magnetic force microscope. IEEE Trans. Mag. 36, 3047–3049 (2000)
Grollier, J. et al. Switching a spin valve back and forth by current-induced domain wall motion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 509–511 (2003)
Tsoi, M., Fontana, R. E. & Parkin, S. S. P. Magnetic domain wall motion triggered by an electric current. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 2617–2619 (2003)
Vernier, N., Allwood, D. A., Atkinson, D., Cooke, M. D. & Cowburn, R. P. Domain wall propagation in magnetic nanowires by spin polarized current injection. Preprint at 〈http://lanl.arXiv.org/abs/cond-mat/0304549〉 (2003).
Yamaguchi, A. et al. Real-space observation of current-driven domain wall motion in submicron magnetic wires. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 077205 (2004)
Ohno, H. Making nonmagnetic semiconductors ferromagnetic. Science 281, 951–956 (1998)
Dietl, T., Ohno, H., Matsukura, F., Cibert, J. & Ferrand, D. Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science 287, 1019–1022 (2000)
Dietl, T., Ohno, H. & Matsukura, F. Hole-mediated ferromagnetism in tetrahedrally coordinated semiconductors. Phys. Rev. B 63, 195205 (2001)
Chiba, D., Takamura, K., Matsukura, F. & Ohno, H. Effect of low-temperature annealing on (Ga,Mn)As trilayer structures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 3020–3022 (2003)
Labaye, Y., Berger, L. & Coey, J. M. D. Domain walls in ferromagnetic nanoconstriction. J. Appl. Phys. 91, 5341–5346 (2002)
Salhi, E. & Berger, L. Current-induced displacements of Bloch walls in Ni-Fe films of thickness 120–740 nm. J. Appl. Phys. 76, 4787–4792 (1994)
Berger, L. Prediction of a domain-drag effect in uniaxial, non-compensated, ferromagnetic metals. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 35, 947–956 (1974)
Berger, L. Motion of magnetic domain wall traversed by fast-rising current pulses. J. Appl. Phys. 71, 2721–2726 (1992)
Tatara, G. & Kohno, H. Theory of current-driven domain wall motion: spin transfer versus momentum transfer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 086601 (2004)
Ohno, H. et al. Electric-field control of ferromagnetism. Nature 408, 944–946 (2000)
Chiba, D., Yamanouchi, M., Matsukura, F. & Ohno, H. Electrical manipulation of magnetization reversal in a ferromagnetic semiconductor. Science 301, 943–945 (2003)
Tang, H. X., Kawakami, R. K., Awschalom, D. D. & Roukes, M. L. Giant planar Hall effect in epitaxial (Ga,Mn)As devices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 107201 (2003)
Ohno, Y. et al. Electrical spin injection in a ferromagnetic semiconductor heterostructure. Nature 402, 790–792 (1999)
Flatté, M. E., Yu, Z. G., Johnston-Halperin, E. & Awschalom, D. D. Theory of semiconductor magnetic bipolar transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 4740–4742 (2003)
Saito, H., Zayets, V., Yamagata, S. & Ando, K. Room-temperature ferromagnetism in a II–VI diluted magnetic semiconductor Zn1-xCrxTe. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 207202 (2003)
Pearton, S. J. et al. Wide band gap ferromagnetic semiconductors and oxides. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 1–13 (2003)
Acknowledgements
We thank T. Dietl, Y. Ohno, K. Ohtani and H. Kurino for discussions and K. Akahane, S. Meguro, S. Ito, K. Ikuo and Y. Sato for their technical assistance. This work was supported in part by the IT programme of ‘RR2002’ from MEXT, grant-in-aids from MEXT/JSPS, research fellowships from JSPS, and the ‘21st Century COE’ programme at Tohoku University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamanouchi, M., Chiba, D., Matsukura, F. et al. Current-induced domain-wall switching in a ferromagnetic semiconductor structure. Nature 428, 539–542 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02441
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02441
This article is cited by
-
Energetic perspective on emergent inductance exhibited by magnetic textures in the pinned regime
npj Spintronics (2023)
-
Symmetry of the emergent inductance tensor exhibited by magnetic textures
npj Spintronics (2023)
-
Magnetism modulation in Co3Sn2S2 by current-assisted domain wall motion
Nature Electronics (2022)
-
Planar-symmetry-breaking induced antisymmetric magnetoresistance in van der Waals ferromagnet Fe3GeTe2
Nano Research (2022)
-
Real-time Hall-effect detection of current-induced magnetization dynamics in ferrimagnets
Nature Communications (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.