Abstract
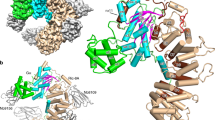
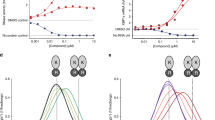
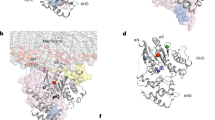
Small GTP-binding (G) proteins are activated by GDP/GTP nucleotide exchange stimulated by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs). Nucleotide dissociation from small G protein–GEF complexes involves transient GDP-bound intermediates whose structures have never been described. In the case of Arf proteins, small G proteins that regulate membrane traffic in eukaryotic cells, such intermediates can be trapped either by the natural inhibitor brefeldin A or by charge reversal at the catalytic glutamate of the Sec7 domain of their GEFs. Here we report the crystal structures of these intermediates that show that membrane recruitment of Arf and nucleotide dissociation are separate reactions stimulated by Sec7. The reactions proceed through sequential rotations of the Arf·GDP core towards the Sec7 catalytic site, and are blocked by interfacial binding of brefeldin A and unproductive stabilization of GDP by charge reversal. The structural characteristics of the reaction and its modes of inhibition reveal unexplored ways in which to inhibit the activation of small G proteins.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malliri, A. et al. Mice deficient in the Rac activator Tiam1 are resistant to Ras-induced skin tumours. Nature 417, 867–871 (2002)
Donaldson, J. G., Finazzi, D. & Klausner, R. D. Brefeldin A inhibits Golgi membrane-catalysed exchange of guanine nucleotide onto ARF protein. Nature 360, 350–352 (1992)
Helms, J. B. & Rothman, J. E. Inhibition by brefeldin A of a Golgi membrane enzyme that catalyses exchange of guanine nucleotide bound to ARF. Nature 360, 352–354 (1992)
Peyroche, A. et al. Brefeldin A acts to stabilize an abortive ARF-GDP-Sec7 domain protein complex: involvement of specific residues of the Sec7 domain. Mol. Cell 3, 275–285 (1999)
Mayer, G. et al. Controlling small guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor function through cytoplasmic RNA intramers. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 4961–4965 (2001)
Schmidt, S., Diriong, S., Mery, J., Fabbrizio, E. & Debant, A. Identification of the first Rho-GEF inhibitor, TRIPα, which targets the RhoA-specific GEF domain of Trio. FEBS Lett. 523, 35–42 (2002)
Klebe, C., Prinz, H., Wittinghofer, A. & Goody, R. S. The kinetic mechanism of Ran-nucleotide exchange catalyzed by RCC1. Biochemistry 34, 12543–12552 (1995)
Lenzen, C., Cool, R. H., Prinz, H., Kuhlmann, J. & Wittinghofer, A. Kinetic analysis by fluorescence of the interaction between Ras and the catalytic domain of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor Cdc25Mm. Biochemistry 37, 7420–7430 (1998)
Goody, R. S. & Hofmann-Goody, W. Exchange factors, effectors, GAPs and motor proteins: common thermodynamic and kinetic principles for different functions. Eur. Biophys. J. 31, 268–274 (2002)
Boriack-Sjodin, P. A., Margarit, S. M., Bar-Sagi, D. & Kuriyan, J. The structural basis of the activation of Ras by Sos. Nature 394, 337–343 (1998)
Goldberg, J. Structural basis for activation of ARF GTPase: mechanisms of guanine nucleotide exchange and GTP-myristoyl switching. Cell 95, 237–248 (1998)
Worthylake, D. K., Rossman, K. L. & Sondek, J. Crystal structure of Rac1 in complex with the guanine nucleotide exchange region of Tiam1. Nature 408, 682–688 (2000)
Renault, L., Kuhlmann, J., Henkel, A. & Wittinghofer, A. Structural basis for guanine nucleotide exchange on Ran by the regulator of chromosome condensation (RCC1). Cell 105, 245–255 (2001)
Nie, Z., Hirsch, D. S. & Randazzo, P. A. Arf and its many interactors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15, 396–404 (2003)
Beraud-Dufour, S. et al. A glutamic finger in the guanine nucleotide exchange factor ARNO displaces Mg2+ and the β-phosphate to destabilize GDP on ARF1. EMBO J. 17, 3651–3659 (1998)
Vetter, I. R. & Wittinghofer, A. The guanine nucleotide-binding switch in three dimensions. Science 294, 1299–1304 (2001)
Pasqualato, S., Renault, L. & Cherfils, J. Arf, Arl, Arp and Sar proteins: a family of GTP-binding proteins with a structural device for ‘front-back’ communication. EMBO Rep. 3, 1035–1041 (2002)
Amor, J. C., Harrison, D. H., Kahn, R. A. & Ringe, D. Structure of the human ADP-ribosylation factor 1 complexed with GDP. Nature 372, 704–708 (1994)
Menetrey, J., Macia, E., Pasqualato, S., Franco, M. & Cherfils, J. Structure of Arf6-GDP suggests a basis for guanine nucleotide exchange factors specificity. Nature Struct. Biol. 7, 466–469 (2000)
Antonny, B., Beraud-Dufour, S., Chardin, P. & Chabre, M. N-terminnal hydrophobic residues of the G-protein ADP-ribosylation factor-1 insert into membrane phospholipids upon GDP to GTP exchange. Biochemistry 36, 4675–4684 (1997)
Jackson, C. L. & Casanova, J. E. Turning on ARF: the Sec7 family of guanine-nucleotide-exchange factors. Trends Cell Biol. 10, 60–67 (2000)
Cherfils, J. et al. Structure of the Sec7 domain of the Arf exchange factor ARNO. Nature 392, 101–105 (1998)
Mansour, S. J. et al. p200 ARF-GEP1: a Golgi-localized guanine nucleotide exchange protein whose Sec7 domain is targeted by the drug brefeldin A. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 7968–7973 (1999)
Jackson, C. L. Brefeldin A revealing the fundamental principles governing membrane dynamics and protein transport. Subcell. Biochem. 34, 233–272 (2000)
Zhu, J. W. et al. Elucidation of strict structural requirements of brefeldin A as an inducer of differentiation and apoptosis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 8, 455–463 (2000)
Chardin, P. et al. A human exchange factor for ARF contains Sec7- and pleckstrin-homology domains. Nature 384, 481–484 (1996)
Claude, A. et al. GBF1: A novel Golgi-associated BFA-resistant guanine nucleotide exchange factor that displays specificity for ADP-ribosylation factor 5. J. Cell Biol. 146, 71–84 (1999)
Donaldson, J. G. & Jackson, C. L. Regulators and effectors of the ARF GTPases. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12, 475–482 (2000)
Donaldson, J. G. Multiple roles for Arf6: Sorting, structuring, and signaling at the plasma membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 11, 41573–41576 (2003)
Sata, M., Moss, J. & Vaughan, M. Structural basis for the inhibitory effect of brefeldin A on guanine nucleotide-exchange proteins for ADP-ribosylation factors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 2752–2757 (1999)
Baumgartner, F., Wiek, S., Paprotka, K., Zauner, S. & Lingelbach, K. A point mutation in an unusual Sec7 domain is linked to brefeldin A resistance in a Plasmodium falciparum line generated by drug selection. Mol. Microbiol. 41, 1151–1158 (2001)
Robineau, S., Chabre, M. & Antonny, B. Binding site of brefeldin A at the interface between the small G protein ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (ARF1) and the nucleotide-exchange factor Sec7 domain. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 9913–9918 (2000)
Chardin, P. & McCormick, F. Brefeldin A: the advantage of being uncompetitive. Cell 97, 153–155 (1999)
Beraud-Dufour, S., Paris, S., Chabre, M. & Antonny, B. Dual interaction of ADP ribosylation factor 1 with Sec7 domain and with lipid membranes during catalysis of guanine nucleotide exchange. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 37629–37636 (1999)
Renault, L., Christova, P., Guibert, B., Pasqualato, S. & Cherfils, J. Mechanism of domain closure of Sec7 domains and role in BFA sensitivity. Biochemistry 41, 3605–3612 (2002)
Weber, H. P., Hauser, D. & Sigg, H. P. Structure of brefeldin A. Helv. Chim. Acta 54, 2763–2766 (1971)
Torii, S. et al. Cytotoxicity of brefeldin A correlates with its inhibitory effect on membrane binding of COP coat proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 11574–11580 (1995)
Pasqualato, S., Renault, L. & Cherfils, J. in The ARF Book (ed. Kahn, R. A.) Ch. 3 (Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, in the press)
McCormick, F. Small-molecule inhibitors of cell signaling. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 11, 593–597 (2000)
Wurtele, M., Jelich-Ottmann, C., Wittinghofer, A. & Oecking, C. Structural view of a fungal toxin acting on a 14-3-3 regulatory complex. EMBO J. 22, 987–994 (2003)
Choi, J., Chen, J., Schreiber, S. L. & Clardy, J. Structure of the FKBP12-rapamycin complex interacting with the binding domain of human FRAP. Science 273, 239–242 (1996)
Cherfils, J. Structural mimicry of DH domains by Arfaptin suggests a model for the recognition of Rac-GDP by its guanine nucleotide exchange factors. FEBS Lett. 507, 280–284 (2001)
Cox, A. D. & Der, C. J. Ras family signaling: therapeutic targeting. Cancer Biol. Ther. 1, 599–606 (2002)
Boettner, B. & Van Aelst, L. The role of Rho GTPases in disease development. Gene 286, 155–174 (2002)
Jones, T. A., Zou, J. Y., Cowan, S. W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr. A 47, 110–119 (1991)
Acknowledgements
We thank the ESRF for provision of synchrotron radiation facilities and the staff of beamlines BM30A, ID14-EH2 and ID14-EH3 for assistance. This work was supported by grants from the Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer, the CNRS, the Ministère de la Recherche and the Human Frontier Science Program. We thank B. Antonny and co-workers at the IPMC (CNRS) for the gift of the plasmids used in this work and for discussions. The Arf1(Δ17)–Gea2-Sec7 coordinates are a gift from J. Goldberg.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Renault, L., Guibert, B. & Cherfils, J. Structural snapshots of the mechanism and inhibition of a guanine nucleotide exchange factor. Nature 426, 525–530 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02197
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02197
This article is cited by
-
Membranes prime the RapGEF EPAC1 to transduce cAMP signaling
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Revealing the activation mechanism of autoinhibited RalF by integrated simulation and experimental approaches
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
PH-domain-binding inhibitors of nucleotide exchange factor BRAG2 disrupt Arf GTPase signaling
Nature Chemical Biology (2019)
-
GLI2 promotes cell proliferation and migration through transcriptional activation of ARHGEF16 in human glioma cells
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018)
-
Role of curcumin in PLD activation by Arf6-cytohesin1 signaling axis in U46619-stimulated pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.