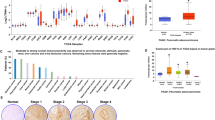
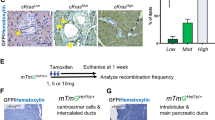
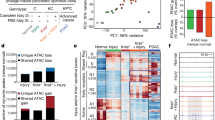
Abstract
Hedgehog signalling—an essential pathway during embryonic pancreatic development, the misregulation of which has been implicated in several forms of cancer—may also be an important mediator in human pancreatic carcinoma1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8. Here we report that sonic hedgehog, a secreted hedgehog ligand, is abnormally expressed in pancreatic adenocarcinoma and its precursor lesions: pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN). Pancreata of Pdx–Shh mice (in which Shh is misexpressed in the pancreatic endoderm) develop abnormal tubular structures, a phenocopy of human PanIN-1 and -2. Moreover, these PanIN-like lesions also contain mutations in K-ras and overexpress HER-2/neu, which are genetic mutations found early in the progression of human pancreatic cancer. Furthermore, hedgehog signalling remains active in cell lines established from primary and metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Notably, inhibition of hedgehog signalling by cyclopamine induced apoptosis and blocked proliferation in a subset of the pancreatic cancer cell lines both in vitro and in vivo. These data suggest that this pathway may have an early and critical role in the genesis of this cancer, and that maintenance of hedgehog signalling is important for aberrant proliferation and tumorigenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Capdevila, J., Estrada, M. P., Sanchez-Herrero, E. & Guerrero, I. The Drosophila segment polarity gene patched interacts with decapentaplegic in wing development. EMBO J. 13, 71–82 (1994)
Hardcastle, Z., Mo, R., Hui, C.-C. & Sharpe, P. T. The Shh signalling pathway in tooth development: defects in Gli2 and Gli3 mutants. Development 125, 2803–2811 (1998)
Marigo, V. & Tabin, C. Regulation of patched by sonic hedgehog in the developing neural tube. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 9346–9351 (1996)
Riddle, R. D., Johnson, R. L., Laufer, E. & Tabin, C. Sonic hedgehog mediates the polarizing activity of the ZPA. Cell 75, 1401–1416 (1993)
St-Jacques, B. et al. Sonic hedgehog signaling is essential for hair development. Curr. Biol. 8, 1058–1068 (1998)
Roberts, D. J. in Development of the Gastrointestinal Tract (eds Sanderson, I. R. & Walker, W. A.) 1–12 (Decker, Hamilton, Ontario, 2000)
Hebrok, M. Hedgehog signaling in pancreas development. Mech. Dev. 120, 45–47 (2003)
Watkins, D. N. et al. Hedgehog signaling within airway epithelial progenitors and in small-cell lung cancer. Nature 422, 313–317 (2003)
van den Brink, G. R. et al. Sonic hedgehog regulates gastric gland morphogenesis in man and mouse. Gastroenterology 121, 317–328 (2001)
Johnson, R. L. et al. Human homolog of patched, a candidate gene for the basal cell nevus syndrome. Science 272, 1668–1671 (1996)
Wicking, C., Smyth, I. & Bale, A. The hedgehog signalling pathway in tumorigenesis and development. Oncogene 18, 7844–7851 (1999)
Hruban, R. et al. Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 25, 579–586 (2001)
Wilentz, R. E. et al. Loss of expression of Dpc4 in pancreatic epithelial neoplasia: evidence that DPC4 inactivation occurs late in neoplastic progression. Cancer Res. 60, 2002–2006 (2000)
Day, J. D. et al. Immunohistochemical evaluation of HER-2/neu oncogene expression in pancreatic adenocarcinoma and pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasms. Hum. Pathol. 27, 119–124 (1996)
Wilentz, R. E. et al. Inactivation of the p16 (INK4A) tumor-suppressor gene in pancreatic duct lesions: loss of intranuclear expression. Cancer Res. 58, 4740–4744 (1998)
Hebrok, M., Kim, S. K., St-Jacques, B., McMahon, A. P. & Melton, D. A. Regulation of pancreas development by hedgehog signaling. Development 127, 4905–4913 (2000)
Jaffee, E. M. et al. Development and characterization of a cytokine-secreting pancreatic adenocarcinoma vaccine from primary tumors for use in clinical trials. Cancer J. Sci. Am. 4, 194–203 (1998)
Taipale, J. et al. Effects of oncogenic mutations in Smoothened and Patched can be reversed by cyclopamine. Nature 406, 1005–1009 (2000)
Berman, D. M. et al. Medulloblastoma growth inhibition by hedgehog pathway blockade. Science 297, 1559–1561 (2002)
Incardona, J. P., Gaffield, W., Kapur, R. P. & Roelink, H. The teratogenic Veratrum alkaloid cyclopamine inhibits sonic hedgehog signal transduction. Development 125, 3553–3562 (1998)
Sasaki, H., Hui, C., Nakafuku, M. & Kondoh, H. A binding site for Gli proteins is essential for HNF-3 beta floor plate enhancer activity in transgenics and can respond to Shh in vitro. Development 124, 1313–1322 (1997)
Lee, J., Platt, K. A., Censullo, P. & Ruiz I Altaba, A. Gli1 is a target of Sonic hedgehog that induces ventral neural tube development. Development 124, 2537–2552 (1997)
Hebrok, M., Kim, S. K. & Melton, D. A. Notochord repression of endodermal Sonic hedgehog permits pancreas development. Genes Dev. 12, 1705–1713 (1998)
Roberts, D. J., Smith, D. M., Goff, D. & Tabin, C. Epithelial-mesenchymal signaling during the regionalization of the chick gut. Development 125, 2791–2801 (1998)
Ramalho-Santos, M., Melton, D. A. & McMahon, A. P. Hedgehog signals regulate multiple aspects of gastrointestinal development. Development 127, 2763–2772 (2000)
Apelqvist, A., Ahlegren, U. & Edlund, H. Sonic hedgehog directs specialised mesoderm differentiation in the intestine and pancreas. Curr. Biol. 7, 801–804 (1997)
Hasegawa, Y. et al. Detection of K-ras mutations in DNAs isolated from feces of patients with colorectal tumors by mutant-allele-specific amplification (MASA). Oncogene 10, 1441–1445 (1995)
Ito, Y. et al. Frequent detection of K-ras mutation in stool samples of colorectal carcinoma patients after improved DNA extraction: Comparison with tissue samples. Int. J. Oncol. 20, 1263–1268 (2002)
Lopez, T. & Hanahan, D. Elevated levels of IGF-1 receptor convey invasive and metastatic capability in a mouse model of pancreatic islet tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 1, 339–353 (2002)
Sander, M. et al. Genetic analysis reveals that PAX6 is required for normal transcription of pancreatic hormone genes and islet development. Genes Dev. 11, 1662–1673 (1997)
Berman, D. M. et al. Widespread requirement for Hedgehog ligand stimulation in growth of digestive tract tumours. Nature doi:10.1038/nature01972 (this issue)
Acknowledgements
S.P.T. and co-workers are grateful to D. A. Melton and P. A. Donahoe for discussion and review of the manuscript; H. Edlund for supplying the construct and initial pancreatic tissue for the Pdx–Shh transgenic mouse; and C. Tabin for the Shh in situ probe. We also thank N. Frost for editorial assistance. This work was supported in part by a grant from the Lustgarten Foundation to S.P.T. M.H. and co-workers thank C. Basbaum, D. Hanahan, I. Herskowitz, T. Kornberg, M. Tempero and members of the Hebrok laboratory for discussions and comments on the manuscript. We thank L. Jaffee for provision of the Panc series of cells. We are grateful to L. Spector for editorial assistance. This work was supported by grants to M.H. from the Juvenile Diabetes Foundation and the National Institutes of Health.
Authors' contributions S.P.T. and M.H. are senior authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thayer, S., di Magliano, M., Heiser, P. et al. Hedgehog is an early and late mediator of pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis. Nature 425, 851–856 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02009
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02009
This article is cited by
-
Hedgehog signaling in tissue homeostasis, cancers, and targeted therapies
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
Epithelial and stromal co-evolution and complicity in pancreatic cancer
Nature Reviews Cancer (2023)
-
Stroma-targeting strategies in pancreatic cancer: a double-edged sword
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry (2023)
-
A clinicopathological exploration of Hedgehog signaling: implications in oral carcinogenesis
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2023)
-
NEDD8-Activating Enzyme Inhibitor MLN4924 Inhibits Both the Tumor Stroma and Angiogenesis in Pancreatic Cancer via Gli1 and REDD1
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.