Abstract
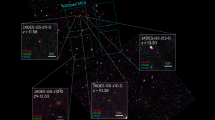
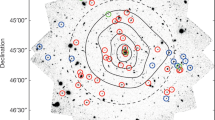
The most massive galaxies in the present-day Universe are found to lie in the centres of rich clusters. They have old, coeval stellar populations suggesting that the bulk of their stars must have formed at early epochs in spectacular starbursts1, which should be luminous phenomena when observed at submillimetre wavelengths2. The most popular model of galaxy formation predicts that these galaxies form in proto-clusters at high-density peaks in the early Universe3. Such peaks are indicated by massive high-redshift radio galaxies4. Here we report deep submillimetre mapping of seven high-redshift radio galaxies and their environments. These data confirm not only the presence of spatially extended regions of massive star-formation activity in the radio galaxies themselves, but also in companion objects previously undetected at any wavelength. The prevalence, orientation, and inferred masses of these submillimetre companion galaxies suggest that we are witnessing the synchronous formation of the most luminous elliptical galaxies found today at the centres of rich clusters of galaxies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ellis, R. S. et al. The homogeneity of spheroidal populations in distant clusters. Astrophys. J. 483, 582–596 (1997)
Dunlop, J. S. et al. Detection of a large mass of dust in a radio galaxy at redshift z = 3.8. Nature 370, 347–349 (1994)
Kauffmann, G. The age of elliptical galaxies and bulges in a merger model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 281, 487–492 (1996)
West, M. J. Anisotropic mergers at high redshifts: the formation of cD galaxies and powerful radio sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 268, 79–102 (1994)
Hughes, D. H., Dunlop, J. S. & Rawlings, S. High-redshift radio galaxies and quasars at submillimetre wavelengths: assessing their evolutionary status. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 289, 766–782 (1997)
Archibald, E. N. et al. A submillimetre survey of the star-formation history of radio galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 323, 417–444 (2001)
Reuland, M., Röttgering, H. & van Breugel, W. in Radio Galaxies: Past, Present and Future (Elsevier, in the press); preprint at 〈http://arXiv.org/astro-ph/0303321〉 (2003).
Holland, W. S. et al. SCUBA: a common-user submillimetre camera operating on the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 303, 659–672 (1999)
Graham, A., Lauer, T. R., Colless, M. & Postman, M. Brightest cluster galaxy profile shapes. Astrophys. J. 465, 534–547 (1996)
Mihos, J. C. & Hernquist, L. Gasdynamics and starbursts in major mergers. Astrophys. J. 464, 641–663 (1996)
Smail, I., Ivison, R. J., Blain, A. W. & Kneib, J.-P. The nature of faint submillimetre selected galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 331, 495–520 (2002)
Scott, S. E. et al. The SCUBA 8-m Jy survey I. Submillimetre maps, sources and number counts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 331, 817–838 (2002)
Chambers, K. C., Miley, G. K. & van Breugel, W. Alignment of radio and optical orientations in high-redshift radio galaxies. Nature 329, 604–606 (1987)
McCarthy, P. J., van Breugel, W., Spinrad, H. & Djorgovski, S. A correlation between the radio and optical morphologies of distant 3CR radio galaxies. Astrophys. J. 321, L29–L33 (1987)
Eales, S. A. A new theory for the alignment effect. Astrophys. J. 397, 49–54 (1992)
Smail, I. et al. A SCUBA galaxy in the protocluster around 52W002 at z = 2.4. Astrophys. J. 583, 551–558 (2003)
Pentericci, L. et al. A Chandra study of X-ray sources in the field of the z = 2.16 radio galaxy MRC 1138-262. Astron. Astrophys. 396, 109–115 (2002)
Hildebrand, R. H. The determination of cloud masses and dust characteristics from submillimetre thermal emission. Q. J. R. Astron. Soc. 24, 267–282 (1983)
Magorrian, J. et al. The demography of massive dark objects in galactic centers. Astron. J. 115, 2285–2305 (1998)
Kauffmann, G. & Haehnelt, M. A unified model for the evolution of galaxies and quasars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 311, 576–588 (2000)
Page, M. J., Stevens, J. A., Mittaz, J. P. D. & Carrera, F. J. Submillimetre evidence for the coeval growth of massive black holes and galaxy bulges. Science 294, 2516–2518 (2001)
Smail, I. et al. Chandra detections of SCUBA galaxies around high-z radio sources. Astrophys. J. (in the press)
De Breuck, C. et al. CO emission and associated HI absorption from a massive gas reservoir surrounding the z = 3 radio galaxy B3 J2330 + 393. Astron. Astrophys. 401, 911–925 (2003)
Papadopoulos, P. P. et al. CO(4-3) and dust emission in two powerful high-z radio galaxies, and CO lines at high redshifts. Astrophys. J. 528, 626–636 (2000)
Gorenstein, P. Empirical relation between interstellar X-ray absorption and optical extinction. Astrophys. J. 198, 95–101 (1975)
Reuland, M. et al. An obscured radio galaxy at high redshift. Astrophys. J. 582, L71–L74 (2003)
Ivison, R. J. et al. An excess of submillimeter sources near 4C41.17: a candidate proto-cluster at z = 3.8? Astrophys. J. 542, 27–34 (2000)
Omont, A. et al. Molecular gas and dust around a radio-quiet quasar at redshift 4.69. Nature 382, 428–431 (1996)
Dunlop, J. S. et al. Quasars, their host galaxies, and their central black holes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 340, 1095–1135 (2003)
Percival, W. J., Scott, D., Peacock, J. A. & Dunlop, J. S. The clustering of halo mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 338, L31–L35 (2003)
Acknowledgements
The JCMT is run by the Joint Astronomy Centre on behalf of the Particle Physics and Astronomy Research Council (PPARC). J.A.S., J.S.D., I.R.S. and W.J.P. acknowledge funding from PPARC, the Royal Society and the Leverhulme Trust. The work of W.J.M.v.B. and M.R. was performed under the auspices of the US Department of Energy, National Nuclear Security Administration by the University of California, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stevens, J., Ivison, R., Dunlop, J. et al. The formation of cluster elliptical galaxies as revealed by extensive star formation. Nature 425, 264–267 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01976
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01976
This article is cited by
-
The realm of the galaxy protoclusters
The Astronomy and Astrophysics Review (2016)
-
Galaxy connections
Nature (2009)
-
Spatial correlation between submillimetre and Lyman-α galaxies in the SSA 22 protocluster
Nature (2009)
-
Distant radio galaxies and their environments
The Astronomy and Astrophysics Review (2008)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.