Abstract
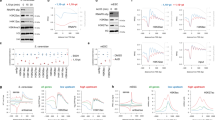
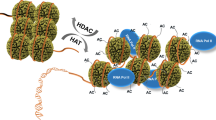
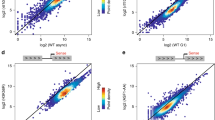
Acetylation is a well-known regulatory post-translational modification1, but a biological function for acetylation in regulating basal transcription factors has not been reported. Here we show that the general transcription factor TFIIB, which is required for the initiation of eukaryotic polymerase II transcription2, is acetylated. TFIIB is also an autoacetyltransferase, although it shares no sequence homology with any known acetyltransferases. In the absence of other enzymes, it binds acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA), and catalyses the transfer of the acetyl group onto a specific lysine residue (K238). Both recombinant and cellular TFIIB can autoacetylate, markedly stabilizing the interaction between TFIIB and transcription factor TFIIF and activating transcription in vitro and in cells. A K238A mutant, which cannot be autoacetylated, does not show this activation of transcription. Our findings suggest that there is a regulatory pathway controlling acetylation of TFIIB, and they link acetyl-CoA with basal gene transcription.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kouzarides, T. Acetylation: A regulatory modification to rival phosphorylation? EMBO J. 19, 1176–1179 (2000)
Orphanides, G., Lagrange, T. & Reinberg, D. The general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev. 10, 2657–2683 (1996)
Bizzozero, O. A., McGarry, J. F. & Lees, M. B. Autoacylation of myelin proteolipid protein with acyl coenzyme A. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 13550–13557 (1987)
Yamashita, A., Watanabe, M., Tonegawa, T., Sugiura, T. & Waku, K. Acyl-CoA binding and acylation of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase isoforms of rat liver: Their effect on enzyme activity. Biochem. J. 312, 301–308 (1995)
Duncan, J. A. & Gilman, A. G. Autoacylation of G protein alpha subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 23594–23600 (1996)
Veit, M. et al. Palmitoylation of rhodopsin with S-protein acyltransferase: Enzyme catalyzed reaction versus autocatalytic acylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1394, 90–98 (1998)
Brownell, J. E. & Allis, C. D. Special HATs for special occasions: Linking histone acetylation to chromatin assembly and gene activation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 6, 176–184 (1996)
Shevchenko, A., Wilm, M., Vorm, O. & Mann, M. Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Chem. 68, 850–858 (1996)
Peng, J. & Gygi, S. P. Proteomics: The move to mixtures. J. Mass Spectrom. 36, 1083–1091 (2001)
Eng, J., McCormack, A. L. & Yates, J. R. I. An approach to correlate tandem mass spectral data of peptides with amino acid sequences in a protein database. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 5, 976–989 (1994)
Bagby, S. et al. Solution structure of the C-terminal core domain of human TFIIB: Similarity to cyclin A and interaction with TATA-binding protein. Cell 82, 857–867 (1995)
Nikolov, D. B. et al. Crystal structure of a TFIIB–TBP–TATA-element ternary complex. Nature 377, 119–128 (1995)
Yan, Y., Harper, S., Speicher, D. W. & Marmorstein, R. The catalytic mechanism of the ESA1 histone acetyltransferase involves a self-acetylated intermediate. Nature Struct. Biol. 9, 862–869 (2002)
Usheva, A. & Shenk, T. YY1 transcriptional initiator: protein interactions and association with a DNA site containing unpaired strands. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 13571–13576 (1996)
Fang, S. M. & Burton, Z. F. RNA polymerase II-associated protein (RAP) 74 binds transcription factor (TF) IIB and blocks TFIIB-RAP30 binding. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 11703–11709 (1996)
Luger, K., Rechsteiner, T. J. & Richmond, T. J. Preparation of nucleosome core particle from recombinant histones. Methods Enzymol. 304, 3–19 (1999)
Mayer, R. T., Holman, G. M. & Bridges, A. C. Phosphorescence detection method for purine-containing compounds on thin-layer chromatograms. J. Chromatogr. 90, 390–391 (1974)
Sawadogo, M. & Roeder, R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by human RNA polymerase II: Analysis by a rapid and quantitative in vitro assay. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 82, 4394–4398 (1985)
Acknowledgements
We thank T. Richmond for the gift of recombinant human histone proteins, S. Gygi for proteolytical analysis on acetyl-TFIIB, and S. Robson and M. Gray for critically reading our manuscript. This work was supported by the NIH (A.U.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, C., Hiromura, M. & Usheva, A. Transcription factor IIB acetylates itself to regulate transcription. Nature 424, 965–969 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01899
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01899
This article is cited by
-
Proteome-wide acetylation dynamics in human cells
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Relevance of HCN2-expressing human mesenchymal stem cells for the generation of biological pacemakers
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2016)
-
A new paradigm for transcription factor TFIIB functionality
Scientific Reports (2014)
-
Cell cycle-dependent acetylation of Rb2/p130 in NIH3T3 cells
Oncogene (2010)
-
Autoacetylation of Purified Calreticulin Transacetylase Utilizing Acetoxycoumarin as the Acetyl Group Donor
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (2009)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.