Abstract
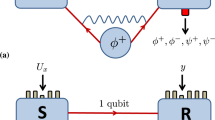
Distribution of entangled states between distant locations is essential for quantum communication1,2,3 over large distances. But owing to unavoidable decoherence in the quantum communication channel, the quality of entangled states generally decreases exponentially with the channel length. Entanglement purification4,5—a way to extract a subset of states of high entanglement and high purity from a large set of less entangled states—is thus needed to overcome decoherence. Besides its important application in quantum communication, entanglement purification also plays a crucial role in error correction for quantum computation, because it can significantly increase the quality of logic operations between different qubits6. Here we demonstrate entanglement purification for general mixed states of polarization-entangled photons using only linear optics7. Typically, one photon pair of fidelity 92% could be obtained from two pairs, each of fidelity 75%. In our experiments, decoherence is overcome to the extent that the technique would achieve tolerable error rates for quantum repeaters in long-distance quantum communication8. Our results also imply that the requirement of high-accuracy logic operations in fault-tolerant quantum computation can be considerably relaxed6.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ekert, A. Quantum cryptography based on Bell's theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 661–663 (1991)
Bennett, C. H. & Wiesner, S. J. Communication via one- and two-particle operators on Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 2881–2884 (1992)
Bennett, C. H. et al. Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 3081–3084 (1993)
Bennett, C. H. et al. Purification of noisy entanglement, and faithful teleportation via noisy channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 722–725 (1996)
Deutsch, D. et al. Quantum privacy amplification and the security of quantum cryptography over noisy channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 2818–2821 (1996)
Duer, W. & Briegel, H.-J. Entanglement purification for quantum computation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 067901 (2003)
Pan, J.-W., Simon, C., Brukner, C. & Zeilinger, A. Entanglement purification for quantum communication. Nature 410, 1067–1070 (2001)
Briegel, H.-J., Duer, W., Cirac, J. I. & Zoller, P. Quantum repeaters: The role of imperfect local operations in quantum communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 5932–5935 (1998)
Gottesman, D. & Chuang, I. L. Demonstrating the viability of universal quantum computation using teleportation and single-qubit operations. Nature 402, 390–393 (1999)
Gisin, N., Ribordy, G., Tittel, W. & Zbinden, H. Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 145–195 (2002)
Mattle, K., Weinfurter, H., Kwiat, P. G. & Zeilinger, A. Dense coding in experimental quantum communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 4656–4659 (1996)
Bouwmeester, D. et al. Experimental quantum teleportation. Nature 390, 575–579 (1997)
Marcikic, I., de Riedmatten, H., Tittel, W., Zbinden, H. & Gisin, N. Long-distance teleportation of qubits at telecommunication wavelengths. Nature 421, 509–513 (2003)
Pan, J.-W., Gasparoni, S., Aspelmeyer, M., Jennewein, T. & Zeilinger, A. Experimental realization of freely propagating teleported qubits. Nature 421, 721–725 (2003)
Jones, J. Quantum computing: Putting it into practice. Nature 421, 28–29 (2003)
Zukowski, M., Zeilinger, A., Horne, M. A. & Ekert, A. “Event-ready-detectors” Bell experiment via entanglement swapping. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 4287–4290 (1993)
Kwiat, P. G., Barraza-Lopez, S., Stefanov, A. & Gisin, N. Experimental entanglement distillation and ‘hidden’ non-locality. Nature 409, 1014–1017 (2001)
Yamamoto, T., Koashi, M., Ozdemir, S. K. & Imoto, N. Experimental extraction of an entangled photon pair from two identically decohered pairs. Nature 421, 343–346 (2003)
Zhao, Z., Yang, T., Chen, Y.-A., Zhang, A.-N. & Pan, J.-W. Experimental realization of entanglement concentration and a quantum repeater. Phys. Rev. Lett. (in the press); preprint available at 〈http://xxx.lanl.gov/quant-ph/0211075〉 (2003).
Bennett, C. H., Bernstein, H. J., Popescu, S. & Schumacher, B. Concentrating partial entanglement by local operations. Phys. Rev. A 53, 2046–2052 (1996)
Kwiat, P. G. et al. New high intensity soure of polarization-entangled photon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 4337–4341 (1995)
Zukowski, M., Zeilinger, A. & Weinfurter, H. Entangling photons radiated by independent pulsed source. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 755, 91–102 (1995)
Simon, C. & Pan, J.-W. Polarization entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 257901 (2002)
Pittman, T. B., Jacobs, B. C. & Franson, J. D. Demonstration of nondeterministic quantum logic operations using linear optical elements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 257902 (2002)
Rudolph, T. & Pan, J.-W. A simple gate for linear optics quantum computing. Preprint available at 〈http://xxx.lanl.gov/quant-ph/0108056〉 (2001).
Knill, E., Laflamme, R. & Milburn, G. J. A scheme for efficient quantum computation with linear optics. Nature 409, 46–52 (2001)
Duan, L.-M., Lukin, M. D., Cirac, J. I. & Zoller, P. Long-distance quantum communication with atomic ensembles and linear optics. Nature 414, 413–418 (2001)
Santori, C., Fattal, D., Vuckovic, J., Solomon, G. S. & Yamamoto, Y. Indistinguishable photons from a single-photon device. Nature 419, 594–596 (2001)
Chen, Z-B., Pan, J.-W., Zhang, Y.-D., Brukner, C. & Zeilinger, A. All-versus-nothing violation of local realism for two entangled photons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 160408 (2003).
Zhao, Z., Yang, T., Chen, Z.-B., Du, J.-F. & Pan, J.-W. Deterministic and highly efficient quantum cryptography with entangled photon pairs. Preprint available at 〈http://xxx.lanl.gov/quant-ph/0211098〉 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank H. Briegel, T. Jennewein and C. Simon for discussions. This work was supported by the Austrian Science Foundation (FWF), and by the TMR and the QuComm programs of the European Commission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, JW., Gasparoni, S., Ursin, R. et al. Experimental entanglement purification of arbitrary unknown states. Nature 423, 417–422 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01623
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01623
This article is cited by
-
Satellite-based quantum information networks: use cases, architecture, and roadmap
Communications Physics (2023)
-
Advances in quantum entanglement purification
Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2023)
-
The hyperentanglement-based quantum secure direct communication protocol with single-photon measurement
Quantum Information Processing (2023)
-
Optimal tripartite quantum teleportation protocol through noisy channels
Quantum Information Processing (2023)
-
Towards entanglement distillation between atomic ensembles using high-fidelity spin operations
Communications Physics (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.