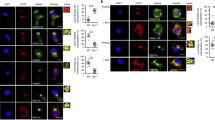
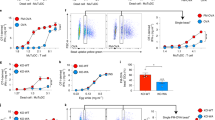
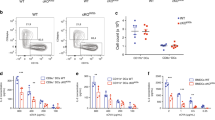
Abstract
Assembly of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules, which present antigen in the form of short peptides to T lymphocytes, occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum; once assembled, these molecules travel from the endoplasmic reticulum to their final destination. MHC class II molecules follow a route that takes them by means of the endocytic pathway, where they acquire peptide, to the cell surface1. The transport of MHC class II molecules in ‘professional’ antigen-presenting cells (APCs) is subject to tight control and responds to inflammatory stimuli such as lipopolysaccharide. To study class II transport in live APCs, we replaced the mouse MHC class II gene with a version that codes for a class II molecule tagged with enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP). The resulting mice are immunologically indistinguishable from wild type. In bone-marrow-derived dendritic cells, we observed class II molecules in late endocytic structures with transport patterns similar to those in Langerhans cells observed in situ. We show that tubular endosomes extend intracellularly and polarize towards the interacting T cell, but only when antigen-laden dendritic cells encounter T cells of the appropriate specificity. We propose that such tubulation serves to facilitate the ensuing T-cell response.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Villadangos, J. A. et al. Proteases involved in MHC class II antigen presentation. Immunol. Rev. 172, 109–120 (1999)
Cosgrove, D. et al. Mice lacking MHC class II molecules. Cell 66, 1051–1066 (1991)
Grusby, M. J., Johnson, R. S., Papaioannou, V. E. & Glimcher, L. H. Depletion of CD4 + T cells in major histocompatibility complex class II-deficient mice. Science 253, 1417–1420 (1991)
Brown, M. S. & Goldstein, J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science 232, 34–47 (1986)
Wubbolts, R. et al. Direct vesicular transport of MHC class II molecules from lysosomal structures to the cell surface. J. Cell Biol. 135, 611–622 (1996)
Kleijmeer, M. et al. Reorganization of multivesicular bodies regulates MHC class II antigen presentation by dendritic cells. J. Cell Biol. 155, 53–63 (2001)
Rowden, G. The Langerhans cell. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 3, 95–180 (1981)
Maric, M. et al. Defective antigen processing in GILT-free mice. Science 294, 1361–1365 (2001)
Hugo, P., Kappler, J. W., Godfrey, D. I. & Marrack, P. C. A cell line that can induce thymocyte positive selection. Nature 360, 679–682 (1992)
Malissen, B., Steinmetz, M., McMillan, M., Pierres, M. & Hood, L. Expression of I-Ak class II genes in mouse L cells after DNA-mediated gene transfer. Nature 305, 440–443 (1983)
Monks, C. R., Freiberg, B. A., Kupfer, H., Sciaky, N. & Kupfer, A. Three-dimensional segregation of supramolecular activation clusters in T cells. Nature 395, 82–86 (1998)
Grakoui, A. et al. The immunological synapse: a molecular machine controlling T cell activation. Science 285, 221–227 (1999)
Valitutti, S., Muller, S., Cella, M., Padovan, E. & Lanzavecchia, A. Serial triggering of many T-cell receptors by a few peptide-MHC complexes. Nature 375, 148–151 (1995)
Underhill, D. M., Bassetti, M., Rudensky, A. & Aderem, A. Dynamic interactions of macrophages with T cells during antigen presentation. J. Exp. Med. 190, 1909–1914 (1999)
Gunzer, M. et al. Antigen presentation in extracellular matrix: interactions of T cells with dendritic cells are dynamic, short lived, and sequential. Immunity 13, 323–332 (2000)
Lanzavecchia, A. & Sallusto, F. Regulation of T cell immunity by dendritic cells. Cell 106, 263–266 (2001)
Scholl, P. R. & Geha, R. S. MHC class II signalling in B-cell activation. Immunol. Today 15, 418–422 (1994)
Mathis, D. J., Benoist, C., Williams, V. E., Kanter, M. & McDevitt, H. O. Several mechanisms can account for defective Eα gene expression in different mouse haplotypes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 80, 273–277 (1983)
Villadangos, J. A., Riese, R. J., Peters, C., Chapman, H. A. & Ploegh, H. L. Degradation of mouse invariant chain: roles of cathepsins S and D and the influence of major histocompatibility complex polymorphism. J. Exp. Med. 186, 549–560 (1997)
Villadangos, J. A. et al. MHC class II expression is regulated in dendritic cells independently of invariant chain degradation. Immunity 14, 739–749 (2001)
Barnden, M. J., Allison, J., Heath, W. R. & Carbone, F. R. Defective TCR expression in transgenic mice constructed using cDNA-based alpha- and beta-chain genes under the control of heterologous regulatory elements. Immunol. Cell Biol. 76, 34–40 (1998)
Turley, S. J. et al. Transport of peptide-MHC class II complexes in developing dendritic cells. Science 288, 522–527 (2000)
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Boxem for help in designing the targeting construct and T. Schmidt for blastocyst microinjections. We thank A. W. M. van der Velden for providing DsRed1-labelled S. typhimurium, and we acknowledge discussions with members of the Ploegh laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boes, M., Cerny, J., Massol, R. et al. T-cell engagement of dendritic cells rapidly rearranges MHC class II transport. Nature 418, 983–988 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01004
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01004
This article is cited by
-
Membrane protein trafficking in the anti-tumor immune response: work of endosomal-lysosomal system
Cancer Cell International (2022)
-
Induction of antigen-specific tolerance by nanobody–antigen adducts that target class-II major histocompatibility complexes
Nature Biomedical Engineering (2021)
-
Adhering interacting cells to two opposing coverslips allows super-resolution imaging of cell-cell interfaces
Communications Biology (2021)
-
Exocytosis of large-diameter lysosomes mediates interferon γ-induced relocation of MHC class II molecules toward the surface of astrocytes
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2020)
-
Investigating immune responses to parasites using transgenesis
Parasites & Vectors (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.