Abstract
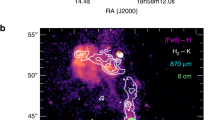
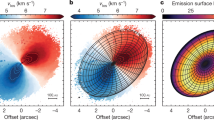
Evolved stars of about one solar mass are in general spherically symmetric, yet the planetary nebulae that they produce in the next phase of their evolution tend not to exhibit such symmetry. Collimated ‘jets’ and outflows of material have been observed1,2,3,4,5 up to ∼0.3 parsec from the central stars of planetary nebulae, and precession of those jets has been proposed1 to explain the observed asymmetries. Moreover, it has recently been shown6 theoretically that magnetic fields could launch and collimate such jets. Here we report the detection of a collimated and precessing jet of molecular gas that is traced by water-vapour maser spots ∼500 astronomical units (au) from the star W43A in Aquila. We conclude that the jet is formed in the immediate vicinity of the star, and infer that elongated planetary nebulae are formed by jets during the short period, of less than 1,000 years, when the star makes its transition through the proto-planetary nebula phase to become a planetary nebula.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sahai, R. & Trauger, J. T. Multipolar bubbles and jets in low-excitation planetary nebulae: toward a new understanding of the formation and shaping of planetary nebulae. Astron. J. 116, 1357–1366 (1998)
Sahai, R., te Lintel Hekkert, P., Morris, M., Zijlstra, A. & Likkel, L. The “Water-Fountain Nebula” IRAS 16342 - 3814: Hubble Space Telescope/Very Large Array study of a bipolar protoplanetary nebula. Astrophys. J. 514, L115–L119 (1999)
Alcolea, J., Bujarrabal, V., Sanchez, C. C., Neri, R. & Zweigle, J. The highly collimated bipolar outflow of OH 231.8 + 4.2. Astron. Astrophys. 373, 932–949 (2001)
Zijlstra, A. A. et al. Bipolar outflows in OH/IR stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 322, 280–308 (2001)
Miranda, L. F., Gómez, Y., Anglada, G. & Torrelles, J. M. Water-maser emission from a planetary nebula with a magnetized torus. Nature 414, 284–286 (2001)
Blackman, E. G., Frank, A., Markiel, J. A., Thomas, J. H. & Van Horn, H. M. Dynamos in asymptotic-giant-branch stars as the origin of magnetic fields shaping planetary nebulae. Nature 409, 485–487 (2001)
Diamond, P. J., Norris, R. P., Rowland, P. R., Booth, R. S. & Nyman, L.-A. The circumstellar envelopes around OH/IR stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 212, 1–21 (1985)
Herman, J. & Habing, H. J. Time variations and shell sizes of OH masers in late-type stars. Astron. Astrophys. 59, 523–555 (1985)
Nyman, L.-A., Hall, P. J. & Olofsson, H. SiO masers in OH/IR stars, proto-planetary and planetary nebulae. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 127, 185–200 (1998)
van der Veen, W. E. C. J. & Habing, H. J. The IRAS two-colour diagram as a tool for studying late stages of stellar evolution. Astron. Astrophys. 194, 125–134 (1988)
Genzel, R. & Downes, D. H2O in the Galaxy: sites of newly formed OB stars. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 30, 145–168 (1977)
Diamond, P. J. & Nyman, L.-A. in VLBI and its Impact on Astrophysics (eds Moran, J. M. & Reid, M. J.) 249–250 (Astronomical Society of the Pacific, San Francisco, 1988)
Likkel, L., Morris, M. & Maddalena, R. J. Evolved stars with high velocity H2O maser features: bipolar outflows with velocity symmetry. Astron. Astrophys. 256, 581–594 (1992)
Nakashima, J. . Observational Study of O-rich Evolved Stars in the Galaxy. PhD thesis, Graduate Univ. Advanced Studies (2002)
Elitzur, M. Astronomical Masers (Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, 1992)
Cooke, B. & Elitzur, M. Water masers in late-type stars. Astrophys. J. 295, 175–182 (1985)
Chapman, J. M. & Cohen, R. J. MERLIN observations of the circumstellar envelope of VX Sagittarius. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 220, 513–528 (1986)
Lane, A. P. et al. H2O masers in circumstellar envelopes. Astrophys. J. 323, 756–765 (1987)
Bachiller, R. Bipolar molecular outflows from young stars and protostars. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 34, 111–154 (1996)
Chandler, F. & Guillateau, S. The jet-driven molecular outflow of HH 211. Astron. Astrophys. 343, 571–584 (1999)
Bloemhof, E. E. Kinematics of the H2O masers in W49N: Analysis of the velocity variance-covariance matrix. Astrophys. J. 533, 893–896 (2000)
Zinneecker, H., McCaughrean, M. J. & Rayner, J. T. A symmetrically pulsed jet of gas from an invisible protostar in Orion. Nature 394, 862–865 (1998)
Elitzur, M., Hollenbach, D. J. & McKee, C. F. Planar H2O masers in star-forming regions. Astrophys. J. 394, 221–227 (1992)
Furuya, R. S. et al. A microjet: a protostar's cry at birth. Astrophys. J. 542, L135–L138 (2000)
Torrelles, J. M. et al. Spherical episodic ejection of material from a young star. Nature 411, 277–280 (2001)
Marvel, K. B. The circumstellar environment of evolved stars as revealed by studies of circumstellar water masers. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacif. 109, 1286–1287 (1997)
Uchida, Y. & Shibata, K. Magnetodynamical acceleration of CO and optical bipolar flows from the region of star formation. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn 37, 515–535 (1985)
Lewis, B. M. On the transience of high-latitude OH/IR stars. II. Thermal pulse link. Astrophys. J. 560, 400–412 (2001)
Morris, M. Mechanisms for mass loss from cool stars. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacif. 99, 1115–1122 (1987)
Howard, B. E. in Asymmetrical Planetary Nebulae II: From Origins to Microstructures, ASP Conference Series (eds Kastner, H., Soker, N. & Rappaport, S.) Vol. 199 115–123 (Astronomical Society of the Pacific, San Francisco, 2000)
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Nakashima and S. Deguchi for providing the information concerning SiO maser emission and infrared images of W43A. NRAO is a facility of the National Science Foundation, operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc. H. I. was financially supported by the Research Fellowship of the Japan Society of the Promotion of Science for Young Scientist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imai, H., Obara, K., Diamond, P. et al. A collimated jet of molecular gas from a star on the asymptotic giant branch. Nature 417, 829–831 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature00788
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature00788
This article is cited by
-
The study of evolved stars with ALMA
Astrophysics and Space Science (2008)
-
A magnetically collimated jet from an evolved star
Nature (2006)
-
A collimated, high-speed outflow from the dying star V Hydrae
Nature (2003)
-
The mystery companion
Nature (2003)
-
Nebulous explanation
Nature (2002)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.