Abstract
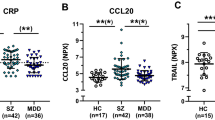
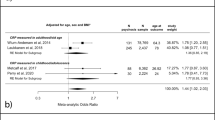
The inflammatory hypothesis of schizophrenia (SZ) posits that inflammatory processes and neural–immune interactions are involved in its pathogenesis, and may underpin some of its neurobiological correlates. SZ is the psychiatric disorder causing the most severe burden of illness, not just owing to its psychiatric impairment, but also owing to its significant medical comorbidity. C-reactive protein (CRP) is a commonly used biomarker of systemic inflammation worldwide. There are some conflicting results regarding the behaviour of CRP in SZ. The aims of this study were to verify whether peripheral CRP levels are indeed increased in SZ, whether different classes of antipsychotics divergently modulate CRP levels and whether its levels are correlated with positive and negative symptomatology. With that in mind, we performed a meta-analysis of all cross-sectional studies of serum and plasma CRP levels in SZ compared to healthy subjects. In addition, we evaluated longitudinal studies on CRP levels before and after antipsychotic use. Our meta-analyses of CRP in SZ included a total of 26 cross-sectional or longitudinal studies comprising 85 000 participants. CRP levels were moderately increased in persons with SZ regardless of the use of antipsychotics and did not change between the first episode of psychosis and with progression of SZ (g=0.66, 95% confidence interval (95% CI) 0.43 to 0.88, P<0.001, 24 between-group comparisons, n=82 962). The extent of the increase in peripheral CRP levels paralleled the increase in severity of positive symptoms, but was unrelated to the severity of negative symptoms. CRP levels were also aligned with an increased body mass index. Conversely, higher age correlated with a smaller difference in CRP levels between persons with SZ and controls. Furthermore, CRP levels did not increase after initiation of antipsychotic medication notwithstanding whether these were typical or atypical antipsychotics (g=0.01, 95% CI −0.20 to 0.22, P=0.803, 8 within-group comparisons, n=713). In summary, our study provides further evidence of the inflammatory hypothesis of SZ. Whether there is a causal relationship between higher CRP levels and the development of SZ and aggravation of psychotic symptoms, or whether they are solely a marker of systemic low-grade inflammation in SZ, remains to be clarified.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maes M . Evidence for an immune response in major depression: a review and hypothesis. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 1995; 19: 11–38.
Gibney SM, Drexhage HA . Evidence for a dysregulated immune system in the etiology of psychiatric disorders. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 2013; 8: 900–920.
Berk M, Williams LJ, Jacka FN, O'Neil A, Pasco JA, Moylan S et al. So depression is an inflammatory disease, but where does the inflammation come from? BMC Med 2013; 11: 200.
Brietzke E, Stertz L, Fernandes B, Kauer-Sant'anna M, Mascarenhas M, Vargas A et al. Comparison of cytokine levels in depressed, manic and euthymic patients with bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord 2009; 116: 214–217.
Kunz M, Cereser KM, Goi PD, Fries GR, Teixeira AL, Fernandes BS et al. Serum levels of IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-alpha in patients with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia: differences in pro- and anti-inflammatory balance. Rev Brasil Psiquiatr 2011; 33: 268–274.
Deh M, Correll CU, Bobes J, Cetkovich-Bakmas M, Cohen D, Asai I et al. Physical illness in patients with severe mental disorders. I. Prevalence, impact of medications and disparities in health care. World Psychiatry 2011; 10: 52–77.
De Hert M, Cohen D, Bobes J, Cetkovich-Bakmas M, Leucht S, Ndetei DM et al. Physical illness in patients with severe mental disorders. II. Barriers to care, monitoring and treatment guidelines, plus recommendations at the system and individual level. World Psychiatry 2011; 10: 138–151.
Canetta S, Sourander A, Surcel HM, Hinkka-Yli-Salomaki S, Leiviska J, Kellendonk C et al. Elevated maternal C-reactive protein and increased risk of schizophrenia in a national birth cohort. Am J Psychiatry 2014; 171: 960–968.
Canetta SE, Bao Y, Co MD, Ennis FA, Cruz J, Terajima M et al. Serological documentation of maternal influenza exposure and bipolar disorder in adult offspring. Am J Psychiatry 2014; 171: 557–563.
Debnath M, Venkatasubramanian G, Berk M . Fetal programming of schizophrenia: Select mechanisms. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2015; 49C: 90–104.
Miller BJ, Buckley P, Seabolt W, Mellor A, Kirkpatrick B . Meta-analysis of cytokine alterations in schizophrenia: clinical status and antipsychotic effects. Biol Psychiatry 2011; 70: 663–671.
Ruth MR, Port AM, Shah M, Bourland AC, Istfan NW, Nelson KP et al. Consuming a hypocaloric high fat low carbohydrate diet for 12 weeks lowers C-reactive protein, and raises serum adiponectin and high density lipoprotein-cholesterol in obese subjects. Metabolism 2013; 62: 1779–1787.
Pasco JA, Nicholson GC, Williams LJ, Jacka FN, Henry MJ, Kotowicz MA et al. Association of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein with de novo major depression. Br J Psychiatry 2010; 197: 372–377.
Wium-Andersen MK, Orsted DD, Nordestgaard BG . Elevated C-reactive protein associated with late- and very-late-onset schizophrenia in the general population: a prospective study. Schizophr Bull 2014; 40: 1117–1127.
Kegel ME, Bhat M, Skogh E, Samuelsson M, Lundberg K, Dahl ML et al. Imbalanced kynurenine pathway in schizophrenia. Int J Tryptophan Res 2014; 7: 15–22.
Campbell BM, Charych E, Lee AW, Moller T . Kynurenines in CNS disease: regulation by inflammatory cytokines. Front Neurosci 2014; 8: 12.
Vuksan-Cusa B, Sagud M, Jakovljevic M, Peles AM, Jaksic N, Mihaljevic S et al. Association between C-reactive protein and homocysteine with the subcomponents of metabolic syndrome in stable patients with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Nord J Psychiatry 2013; 67: 320–325.
Suvisaari J, Loo BM, Saarni SE, Haukka J, Perala J, Saarni SI et al. Inflammation in psychotic disorders: a population-based study. Psychiatry Res 2011; 189: 305–311.
Stojanovic A, Martorell L, Montalvo I, Ortega L, Monseny R, Vilella E et al. Increased serum interleukin-6 levels in early stages of psychosis: associations with at-risk mental states and the severity of psychotic symptoms. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2014; 41: 23–32.
Schwarz E, Guest PC, Steiner J, Bogerts B, Bahn S . Identification of blood-based molecular signatures for prediction of response and relapse in schizophrenia patients. Transl Psychiatry 2012; 2: e82.
Sarandol A, Kirli S, Akkaya C, Ocak N, Eroz E, Sarandol E . Coronary artery disease risk factors in patients with schizophrenia: effects of short term antipsychotic treatment. J Psychopharmacol 2007; 21: 857–863.
Meyer JM, McEvoy JP, Davis VG, Goff DC, Nasrallah HA, Davis SM et al. Inflammatory markers in schizophrenia: comparing antipsychotic effects in phase 1 of the clinical antipsychotic trials of intervention effectiveness study. Biol Psychiatry 2009; 66: 1013–1022.
Loffler S, Loffler-Ensgraber M, Fehsel K, Klimke A . Clozapine therapy raises serum concentrations of high sensitive C-reactive protein in schizophrenic patients. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 2010; 25: 101–106.
Lin CC, Chang CM, Liu CY, Huang TL . Increased high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels in Taiwanese schizophrenic patients. Asia Pac Psychiatry 2013; 5: E58–E63.
Kuo FC, Lee CH, Hsieh CH, Kuo P, Chen YC, Hung YJ . Lifestyle modification and behavior therapy effectively reduce body weight and increase serum level of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in obese non-diabetic patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 2013; 209: 150–154.
Kraemer S, Minarzyk A, Forst T, Kopf D, Hundemer HP . Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with schizophrenia, and metabolic changes after 3 months of treatment with antipsychotics—results from a German observational study. BMC Psychiatry 2011; 11: 173.
Kliushnik TP, Siriachenko TM, Sarmanova ZV, Otman IN, Dupin AM, Sokolov RE . [Changes of the level of serum antibodies to neuroantigens in patients with schizophrenia during the treatment]. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova 2008; 108: 61–64.
Klemettila JP, Kampman O, Seppala N, Viikki M, Hamalainen M, Moilanen E et al. Cytokine and adipokine alterations in patients with schizophrenia treated with clozapine. Psychiatry Res 2014; 218: 277–283.
Joshi KB, Nillawar A, Thorat AP . Cardiovascular disease risk in schizophrenia patients: a case control study. J Clin Diagn Res 2013; 7: 2694–2696.
Hope S, Dieset I, Agartz I, Steen NE, Ueland T, Melle I et al. Affective symptoms are associated with markers of inflammation and immune activation in bipolar disorders but not in schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 2011; 45: 1608–1616.
Hepgul N, Pariante CM, Dipasquale S, DiForti M, Taylor H, Marques TR et al. Childhood maltreatment is associated with increased body mass index and increased C-reactive protein levels in first-episode psychosis patients. PsycholMed 2012; 42: 1893–1901.
Henderson DC, Fan X, Copeland PM, Sharma B, Borba CP, Boxill R et al. Aripiprazole added to overweight and obese olanzapine-treated schizophrenia patients. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2009; 29: 165–169.
Frydecka D, Misiak B, Pawlak-Adamska E, Karabon L, Tomkiewicz A, Sedlaczek P et al. Interleukin-6: the missing element of the neurocognitive deterioration in schizophrenia? The focus on genetic underpinnings, cognitive impairment and clinical manifestation. Eur Arch Psychiatry Neurosci 2014.
Fernandez-Egea E, Bernardo M, Donner T, Conget I, Parellada E, Justicia A et al. Metabolic profile of antipsychotic-naive individuals with non-affective psychosis. Br J Psychiatry 2009; 194: 434–438.
Fawzi MH, Fawzi MM, Fawzi MM, Said NS . C-reactive protein serum level in drug-free male Egyptian patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 2011; 190: 91–97.
Dickerson F, Stallings C, Origoni A, Vaughan C, Khushalani S, Yang S et al. C-reactive protein is elevated in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2013; 143: 198–202.
Diaz FJ, Perez-Iglesias R, Mata I, Martinez-Garcia O, Vazquez-Barquero JL, de Leon J et al. Possible effects of some antipsychotic drugs on C-reactive protein in a drug-naive psychotic sample. Schizophr Res 2010; 121: 207–212.
De Berardis D, Conti CM, Marini S, Serroni N, Moschetta FS, Carano A . C-reactive protein level and its relationship with suicide risk and alexithymia among newly diagnosed, drug-naive patients with non-affective psychosis. Eur J Inflammation 2013; 11: 0–0.
Carrizo E, Fernandez V, Quintero J, Connell L, Rodriguez Z, Mosquera M et al. Coagulation and inflammation markers during atypical or typical antipsychotic treatment in schizophrenia patients and drug-free first-degree relatives. Schizophr Res 2008; 103: 83–93.
Baptista T, Davila A, El Fakih Y, Uzcategui E, Rangel NN, Olivares Y et al. Similar frequency of abnormal correlation between serum leptin levels and BMI before and after olanzapine treatment in schizophrenia. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 2007; 22: 205–211.
Akanji AO, Ohaeri JU, Al-Shammri S, Fatania HR . Association of blood levels of C-reactive protein with clinical phenotypes in Arab schizophrenic patients. Psychiatry Res 2009; 169: 56–61.
McNamara RK, Jandacek R, Rider T, Tso P . Chronic risperidone normalizes elevated pro-inflammatory cytokine and C-reactive protein production in omega-3 fatty acid deficient rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2011; 652: 152–156.
JP H . Handbook for systematic reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration 2011.
Egger M, Zellweger-Zahner T, Schneider M, Junker C, Lengeler C, Antes G . Language bias in randomised controlled trials published in English and German. Lancet 1997; 350: 326–329.
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C . Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997; 315: 629–634.
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA . The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 1987; 13: 261–276.
Sistrom CL, Mergo PJ . A simple method for obtaining original data from published graphs and plots. Am J Roentgenol 2000; 174: 1241–1244.
Stang A . Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol 2010; 25: 603–605.
Soeken KL, Sripusanapan A . Assessing publication bias in meta-analysis. Nurs Res 2003; 52: 57–60.
Bowden J, Tierney JF, Copas AJ, Burdett S . Quantifying, displaying and accounting for heterogeneity in the meta-analysis of RCTs using standard and generalised Q statistics. BMC Med Res Methodol 2011; 11: 41.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG . Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003; 327: 557–560.
Lau J, Ioannidis JP, Schmid CH . Quantitative synthesis in systematic reviews. Ann Int Med 1997; 127: 820–826.
Goto M, Sugimoto K, Hayashi S, Ogino T, Sugimoto M, Furuichi Y et al. Aging-associated inflammation in healthy Japanese individuals and patients with Werner syndrome. Exp Gerontol 2012; 47: 936–939.
Najjar S, Pearlman DM, Devinsky O, Najjar A, Zagzag D . Neurovascular unit dysfunction with blood-brain barrier hyperpermeability contributes to major depressive disorder: a review of clinical and experimental evidence. J Neuroinflammation 2013; 10: 142.
Uranova NA, Zimina IS, Vikhreva OV, Krukov NO, Rachmanova VI, Orlovskaya DD . Ultrastructural damage of capillaries in the neocortex in schizophrenia. World J Biol Psychiatry 2010; 11: 567–578.
Adami C, Sorci G, Blasi E, Agneletti AL, Bistoni F, Donato R . S100B expression in and effects on microglia. Glia 2001; 33: 131–142.
Schwieler L, Larsson MK, Skogh E, Kegel ME, Orhan F, Abdelmoaty S et al. Increased levels of IL-6 in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with chronic schizophrenia - significance for activation of the kynurenine pathway. J Psychiatry Neurosci 2015; 40: 126–133.
Koshy Cherian A, Gritton H, Johnson DE, Young D, Kozak R, Sarter M . A systemically-available kynurenine aminotransferase II (KAT II) inhibitor restores nicotine-evoked glutamatergic activity in the cortex of rats. Neuropharmacology 2014; 82: 41–48.
Schwarcz R, Bruno JP, Muchowski PJ, Wu HQ . Kynurenines in the mammalian brain: when physiology meets pathology. Nat Rev Neurosci 2012; 13: 465–477.
Wu HQ, Okuyama M, Kajii Y, Pocivavsek A, Bruno JP, Schwarcz R . Targeting kynurenine aminotransferase II in psychiatric diseases: promising effects of an orally active enzyme inhibitor. Schizophr Bull 2014; 40: S152–S158.
Catts VS, Wong J, Fillman SG, Fung SJ, Shannon Weickert C . Increased expression of astrocyte markers in schizophrenia: association with neuroinflammation. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 2014; 48: 722–734.
Fillman SG, Cloonan N, Miller LC, Weickert CS . Markers of inflammation in the prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2013; 18: 133.
Schroeter ML, Steiner J . Elevated serum levels of the glial marker protein S100B are not specific for schizophrenia or mood disorders. Mol Psychiatry 2009; 14: 235–237.
Fernandes BS, Berk M, Turck CW, Steiner J, Goncalves CA . Decreased peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels are a biomarker of disease activity in major psychiatric disorders: a comparative meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry 2014; 19: 749–751.
Fernandes BS, Steiner J, Berk M, Molendijk ML, Gonzalez-Pinto A, Turck CW et al. Peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor in schizophrenia and the role of antipsychotics: meta-analysis and implications. Mol Psychiatry 2014; doi:10.1038/mp.2014.117 (e-pub ahead of print).
ON A, Jacka FN, Quirk SE, Cocker F, Taylor C, Oldenburg B et al. A shared framework for the common mental disorders and non-communicable disease: key considerations for disease prevention and control. BMC Psychiatry 2015; 15: 15.
Frey BN, Andreazza AC, Houenou J, Jamain S, Goldstein BI, Frye MA et al. Biomarkers in bipolar disorder: a positional paper from the International Society for Bipolar Disorders Biomarkers Task Force. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 2013; 47: 321–332.
Fernandes BS, Gama C, Kauer-Sant'anna M, Lobato M, Belmonte-De-Abreu P, Kapczinski F . Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor in bipolar and unipolar depression: a potential adjunctive tool for differential diagnosis. J Psychiatric Res 2009; 43: 1200–1204.
Fernandes BS, Gama CS, Cereser KM, Yatham LN, Fries GR, Colpo G et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor as a state-marker of mood episodes in bipolar disorders: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis. J Psychiatric Res 2011; 45: 995–1004.
Kapczinski F, Fernandes B, Kauer-Sant'anna M, Gama C, Yatham L, Berk M . The concept of staging in bipolar disorder: the role of BDNF and TNF-alpha as biomarkers. ACTA Neuropsychiatr 2009; 21: 272–274.
Davis J, Maes M, Andreazza A, McGrath JJ, Tye SJ, Berk M . Towards a classification of biomarkers of neuropsychiatric disease: from encompass to compass. Mol Psychiatry 2015; 20: 152–153.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the authors of the included papers, in particular Drs Domenico De Berardis, Nilay Hepgul, Susanne Kraemer, Vanessa Mondelli and Jaana Suvisaari, who very kindly provided us with unpublished data for our paper. BSF is supported by a scholarship and by a research grant MCTI/CNPQ/Universal 14/2014461833/2014-0, both from CNPq, Brazil. MB is supported by a NHMRC Senior Principal Research Fellowship 1059660.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandes, B., Steiner, J., Bernstein, HG. et al. C-reactive protein is increased in schizophrenia but is not altered by antipsychotics: meta-analysis and implications. Mol Psychiatry 21, 554–564 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2015.87
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2015.87