Abstract
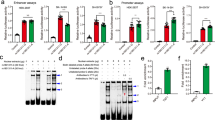
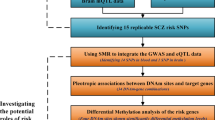
Recently, two genome-wide association studies (GWASs) of schizophrenia (SCZ) in Han Chinese identified several susceptibility loci. Replication efforts aiming to validate the GWAS findings were made and focused on the top hits. We conducted a more extensive follow-up study in an independent sample of 1471 cases and 1528 matched controls to verify 26 genetic variants by including nine top single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that reached genome-wide significance and 17 promising SNPs nominated in the initial discovery phase. rs8073471 in an intron of tubulin-folding cofactor D (TBCD) obtained nominal significance (P<0.01) in single SNP analysis. Logistic regression identified significant interaction between rs3744165 (5’-untranslated region variant of exon 2 of zinc finger protein 750 (ZNF750), and in an intron of TBCD) and rs8073471 (Deviance test P-value=2.77 × 10−34). Both SNPs are located at 17q25, an interesting region that has been implicated in SCZ. By using the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) data set, we implemented an expression quantitative trait loci epistasis analysis to explore the association between the genotype combinations of the two SNPs and gene expression levels in 13 areas of human central nervous system. We observed that rs3744165 × rs8073471 interaction modulated the expression profile of TEAD3 (P=1.87 × 10−8), SH3TC2 (P=2.00 × 10−8), KCNK9 (P=5.20 × 10−7) and PPDPF (P=1.13 × 10−6) in postmortem cortex tissue; EFNA1 (P=7.26 × 10−9), RNU4ATAC (P=2.32 × 10−8) and NUPL2 (P=6.79 × 10−8) in cerebellum tissue. To the best of our knowledge, our study is the first one that links TBCD and ZNF750 mutations to SCZ susceptibility and to the transcript levels in human brain tissues. Further efforts are needed to understand the role of those variants in the pathogenesis of SCZ.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGrath J, Saha S, Chant D, Welham J . Schizophrenia: a concise overview of incidence, prevalence, and mortality. Epidemiol Rev 2008; 30: 67–76.
Sullivan PF, Kendler KS, Neale MC . Schizophrenia as a complex trait: evidence from a meta-analysis of twin studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2003; 60: 1187–1192.
Lichtenstein P, Yip BH, Bjork C, Pawitan Y, Cannon TD, Sullivan PF et al. Common genetic determinants of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder in Swedish families: a population-based study. Lancet 2009; 373: 234–239.
O'Donovan MC, Craddock N, Norton N, Williams H, Peirce T, Moskvina V et al. Identification of loci associated with schizophrenia by genome-wide association and follow-up. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 1053–1055.
Stefansson H, Ophoff RA, Steinberg S, Andreassen OA, Cichon S, Rujescu D et al. Common variants conferring risk of schizophrenia. Nature 2009; 460: 744–747.
Schizophrenia Psychiatric Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) Consortium. Genome-wide association study identifies five new schizophrenia loci. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 969–976.
Ripke S, O'Dushlaine C, Chambert K, Moran JL, Kahler AK, Akterin S et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies 13 new risk loci for schizophrenia. Nat Genet 2013; 45: 1150–1159.
Harrison PJ . Recent genetic findings in schizophrenia and their therapeutic relevance. J Psychopharmacol 2015; 29: 85–96.
Yue WH, Wang HF, Sun LD, Tang FL, Liu ZH, Zhang HX et al. Genome-wide association study identifies a susceptibility locus for schizophrenia in Han Chinese at 11p11.2. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 1228–1231.
Shi Y, Li Z, Xu Q, Wang T, Li T, Shen J et al. Common variants on 8p12 and 1q24.2 confer risk of schizophrenia. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 1224–1227.
Ma L, Tang J, Wang D, Zhang W, Liu W, Liu XH et al. Evaluating risk loci for schizophrenia distilled from genome-wide association studies in Han Chinese from Central China. Mol Psychiatry 2013; 18: 638–639.
Jin C, Zhang Y, Wang J, Zhou Z, Sha W, Wang M et al. Lack of association between MPC2 variants and schizophrenia in a replication study of Han Chinese. Neurosci Lett 2013; 552: 120–123.
Yuan J, Jin C, Qin HD, Wang J, Sha W, Wang M et al. Replication study confirms link between TSPAN18 mutation and schizophrenia in Han Chinese. PLoS One 2013; 8: e58785.
Zhang Y, Lu T, Yan H, Ruan Y, Wang L, Zhang D et al. Replication of association between schizophrenia and chromosome 6p21-6p22.1 polymorphisms in Chinese Han population. PLoS One 2013; 8: e56732.
Pandey A, Davis NA, White BC, Pajewski NM, Savitz J, Drevets WC et al. Epistasis network centrality analysis yields pathway replication across two GWAS cohorts for bipolar disorder. Transl Psychiatry 2012; 2: e154.
Manolio TA, Collins FS, Cox NJ, Goldstein DB, Hindorff LA, Hunter DJ et al. Finding the missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature 2009; 461: 747–753.
Zuk O, Hechter E, Sunyaev SR, Lander ES . The mystery of missing heritability: Genetic interactions create phantom heritability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 1193–1198.
Verhoeven KJ, Casella G, McIntyre LM . Epistasis: obstacle or advantage for mapping complex traits? PLoS One 2010; 5: e12264.
Huang Y, Wuchty S, Przytycka TM . eQTL Epistasis - challenges and computational approaches. Front Genet 2013; 4: 51.
Mackay TF . Epistasis and quantitative traits: using model organisms to study gene-gene interactions. Nat Rev Genet 2014; 15: 22–33.
Consortium TG. The genotype-tissue expression (GTEx) project. Nat Genet 2013; 45: 580–585.
Rajkumar AP, Christensen JH, Mattheisen M, Jacobsen I, Bache I, Pallesen J et al. Analysis of t(9;17)(q33.2;q25.3) chromosomal breakpoint regions and genetic association reveals novel candidate genes for bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord 2014; 17: 205–211.
Logue MW, Brzustowicz LM, Bassett AS, Chow EW, Vieland VJ . A posterior probability of linkage-based re-analysis of schizophrenia data yields evidence of linkage to chromosomes 1 and 17. Hum Hered 2006; 62: 47–54.
Zhang F, Liu C, Xu Y, Qi G, Yuan G, Cheng Z et al. A two-stage association study suggests BRAP as a susceptibility gene for schizophrenia. PLoS One 2014; 9: e86037.
Huang L, Hu F, Zeng X, Gan L, Luo XJ . Further evidence for the association between the LSM1 gene and schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2013; 150: 588–589.
Syu A, Ishiguro H, Inada T, Horiuchi Y, Tanaka S, Ishikawa M et al. Association of the HSPG2 gene with neuroleptic-induced tardive dyskinesia. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010; 35: 1155–1164.
Tian G, Thomas S, Cowan NJ . Effect of TBCD and its regulatory interactor Arl2 on tubulin and microtubule integrity. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken) 2010; 67: 706–714.
Lundin VF, Leroux MR, Stirling PC . Quality control of cytoskeletal proteins and human disease. Trends Biochem Sci 2010; 35: 288–297.
Lopez-Fanarraga M, Avila J, Guasch A, Coll M, Zabala JC . Review: postchaperonin tubulin folding cofactors and their role in microtubule dynamics. J Struct Biol 2001; 135: 219–229.
Fanarraga ML, Bellido J, Jaen C, Villegas JC, Zabala JC . TBCD links centriologenesis, spindle microtubule dynamics, and midbody abscission in human cells. PLoS One 2010; 5: e8846.
Poulton CJ, Schot R, Seufert K, Lequin MH, Accogli A, Annunzio GD et al. Severe presentation of WDR62 mutation: is there a role for modifying genetic factors? Am J Med Genet A 2014; 164A: 2161–2171.
Paschou P, Feng Y, Pakstis AJ, Speed WC, DeMille MM, Kidd JR et al. Indications of linkage and association of Gilles de la Tourette syndrome in two independent family samples: 17q25 is a putative susceptibility region. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 75: 545–560.
Moehle MS, Luduena RF, Haroutunian V, Meador-Woodruff JH, McCullumsmith RE . Regional differences in expression of beta-tubulin isoforms in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2012; 135: 181–186.
Solis-Chagoyan H, Calixto E, Figueroa A, Montano LM, Berlanga C, Rodriguez-Verdugo MS et al. Microtubule organization and L-type voltage-activated calcium current in olfactory neuronal cells obtained from patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Schizophr Res 2013; 143: 384–389.
Fullston T, Gabb B, Callen D, Ullmann R, Woollatt E, Bain S et al. Inherited balanced translocation t(9;17)(q33.2;q25.3) concomitant with a 16p13.1 duplication in a patient with schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2011; 156: 204–214.
Brown AS, Borgmann-Winter K, Hahn CG, Role L, Talmage D, Gur R et al. Increased stability of microtubules in cultured olfactory neuroepithelial cells from individuals with schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2014; 48: 252–258.
Sen GL, Boxer LD, Webster DE, Bussat RT, Qu K, Zarnegar BJ et al. ZNF750 is a p63 target gene that induces KLF4 to drive terminal epidermal differentiation. Dev Cell 2012; 22: 669–677.
Boxer LD, Barajas B, Tao S, Zhang J, Khavari PA . ZNF750 interacts with KLF4 and RCOR1, KDM1A, and CTBP1/2 chromatin regulators to repress epidermal progenitor genes and induce differentiation genes. Genes Dev 2014; 28: 2013–2026.
Hwu WL, Yang CF, Fann CS, Chen CL, Tsai TF, Chien YH et al. Mapping of psoriasis to 17q terminus. J Med Genet 2005; 42: 152–158.
Yang CF, Hwu WL, Yang LC, Chung WH, Chien YH, Hung CF et al. A promoter sequence variant of ZNF750 is linked with familial psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 2008; 128: 1662–1668.
Birnbaum RY, Hayashi G, Cohen I, Poon A, Chen H, Lam ET et al. Association analysis identifies ZNF750 regulatory variants in psoriasis. BMC Med Genet 2011; 12: 167.
Benros ME, Eaton WW, Mortensen PB . The epidemiologic evidence linking autoimmune diseases and psychosis. Biol Psychiatry 2014; 75: 300–306.
Benros ME, Pedersen MG, Rasmussen H, Eaton WW, Nordentoft M, Mortensen PB . A nationwide study on the risk of autoimmune diseases in individuals with a personal or a family history of schizophrenia and related psychosis. Am J Psychiatry 2014; 171: 218–226.
Chen SJ, Chao YL, Chen CY, Chang CM, Wu EC, Wu CS et al. Prevalence of autoimmune diseases in in-patients with schizophrenia: nationwide population-based study. Br J Psychiatry 2012; 200: 374–380.
Kumar V, Mattoo SK, Handa S . Psychiatric morbidity in pemphigus and psoriasis: a comparative study from India. Asian J Psychiatr 2013; 6: 151–156.
Andreassen OA, Harbo HF, Wang Y, Thompson WK, Schork AJ, Mattingsdal M et al. Genetic pleiotropy between multiple sclerosis and schizophrenia but not bipolar disorder: differential involvement of immune-related gene loci. Mol Psychiatry 2014; 20: 207–214.
Schroder A, Klein K, Winter S, Schwab M, Bonin M, Zell A et al. Genomics of ADME gene expression: mapping expression quantitative trait loci relevant for absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of drugs in human liver. Pharmacogenomics J 2013; 13: 12–20.
Xie Q, Chen J, Feng H, Peng S, Adams U, Bai Y et al. YAP/TEAD-mediated transcription controls cellular senescence. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 3615–3624.
Senderek J, Bergmann C, Stendel C, Kirfel J, Verpoorten N, De Jonghe P et al. Mutations in a gene encoding a novel SH3/TPR domain protein cause autosomal recessive Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 4C neuropathy. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 1106–1119.
Vincent JB, Noor A, Windpassinger C, Gianakopoulos PJ, Schwarzbraun T, Alfred SE et al. Characterization of a de novo translocation t(5;18)(q33.1;q12.1) in an autistic boy identifies a breakpoint close to SH3TC2, ADRB2, and HTR4 on 5q, and within the desmocollin gene cluster on 18q. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2009; 150B: 817–826.
Barel O, Shalev SA, Ofir R, Cohen A, Zlotogora J, Shorer Z et al. Maternally inherited Birk Barel mental retardation dysmorphism syndrome caused by a mutation in the genomically imprinted potassium channel KCNK9. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 83: 193–199.
Bando Y, Hirano T, Tagawa Y . Dysfunction of KCNK potassium channels impairs neuronal migration in the developing mouse cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex 2014; 24: 1017–1029.
Reddy S, Dolzhanskaya N, Krogh J, Velinov M . A novel 1.4 Mb de novo microdeletion of chromosome 1q21.3 in a child with microcephaly, dysmorphic features and mental retardation. Eur J Med Genet 2009; 52: 443–445.
Abdel-Salam GM, Miyake N, Eid MM, Abdel-Hamid MS, Hassan NA, Eid OM et al. A homozygous mutation in RNU4ATAC as a cause of microcephalic osteodysplastic primordial dwarfism type I (MOPD I) with associated pigmentary disorder. Am J Med Genet A 2011; 155A: 2885–2896.
Le Rouzic E, Mousnier A, Rustum C, Stutz F, Hallberg E, Dargemont C et al. Docking of HIV-1 Vpr to the nuclear envelope is mediated by the interaction with the nucleoporin hCG1. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 45091–45098.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support from the National Basic Research Program of China (2014CB744600), and National Nature Science Foundation of China (81201039). We highly appreciated the solid supports from Professor Xin Yu and Professor Rene Kahn on organizing the GREAT-CN network. The GTEx Project was supported by the Common Fund of the Office of the Director of the National Institutes of Health (commonfund.nih.gov/GTEx). Additional funds were provided by the NCI, NHGRI, NHLBI, NIDA, HIMH and NINDS. Donors were enrolled at Biospecimen Source Sites funded by NCI\Leidos Biomedical Research subcontracts to the National Disease Research Interchange (10XS170), Roswell Park Cancer Institute (10XS171), and Science Care (X10S172). The Laboratory, Data Analysis and Coordinating Center (LDACC) were funded through a contract (HHSN268201000029C) to The Broad Institute. Biorepository operations were funded through a Leidos Biomedical Research subcontract to Van Andel Research Institute (10ST1035). Additional Data repository and project management were provided by Leidos Biomedical Research (HHSN261200800001E). The Brain Bank was supported supplements to University of Miami grant DA006227. Statistical Methods development grants were made to the University of Geneva (MH090941 and MH101814), the University of Chicago (MH090951, MH090937, MH101825 and MH101820), the University of North Carolina—Chapel Hill (MH090936), North Carolina State University (MH101819), Harvard University (MH090948), Stanford University (MH101782), Washington University (MH101810) and to the University of Pennsylvania (MH101822). The data sets used for the analyses described in this manuscript were obtained from dbGaP at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gap through dbGaP accession number phs000424.v4.p1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Supplementary information
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, L., Wang, Q., Wang, L. et al. Common variants on 17q25 and gene–gene interactions conferring risk of schizophrenia in Han Chinese population and regulating gene expressions in human brain. Mol Psychiatry 21, 1244–1250 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2015.204
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2015.204
This article is cited by
-
Replicated associations of FADS1, MAD1L1, and a rare variant at 10q26.13 with bipolar disorder in Chinese population
Translational Psychiatry (2018)
-
Genetic association and meta-analysis of a schizophrenia GWAS variant rs10489202 in East Asian populations
Translational Psychiatry (2018)
-
Progress in genome-wide association studies of schizophrenia in Han Chinese populations
npj Schizophrenia (2017)