Abstract
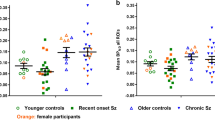
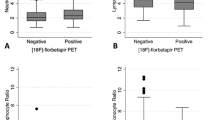
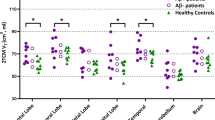
Our primary aim was to compare neuroinflammation in cognitively intact control subjects and patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) by using positron emission tomography (PET) with translocator protein 18kDa (TSPO)-specific radioligand [18F]-FEPPA. [18F]-FEPPA PET scans were acquired on a high-resolution research tomograph in 21 patients with AD (47– 81 years) and 21 control subjects (49–82 years). They were analyzed by using a 2-tissue compartment model with arterial plasma input function. Differences in neuroinflammation, indexed as [18F]-FEPPA binding were compared, adjusting for differences in binding affinity class as determined by a single polymorphism in the TSPO gene (rs6971). In grey matter areas, [18F]-FEPPA was significantly higher in AD compared with healthy control subjects. Large increases were seen in the hippocampus, prefrontal, temporal, parietal and occipital cortex (average Cohen’s d= 0.89). Voxel-based analyses confirmed significant clusters of neuroinflammation in the frontal, temporal and parietal cortex in patients with AD. In white matter, [18F]-FEPPA binding was elevated in the posterior limb of the internal capsule, and the cingulum bundle. Higher neuroinflammation in the parietal cortex (r= −0.7, P= 0.005), and posterior limb of the internal capsule (r= −0.8, P=0.001) was associated with poorer visuospatial function. In addition, a higher [18F]-FEPPA binding in the posterior limb of the internal capsule was associated with a greater impairment in language ability (r= −0.7, P=0.004). Elevated neuroinflammation can be detected in AD patients throughout the brain grey and white matter by using [18F]-FEPPA PET. Our results also suggest that neuroinflammation is associated with some cognitive deficits.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM et al. Inflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 2000; 21: 383–421.
Wegiel J, Wisniewski HM . The complex of microglial cells and amyloid star in three-dimensional reconstruction. Acta Neuropathol 1990; 81: 116–124.
Luber-Narod J, Rogers J . Immune system associated antigens expressed by cells of the human central nervous system. Neurosci Lett 1988; 94: 17–22.
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, McGeer EG . Expression of the histocompatibility glycoprotein HLA-DR in neurological disease. Acta Neuropathol 1988; 76: 550–557.
Kreutzberg GW . Mic roglia: a sensor for pathological events in the CNS. Trends Neurosci 1996; 19: 312–318.
Chen MK, Guilarte TR . Translocator protein 18 kDa (TSPO): molecular sensor of brain injury and repair. Pharmacol Ther 2008; 118: 1–17.
Cosenza-Nashat M, Zhao ML, Suh HS, Morgan J, Natividad R, Morgello S et al. Expression of the translocator protein of 18 kDa by microglia, macrophages and astrocytes based on immunohistochemical localization in abnormal human brain. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2009; 35: 306–328.
Venneti S, Wiley CA, Kofler J . Imaging microglial activation during neuroinflammation and Alzheimer's disease. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 2009; 4: 227–243.
Cagnin A, Brooks DJ, Kennedy AM, Gunn RN, Myers R, Turkheimer FE et al. In-vivo measurement of activated microglia in dementia. Lancet 2001; 358: 461–467.
Edison P, Archer HA, Gerhard A, Hinz R, Pavese N, Turkheimer FE et al. Microglia, amyloid, and cognition in Alzheimer's disease: An [11C](R)PK11195-PET and [11C]PIB-PET study. Neurobiol Dis 2008; 32: 412–419.
Schuitemaker A, Kropholler MA, Boellaard R, van der Flier WM, Kloet RW, van der Doef TF et al. Microglial activation in Alzheimer's disease: an (R)-[(1)(1)C]PK11195 positron emission tomography study. Neurobiol Aging 2013; 34: 128–136.
Okello A, Edison P, Archer HA, Turkheimer FE, Kennedy J, Bullock R et al. Microglial activation and amyloid deposition in mild cognitive impairment: a PET study. Neurology 2009; 72: 56–62.
Wiley CA, Lopresti BJ, Venneti S, Price J, Klunk WE, DeKosky ST et al. Carbon 11-labeled Pittsburgh Compound B and carbon 11-labeled (R)-PK11195 positron emission tomographic imaging in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 2009; 66: 60–67.
Chauveau F, Boutin H, Van Camp N, Dolle F, Tavitian B . Nuclear imaging of neuroinflammation: a comprehensive review of [11C]PK11195 challengers. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008; 35: 2304–2319.
Wilson AA, Garcia A, Parkes J, McCormick P, Stephenson KA, Houle S et al. Radiosynthesis and initial evaluation of [18F]-FEPPA for PET imaging of peripheral benzodiazepine receptors. Nucl Med Biol 2008; 35: 305–314.
Rusjan PM, Wilson AA, Bloomfield PM, Vitcu I, Meyer JH, Houle S et al. Quantitation of translocator protein binding in human brain with the novel radioligand [(18)F]-FEPPA and positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2011; 31: 1807–1816.
Kreisl WC, Jenko KJ, Hines CS, Hyoung Lyoo C, Corona W, Morse CL et al. A genetic polymorphism for translocator protein 18 kDa affects both in vitro and in vivo radioligand binding in human brain to this putative biomarker of neuroinflammation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2013; 33: 53–58.
Mizrahi R, Rusjan PM, Kennedy J, Pollock B, Mulsant B, Suridjan I et al. Translocator protein (18 kDa) polymorphism (rs6971) explains in-vivo brain binding affinity of the PET radioligand [(18)F]-FEPPA. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2012; 32: 968–972.
Guo Q, Owen DR, Rabiner EA, Turkheimer FE, Gunn RN . Identifying improved TSPO PET imaging probes through biomathematics: The impact of multiple TSPO binding sites in vivo. Neuroimage 2012; 60: 902–910.
Owen DR, Howell OW, Tang SP, Wells LA, Bennacef I, Bergstrom M et al. Two binding sites for [3H]PBR28 in human brain: implications for TSPO PET imaging of neuroinflammation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2010; 30: 1608–1618.
Owen DR, Gunn RN, Rabiner EA, Bennacef I, Fujita M, Kreisl WC et al. Mixed-affinity binding in humans with 18-kDa translocator protein ligands. J Nucl Med 2011; 52: 24–32.
Sexton CE, Kalu UG, Filippini N, Mackay CE, Ebmeier KP . A meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 2010; 32, 2322. e5–e18.
Canu E, Agosta F, Spinelli EG, Magnani G, Marcone A, Scola E et al. White matter microstructural damage in Alzheimer's disease at different ages of onset. Neurobiol Aging 2013; 34: 2331–2340.
Migliaccio R, Agosta F, Possin KL, Rabinovici GD, Miller BL, Gorno-Tempini ML . White matter atrophy in Alzheimer's disease variants. Alzheimers Dement 2012; 8, S78-87, e71–e72.
Rose SE, Chen F, Chalk JB, Zelaya FO, Strugnell WE, Benson M et al. Loss of connectivity in Alzheimer's disease: an evaluation of white matter tract integrity with colour coded MR diffusion tensor imaging. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2000; 69: 528–530.
Duan JH, Wang HQ, Xu J, Lin X, Chen SQ, Kang Z et al. White matter damage of patients with Alzheimer's disease correlated with the decreased cognitive function. Surg Radiol Anat 2006; 28: 150–156.
Zhang Y, Schuff N, Jahng GH, Bayne W, Mori S, Schad L et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of cingulum fibers in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2007; 68: 13–19.
Scheltens P, Barkhof F, Leys D, Wolters EC, Ravid R, Kamphorst W . Histopathologic correlates of white matter changes on MRI in Alzheimer's disease and normal aging. Neurology 1995; 45: 883–888.
Sjobeck M, Haglund M, Englund E . Decreasing myelin density reflected increasing white matter pathology in Alzheimer's disease – a neuropathological study. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 2005; 20: 919–926.
Sjobeck M, Englund E . Glial levels determine severity of white matter disease in Alzheimer's disease: a neuropathological study of glial changes. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2003; 29: 159–169.
Yokokura M, Mori N, Yagi S, Yoshikawa E, Kikuchi M, Yoshihara Y et al. In vivo changes in microglial activation and amyloid deposits in brain regions with hypometabolism in Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2011; 38: 343–351.
Kreisl WC, Lyoo CH, McGwier M, Snow J, Jenko KJ, Kimura N et al. In vivo radioligand binding to translocator protein correlates with severity of Alzheimer's disease. Brain 2013; 136: 2228–2238.
Yasuno F, Ota M, Kosaka J, Ito H, Higuchi M, Doronbekov TK et al. Increased binding of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor in Alzheimer's disease measured by positron emission tomography with [11C]DAA1106. Biol Psychiatry 2008; 64: 835–841.
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM . Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology 1984; 34: 939–944.
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR . ‘Mini-mental state’. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 1975; 12: 189–198.
Smith T, Gildeh N, Holmes C . The Montreal Cognitive Assessment: validity and utility in a memory clinic setting. Can J Psychiatry 2007; 52: 329–332.
Tombaugh TN . Trail Making Test A and B: normative data stratified by age and education. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 2004; 19: 203–214.
Trenerry MR . Stroop Neuropsychological Screening Test Manual. Psychological Assessment Resources: Odessa, FL, 1989.
Wechsler D . Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale– Third Edition (WAIS–III). Texas: Pearson Corp, San Antonio, 1997.
Duff K, Humphreys Clark JD, O'Bryant SE, Mold JW, Schiffer RB, Sutker PB . Utility of the RBANS in detecting cognitive impairment associated with Alzheimer's disease: sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive powers. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 2008; 23: 603–612.
Morris JC . The Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR): current version and scoring rules. Neurology 1993; 43: 2412–2414.
Gelinas I, Gauthier L, McIntyre M, Gauthier S . Development of a functional measure for persons with Alzheimer's disease: the disability assessment for dementia. Am J Occup Ther 1999; 53: 471–481.
Cummings JL, Mega M, Gray K, Rosenberg-Thompson S, Carusi DA, Gornbein J . The Neuropsychiatric Inventory: comprehensive assessment of psychopathology in dementia. Neurology 1994; 44: 2308–2314.
Alexopoulos GS, Abrams RC, Young RC, Shamoian CA . Cornell Scale for Depression in Dementia. Biol Psychiatry 1988; 23: 271–284.
Suridjan I, Rusjan PM, Voineskos AN, Selvanathan T, Setiawan E, Strafella AP et al. Neuroinflammation in healthy aging: a PET study using a novel Translocator Protein 18kDa (TSPO) radioligand, [(18)F]-FEPPA. Neuroimage 2014; 84: 868–875.
Scheltens P, Barkhof F, Valk J, Algra PR, van der Hoop RG, Nauta J et al. White matter lesions on magnetic resonance imaging in clinically diagnosed Alzheimer's disease. Evidence for heterogeneity. Brain 1992; 115: 735–748.
Rusjan P, Mamo D, Ginovart N, Hussey D, Vitcu I, Yasuno F et al. An automated method for the extraction of regional data from PET images. Psychiatry Res 2006; 147: 79–89.
Braak H, Braak E . Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 1991; 82: 239–259.
Duvernoy H . The Human Brain: Surface, Blood Supply and Three Dimensional Sectional Anatomy. SpringerWien: New York, 1999.
Mori S, Oishi K, Jiang H, Jiang L, Li X, Akhter K et al. Stereotaxic white matter atlas based on diffusion tensor imaging in an ICBM template. Neuroimage 2008; 40: 570–582.
Suridjan I, Rusjan P, Kenk M, Verhoeff NP, Voineskos AN, Rotenberg D et al. Quantitative imaging of neuroinflammation in human white matter: a positron emission tomography (PET) study with translocator protein 18kDA (TSPO) radioligand, [18F]-FEPPA. Synapse 2014; 68: 536–547.
Muller-Gartner HW, Links JM, Prince JL, Bryan RN, McVeigh E, Leal JP et al. Measurement of radiotracer concentration in brain gray matter using positron emission tomography: MRI-based correction for partial volume effects. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1992; 12: 571–583.
Bencherif B, Stumpf MJ, Links JM, Frost JJ . Application of MRI-based partial-volume correction to the analysis of PET images of mu-opioid receptors using statistical parametric mapping. J Nucl Med 2004; 45: 402–408.
Turkheimer FE, Banati RB, Visvikis D, Aston JA, Gunn RN, Cunningham VJ . Modeling dynamic PET-SPECT studies in the wavelet domain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2000; 20: 879–893.
Lahiri DK, Nurnberger JI Jr . A rapid non-enzymatic method for the preparation of HMW DNA from blood for RFLP studies. Nucleic Acids Res 1991; 19: 5444.
Owen DR, Yeo AJ, Gunn RN, Song K, Wadsworth G, Lewis A et al. An 18-kDa Translocator Protein (TSPO) polymorphism explains differences in binding affinity of the PET radioligand PBR28. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2011; 32: 1–5.
Gulyas B, Makkai B, Kasa P, Gulya K, Bakota L, Varszegi S et al. A comparative autoradiography study in post mortem whole hemisphere human brain slices taken from Alzheimer patients and age-matched controls using two radiolabelled DAA1106 analogues with high affinity to the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor (PBR) system. Neurochem Int 2009; 54: 28–36.
Diorio D, Welner SA, Butterworth RF, Meaney MJ, Suranyi-Cadotte BE . Peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites in Alzheimer's disease frontal and temporal cortex. Neurobiol Aging 1991; 12: 255–258.
Venneti S, Wang G, Nguyen J, Wiley CA . The positron emission tomography ligand DAA1106 binds with high affinity to activated microglia in human neurological disorders. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2008; 67: 1001–1010.
Wirths O, Breyhan H, Marcello A, Cotel MC, Bruck W, Bayer TA . Inflammatory changes are tightly associated with neurodegeneration in the brain and spinal cord of the APP/PS1KI mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 2010; 31: 747–757.
Ou-Yang MH, Van Nostrand WE . The absence of myelin basic protein promotes neuroinflammation and reduces amyloid beta-protein accumulation in Tg-5xFAD mice. J Neuroinflammation 2013; 10: 134.
Bai F, Zhang Z, Watson DR, Yu H, Shi Y, Yuan Y et al. Abnormal integrity of association fiber tracts in amnestic mild cognitive impairment. J Neurol Sci 2009; 278: 102–106.
Fellgiebel A, Schermuly I, Gerhard A, Keller I, Albrecht J, Weibrich C et al. Functional relevant loss of long association fibre tracts integrity in early Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychologia 2008; 46: 1698–1706.
Meng JZ, Guo LW, Cheng H, Chen YJ, Fang L, Qi M et al. Correlation between cognitive function and the association fibers in patients with Alzheimer's disease using diffusion tensor imaging. J Clin Neurosci 2012; 19: 1659–1663.
Xie S, Xiao JX, Wang YH, Wu HK, Gong GL, Jiang XX . Evaluation of bilateral cingulum with tractography in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neuroreport 2005; 16: 1275–1278.
Fellgiebel A, Muller MJ, Wille P, Dellani PR, Scheurich A, Schmidt LG et al. Color-coded diffusion-tensor-imaging of posterior cingulate fiber tracts in mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging 2005; 26: 1193–1198.
Arends YM, Duyckaerts C, Rozemuller JM, Eikelenboom P, Hauw JJ . Microglia, amyloid and dementia in alzheimer disease. A correlative study. Neurobiol Aging 2000; 21: 39–47.
Vehmas AK, Kawas CH, Stewart WF, Troncoso JC . Immune reactive cells in senile plaques and cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 2003; 24: 321–331.
Maeda J, Zhang MR, Okauchi T, Ji B, Ono M, Hattori S et al. In vivo positron emission tomographic imaging of glial responses to amyloid-beta and tau pathologies in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease and related disorders. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 4720–4730.
Yoshiyama Y, Higuchi M, Zhang B, Huang SM, Iwata N, Saido TC et al. Synapse loss and microglial activation precede tangles in a P301S tauopathy mouse model. Neuron 2007; 53: 337–351.
Tynan RJ, Weidenhofer J, Hinwood M, Cairns MJ, Day TA, Walker FR . A comparative examination of the anti-inflammatory effects of SSRI and SNRI antidepressants on LPS stimulated microglia. Brain Behav Immun 2012; 26: 469–479.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Alzheimer’s society of Canada and the Scottish Rite Charitable Foundation. We thank Alan A. Wilson, Peter Bloomfield, Armando Garcia, Winston Stableford, Min Wong, Alvina Ng, Laura Nguyen and Wanna Mar for their assistance and expertise.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suridjan, I., Pollock, B., Verhoeff, N. et al. In-vivo imaging of grey and white matter neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: a positron emission tomography study with a novel radioligand, [18F]-FEPPA. Mol Psychiatry 20, 1579–1587 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2015.1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2015.1
This article is cited by
-
Microglia in neurodegenerative diseases: mechanism and potential therapeutic targets
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
Targeting innate immunity to protect and cure Alzheimer’s disease: opportunities and pitfalls
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
Disrupted white matter functional connectivity in aMCI APOEε4 carriers: a resting-state study
Brain Imaging and Behavior (2021)
-
TSPO PET detects acute neuroinflammation but not diffuse chronically activated MHCII microglia in the rat
EJNMMI Research (2020)
-
The Interaction Between Neuroinflammation and β-Amyloid in Cognitive Decline in Parkinson’s Disease
Molecular Neurobiology (2020)