Abstract
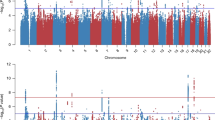
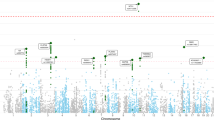
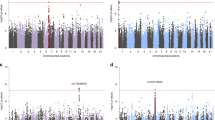
We describe the results of the first genome-wide association study (GWAS) of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) performed using trauma-exposed white non-Hispanic participants from a cohort of veterans and their intimate partners (295 cases and 196 controls). Several single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) yielded evidence of association. One SNP (rs8042149), located in the retinoid-related orphan receptor alpha gene (RORA), reached genome-wide significance. Nominally significant associations were observed for other RORA SNPs in two African-American replication samples—one from the veteran cohort (43 cases and 41 controls) and another independent cohort (100 cases and 421 controls). However, only the associated SNP from the veteran African-American replication sample survived gene-level multiple-testing correction. RORA has been implicated in prior GWAS studies of psychiatric disorders and is known to have an important role in neuroprotection and other behaviorally relevant processes. This study represents an important step toward identifying the genetic underpinnings of PTSD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edn. Washington, DC, 1994.
Kessler RC, Sonnega A, Bromet E, Hughes M, Nelson CB . Posttraumatic stress disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1995; 52: 1048–1060.
Cornelis MC, Nugent NR, Amstadter AB, Koenen KC . Genetics of post-traumatic stress disorder: review and recommendations for genome-wide association studies. Curr Psychiatry Rep 2010; 12: 313–326.
Koenen KC, Amstadter AB, Nugent NR . Gene-environment interaction in posttraumatic stress disorder: an update. J Trauma Stress 2009; 22: 416–426.
True WR, Rice J, Eisen SA, Heath AC, Goldberg J, Lyons MJ et al. A twin study of genetic and environmental contributions to liability for posttraumatic stress symptoms. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1993; 50: 257–264.
Stein MB, Jang KL, Taylor S, Vernon PA, Livesley WJ . Genetic and environmental influences on trauma exposure and posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms: a twin study. Am J Psychiatry 2002; 159: 1675–1681.
Sartor CE, McCutcheon VV, Pommer NE, Nelson EC, Grant JD, Duncan AE et al. Common genetic and environmental contributions to post-traumatic stress disorder and alcohol dependence in young women. Psychol Med 2011; 41: 1497–1505.
Uddin M, Aiello AE, Wildman DE, Koenen KC, Pawelec G, de Los Santos R et al. Epigenetic and immune function profiles associated with posttraumatic stress disorder. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 9470–9475.
Blake DD, Weathers FW, Nagy LM, Kaloupek DG, Gusman FD, Charney DS et al. The development of a Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale. J Trauma Stress 1995; 8: 75–90.
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P . Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000; 155: 945–959.
Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK . Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 2003; 164: 1567–1587.
Kubany ES, Haynes SN, Leisen MB, Owens JA, Kaplan AS, Watson SB et al. Development and preliminary validation of a brief broad-spectrum measure of trauma exposure: the Traumatic Life Events Questionnaire. Psychol Assessment 2000; 12: 210–224.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ . Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005; 21: 263–265.
Pruim RJ, Welch RP, Sanna S, Teslovich TM, Chines PS, Gliedt TP et al. LocusZoom: regional visualization of genome-wide association scan results. Bioinformatics 2010; 26: 2336–2337.
R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing 2008.
Goldmann E, Aiello A, Uddin M, Delva J, Koenen K, Gant LM et al. Pervasive exposure to violence and posttraumatic stress disorder in a predominantly African American Urban Community: the Detroit Neighborhood Health Study. J Trauma Stress 2011; 24: 747–751.
Neale BM, Lasky-Su J, Anney R, Franke B, Zhou K, Maller JB et al. Genome-wide association scan of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genetthe Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics 2008; 147B: 1337–1344.
Le-Niculescu H, Patel SD, Bhat M, Kuczenski R, Faraone SV, Tsuang MT et al. Convergent functional genomics of genome-wide association data for bipolar disorder: comprehensive identification of candidate genes, pathways and mechanisms. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet the Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics 2009; 150B: 155–181.
Nguyen A, Rauch TA, Pfeifer GP, Hu VW . Global methylation profiling of lymphoblastoid cell lines reveals epigenetic contributions to autism spectrum disorders and a novel autism candidate gene, RORA, whose protein product is reduced in autistic brain. FASEB J 2010; 24: 3036–3051.
Sarachana T, Xu M, Wu RC, Hu VW . Sex hormones in autism: androgens and estrogens differentially and reciprocally regulate RORA, a novel candidate gene for autism. PLoS One 2011; 6: e17116.
Fu Q, Koenen KC, Miller MW, Heath AC, Bucholz KK, Lyons MJ et al. Differential etiology of posttraumatic stress disorder with conduct disorder and major depression in male veterans. Biol Psychiatry 2007; 62: 1088–1094.
Wolf EJ, Miller MW, Krueger RF, Lyons MJ, Tsuang MT, Koenen KC . Posttraumatic stress disorder and the genetic structure of comorbidity. J Abnorm Psychol 2010; 119: 320–330.
Garriock HA, Kraft JB, Shyn SI, Peters EJ, Yokoyama JS, Jenkins GD et al. A genome wide association study of citalopram response in major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2010; 67: 133–138.
Terracciano A, Tanaka T, Sutin AR, Sanna S, Deiana B, Lai S et al. Genome-wide association scan of trait depression. Biol Psychiatry 2010; 68: 811–817.
Lavebratt C, Sjoholm LK, Partonen T, Schalling M, Forsell Y . PER2 variantion is associated with depression vulnerability. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet: the Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics 2010; 153B: 570–581.
Krueger RF . The structure of common mental disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1999; 56: 921–926.
Watson D, Clark LA . Negative affectivity: the disposition to experience aversive emotional states. Psychol Bull 1984; 96: 465–490.
Miller MW . Personality and the etiology and expression of PTSD: a three-factor model perspective. Clin Psychol Sci Practice 2003; 10: 373–393.
Miller MW, Wolf EJ, Reardon AF, Greene A, Ofrat S, McInerney S . Personality and the latent structure of PTSD comorbidity. J Anxiety Disord 2012; 26: 599–607.
Ino H . Immunohistochemical characterization of the orphan nuclear receptor ROR alpha in the mouse nervous system. J Histochem Cytochem 2004; 52: 311–323.
Boukhtouche F, Vodjdani G, Jarvis CI, Bakouche J, Staels B, Mallet J et al. Human retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor alpha1 overexpression protects neurones against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. J Neurochem 2006; 96: 1778–1789.
Jolly S, Journiac N, Vernet-der Garabedian B, Mariani J . RORalpha, a key to the development and functioning of the brain. Cerebellum 2012; 11: 451–452.
Oosthuizen F, Wegener G, Harvey BH . Nitric oxide as inflammatory mediator in post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): evidence from an animal model. Neuropsychiatr Disease Treatment 2005; 1: 109–123.
Woon FL, Sood S, Hedges DW . Hippocampal volume deficits associated with exposure to psychological trauma and posttraumatic stress disorder in adults: a meta-analysis. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2010; 34: 1181–1188.
Etkin A, Wager TD . Functional neuroimaging of anxiety: a meta-analysis of emotional processing in PTSD, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobia. Am J Psychiatry 2007; 164: 1476–1488.
Lyoo IK, Kim JE, Yoon SJ, Hwang J, Bae S, Kim DJ . The neurobiological role of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in recovery from trauma. Longitudinal brain imaging study among survivors of the South Korean subway disaster. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2011; 68: 701–713.
Woodward SH, Kaloupek DG, Streeter CC, Martinez C, Schaer M, Eliez S . Decreased anterior cingulate volume in combat-related PTSD. Biol Psychiatry 2006; 59: 582–587.
Schuff N, Zhang Y, Zhan W, Lenoci M, Ching C, Boreta L et al. Patterns of altered cortical perfusion and diminished subcortical integrity in posttraumatic stress disorder: an MRI study. NeuroImage 2011; 54 (Suppl 1): S62–S68.
Lanius RA, Bluhm R, Lanius U, Pain C . A review of neuroimaging studies in PTSD: heterogeneity of response to symptom provocation. J Psychiatric Res 2006; 40: 709–729.
Kochunov P, Glahn DC, Nichols TE, Winkler AM, Hong EL, Holcomb HH et al. Genetic analysis of cortical thickness and fractional anisotropy of water diffusion in the brain. Front Neurosci 2011; 5: 120.
Ripke S, Sanders AR, Kendler KS, Levinson DF, Sklar P, Holmans PA et al. Genome-wide association study identifies five new schizophrenia loci. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 969–976.
Sklar P, Ripke S, Scott LJ, Andreassen OA, Cichon S, Craddock N et al. Large-scale genome-wide association analysis of bipolar disorder identifies a new susceptibility locus near ODZ4. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 977–983.
Valiente A, Lafuente A, Bernardo M . Systematic review of the Genome wide Association Studies (GWAS) in schizophrenia. Rev Psiquiatr Salud Ment (Barc) 2011; 4: 218–227.
Acknowledgements
Funding for this study was provided by National Institute on Mental Health award RO1 MH079806 and a Department of Veterans Affairs Merit Review Grant awarded to MWM. MWL is funded by National Institute on Mental Health award K01 MH076100. The Detroit Neighborhood Health Study (PI: Allison Aiello) is funded by DA022720, DA022720-S1 and MH088283. KCK is funded by MH093612, MH078928, P51RR000165 and RC4MH092707. Funding for genotyping of the VA sample was provided by the VA National Center for PTSD.
Author contributions
Study concept and design: MWM, CB and MWL. Sample collection and interpretation of VA data: MWM, AFR and EJW. Genotyping of VA sample: CB and EM. Data cleaning and management of VA sample data: MWL, AFR and EJW. Analysis of VA genotype data: MWL. Sample collection and interpretation of DNHS data: SG, Aiello, DW, MU and KCK. Genotyping of DNHS data: MU and DW. Data cleaning and management of DNHS data: Aiello, GG and KCK. Analysis of DNHS genotype data: GG and KCK. Drafting and critical revision of the manuscript: MWM, CB, MWL, GG and KCK. All authors gave approval to the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Supplementary information
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Logue, M., Baldwin, C., Guffanti, G. et al. A genome-wide association study of post-traumatic stress disorder identifies the retinoid-related orphan receptor alpha (RORA) gene as a significant risk locus. Mol Psychiatry 18, 937–942 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2012.113
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2012.113
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
For whom the bell tolls: psychopathological and neurobiological correlates of a DNA methylation index of time-to-death
Translational Psychiatry (2022)
-
Integration of peripheral transcriptomics, genomics, and interactomics following trauma identifies causal genes for symptoms of post-traumatic stress and major depression
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
Reduction of DNMT3a and RORA in the nucleus accumbens plays a causal role in post-traumatic stress disorder-like behavior: reversal by combinatorial epigenetic therapy
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
An integrative analysis of genome-wide association study and regulatory SNP annotation datasets identified candidate genes for bipolar disorder
International Journal of Bipolar Disorders (2020)
-
Effects of COMT rs4680 and BDNF rs6265 polymorphisms on brain degree centrality in Han Chinese adults who lost their only child
Translational Psychiatry (2020)