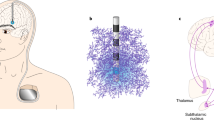
Abstract
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) has emerged as a powerful surgical therapy for the management of treatment-resistant movement disorders, epilepsy and neuropsychiatric disorders. Although DBS may be clinically effective in many cases, its mode of action is still elusive. It is unclear which neural cell types are involved in the mechanism of DBS, and how high-frequency stimulation of these cells may lead to alleviation of the clinical symptoms. Neurons have commonly been a main focus in the many theories explaining the working mechanism of DBS. Recent data, however, demonstrates that astrocytes may be active players in the DBS mechanism of action. In this review article, we will discuss the potential role of reactive and neurogenic astrocytes (neural progenitors) in DBS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tan TC, Black PM . Sir Victor Horsley (1857-1916): pioneer of neurological surgery. Neurosurgery 2002; 50: 607–611.
Schwalb JM, Hamani C . The history and future of deep brain stimulation. Neurotherapeutics 2008; 5: 3–13.
Bucy PC . Cortical extirpation in the treatment of involuntary movements. Am J Surg 1948; 75: 257–263.
Ohye C, Kubota K, Hongo T, Nagao T, Narabayashi H . Ventrolateral and subventrolateral thalamic stimulation. Motor effects. Arch Neurol 1964; 11: 427–434.
Cooper IS . Effect of chronic stimulation of anterior cerebellum on neurological disease. Lancet 1973; 1: 206.
Cooper IS, Riklan M, Amin I, Waltz JM, Cullinan T . Chronic cerebellar stimulation in cerebral palsy. Neurology 1976; 26: 744–753.
Benabid AL, Pollak P, Gervason C, Hoffmann D, Gao DM, Hommel M et al. Long-term suppression of tremor by chronic stimulation of the ventral intermediate thalamic nucleus. Lancet 1991; 337: 403–406.
Benabid AL, Chabardes S, Torres N, Piallat B, Krack P, Fraix V et al. Functional neurosurgery for movement disorders: a historical perspective. Prog Brain Res 2009; 175: 379–391.
Benabid AL, Chabardes S, Mitrofanis J, Pollak P . Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol 2009; 8: 67–81.
Ward HE, Hwynn N, Okun MS . Update on deep brain stimulation for neuropsychiatric disorders. Neurobiol Dis 2010; 38: 346–353.
Fisher R, Salanova V, Witt T, Worth R, Henry T, Gross R et al. Electrical stimulation of the anterior nucleus of thalamus for treatment of refractory epilepsy. Epilepsia 2010; 51: 899–908.
Andrade P, Noblesse LH, Temel Y, Ackermans L, Lim LW, Steinbusch HW et al. Neurostimulatory and ablative treatment options in major depressive disorder: a systematic review. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2010; 152: 565–577.
Levy R, Deer TR, Henderson J . Intracranial neurostimulation for pain control: a review. Pain Physician 2010; 13: 157–165.
Visser-Vandewalle V, Temel Y, Boon P, Vreeling F, Colle H, Hoogland G et al. Chronic bilateral thalamic stimulation: a new therapeutic approach in intractable Tourette syndrome. Report of three cases. J Neurosurg 2003; 99: 1094–1100.
Denys D, Mantione M . Deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Prog Brain Res 2009; 175: 419–427.
Kringelbach ML, Jenkinson N, Owen SL, Aziz TZ . Translational principles of deep brain stimulation. Nat Rev Neurosci 2007; 8: 623–635.
Giaume C, Koulakoff A, Roux L, Holcman D, Rouach N . Astroglial networks: a step further in neuroglial and gliovascular interactions. Nat Rev Neurosci 2010; 11: 87–99.
Halassa MM, Haydon PG . Integrated brain circuits: astrocytic networks modulate neuronal activity and behavior. Annu Rev Physiol 2010; 72: 335–355.
Perea G, Araque A . Properties of synaptically evoked astrocyte calcium signal reveal synaptic information processing by astrocytes. J Neurosci 2005; 25: 2192–2203.
Tawfik VL, Chang SY, Hitti FL, Roberts DW, Leiter JC, Jovanovic S et al. Deep brain stimulation results in local glutamate and adenosine release: investigation into the role of astrocytes. Neurosurgery 2010; 67: 367–375.
DiLorenzo DJ, Jankovic J, Simpson RK, Takei H, Powell SZ . Long-term deep brain stimulation for essential tremor: 12-year clinicopathologic follow-up. Mov Disord 2010; 25: 232–238.
Pekny M, Nilsson M . Astrocyte activation and reactive gliosis. Glia 2005; 50: 427–434.
Sofroniew MV . Molecular dissection of reactive astrogliosis and glial scar formation. Trends Neurosci 2009; 32: 638–647.
Doetsch F, Caille I, Lim DA, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A . Subventricular zone astrocytes are neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain. Cell 1999; 97: 703–716.
van den Berge SA, Middeldorp J, Zhang CE, Curtis MA, Leonard BW, Mastroeni D et al. Longterm quiescent cells in the aged human subventricular neurogenic system specifically express GFAP-delta. Aging Cell 2010; 9: 313–326.
Buffo A, Rite I, Tripathi P, Lepier A, Colak D, Horn AP et al. Origin and progeny of reactive gliosis: a source of multipotent cells in the injured brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 3581–3586.
Malatesta P, Hartfuss E, Gotz M . Isolation of radial glial cells by fluorescent-activated cell sorting reveals a neuronal lineage. Development 2000; 127: 5253–5263.
Hartfuss E, Galli R, Heins N, Gotz M . Characterization of CNS precursor subtypes and radial glia. Dev Biol 2001; 229: 15–30.
Gotz M, Hartfuss E, Malatesta P . Radial glial cells as neuronal precursors: a new perspective on the correlation of morphology and lineage restriction in the developing cerebral cortex of mice. Brain Res Bull 2002; 57: 777–788.
Gubellini P, Salin P, Kerkerian-Le GL, Baunez C . Deep brain stimulation in neurological diseases and experimental models: from molecule to complex behavior. Prog Neurobiol 2009; 89: 79–123.
McIntyre CC, Savasta M, Kerkerian-Le GL, Vitek JL . Uncovering the mechanism(s) of action of deep brain stimulation: activation, inhibition, or both. Clin Neurophysiol 2004; 115: 1239–1248.
McIntyre CC, Grill WM, Sherman DL, Thakor NV . Cellular effects of deep brain stimulation: model-based analysis of activation and inhibition. J Neurophysiol 2004; 91: 1457–1469.
Lozano AM, Dostrovsky J, Chen R, Ashby P . Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease: disrupting the disruption. Lancet Neurol 2002; 1: 225–231.
McIntyre CC, Hahn PJ . Network perspectives on the mechanisms of deep brain stimulation. Neurobiol Dis 2010; 38: 329–337.
Dorval AD, Russo GS, Hashimoto T, Xu W, Grill WM, Vitek JL . Deep brain stimulation reduces neuronal entropy in the MPTP-primate model of Parkinson's disease. J Neurophysiol 2008; 100: 2807–2818.
Hahn PJ, Russo GS, Hashimoto T, Miocinovic S, Xu W, McIntyre CC et al. Pallidal burst activity during therapeutic deep brain stimulation. Exp Neurol 2008; 211: 243–251.
Birdno MJ, Kuncel AM, Dorval AD, Turner DA, Grill WM . Tremor varies as a function of the temporal regularity of deep brain stimulation. Neuroreport 2008; 19: 599–602.
Perea G, Navarrete M, Araque A . Tripartite synapses: astrocytes process and control synaptic information. Trends Neurosci 2009; 32: 421–431.
Bushong EA, Martone ME, Jones YZ, Ellisman MH . Protoplasmic astrocytes in CA1 stratum radiatum occupy separate anatomical domains. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 183–192.
Konietzko U, Muller CM . Astrocytic dye coupling in rat hippocampus: topography, developmental onset, and modulation by protein kinase C. Hippocampus 1994; 4: 297–306.
Ventura R, Harris KM . Three-dimensional relationships between hippocampal synapses and astrocytes. J Neurosci 1999; 19: 6897–6906.
Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP, Haydon PG . Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci 1999; 22: 208–215.
Takano T, Tian GF, Peng W, Lou N, Libionka W, Han X et al. Astrocyte-mediated control of cerebral blood flow. Nat Neurosci 2006; 9: 260–267.
Oberheim NA, Wang X, Goldman S, Nedergaard M . Astrocytic complexity distinguishes the human brain. Trends Neurosci 2006; 29: 547–553.
Agulhon C, Petravicz J, McMullen AB, Sweger EJ, Minton SK, Taves SR et al. What is the role of astrocyte calcium in neurophysiology? Neuron 2008; 59: 932–946.
Zhang Y, Barres BA . Astrocyte heterogeneity: an underappreciated topic in neurobiology. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2010; 20: 588–594.
Hamilton NB, Attwell D . Do astrocytes really exocytose neurotransmitters? Nat Rev Neurosci 2010; 11: 227–238.
Kang J, Jiang L, Goldman SA, Nedergaard M . Astrocyte-mediated potentiation of inhibitory synaptic transmission. Nat Neurosci 1998; 1: 683–692.
Kefalopoulou Z, Paschali A, Markaki E, Ellul J, Chroni E, Vassilakos P et al. Regional cerebral blood flow changes induced by deep brain stimulation in secondary dystonia. Acta Neurochir (Wien ) 2010; 152: 1007–1014.
Perlmutter JS, Mink JW, Bastian AJ, Zackowski K, Hershey T, Miyawaki E et al. Blood flow responses to deep brain stimulation of thalamus. Neurology 2002; 58: 1388–1394.
Wyckhuys T, Staelens S, Van NB, Deleye S, Hallez H, Vonck K et al. Hippocampal deep brain stimulation induces decreased rCBF in the hippocampal formation of the rat. Neuroimage 2010; 52: 55–61.
Attwell D, Buchan AM, Charpak S, Lauritzen M, Macvicar BA, Newman EA . Glial and neuronal control of brain blood flow. Nature 2010; 468: 232–243.
Bekar L, Libionka W, Tian GF, Xu Q, Torres A, Wang X et al. Adenosine is crucial for deep brain stimulation-mediated attenuation of tremor. Nat Med 2008; 14: 75–80.
Carmignoto G, Pasti L, Pozzan T . On the role of voltage-dependent calcium channels in calcium signaling of astrocytes in situ. J Neurosci 1998; 18: 4637–4645.
Haydon PG, Carmignoto G . Astrocyte control of synaptic transmission and neurovascular coupling. Physiol Rev 2006; 86: 1009–1031.
Dunwiddie TV, Masino SA . The role and regulation of adenosine in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci 2001; 24: 31–55.
Trussell LO, Jackson MB . Adenosine-activated potassium conductance in cultured striatal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1985; 82: 4857–4861.
Macdonald RL, Skerritt JH, Werz MA . Adenosine agonists reduce voltage-dependent calcium conductance of mouse sensory neurones in cell culture. J Physiol 1986; 370: 75–90.
Shon YM, Chang SY, Tye SJ, Kimble CJ, Bennet KE, Blaha CD et al. Comonitoring of adenosine and dopamine using the Wireless Instantaneous Neurotransmitter Concentration System: proof of principle. J Neurosurg 2010; 112: 539–548.
Chang SY, Shon YM, Agnesi F, Lee KH . Microthalamotomy effect during deep brain stimulation: potential involvement of adenosine and glutamate efflux. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2009; 2009: 3294–3297.
Newman EA, Zahs KR . Modulation of neuronal activity by glial cells in the retina. J Neurosci 1998; 18: 4022–4028.
Kozlov AS, Angulo MC, Audinat E, Charpak S . Target cell-specific modulation of neuronal activity by astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 10058–10063.
Morishita T, Foote KD, Wu SS, Jacobson CE, Rodriguez RL, Haq IU et al. Brain penetration effects of microelectrodes and deep brain stimulation leads in ventral intermediate nucleus stimulation for essential tremor. J Neurosurg 2010; 112: 491–496.
Mann JM, Foote KD, Garvan CW, Fernandez HH, Jacobson CE, Rodriguez RL et al. Brain penetration effects of microelectrodes and DBS leads in STN or GPi. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2009; 80: 794–797.
Gradinaru V, Mogri M, Thompson KR, Henderson JM, Deisseroth K . Optical deconstruction of parkinsonian neural circuitry. Science 2009; 324: 354–359.
Stock G, Sturm V, Schmitt HP, Schlor KH . The influence of chronic deep brain stimulation on excitability and morphology of the stimulated tissue. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1979; 47: 123–129.
Vedam-Mai V, Krock N, Ullman M, Foote KD, Shain W, Smith K et al. The national DBS brain tissue network pilot study: need for more tissue and more standardization. Cell Tissue Bank 2010; e-pub ahead of print.
Haberler C, Alesch F, Mazal PR, Pilz P, Jellinger K, Pinter MM et al. No tissue damage by chronic deep brain stimulation in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 2000; 48: 372–376.
Pilitsis JG, Metman LV, Toleikis JR, Hughes LE, Sani SB, Bakay RA . Factors involved in long-term efficacy of deep brain stimulation of the thalamus for essential tremor. J Neurosurg 2008; 109: 640–646.
Sun DA, Yu H, Spooner J, Tatsas AD, Davis T, Abel TW et al. Postmortem analysis following 71 months of deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus for Parkinson disease. J Neurosurg 2008; 109: 325–329.
van Kuyck K, Welkenhuysen M, Arckens L, Sciot R, Nuttin B . Histological alterations induced by electrode implantation and electrical stimulation in the human brain: a review. Neuromodulation 2007; 10: 244–261.
Moss J, Ryder T, Aziz TZ, Graeber MB, Bain PG . Electron microscopy of tissue adherent to explanted electrodes in dystonia and Parkinson's disease. Brain 2004; 127: 2755–2763.
Griffith RW, Humphrey DR . Long-term gliosis around chronically implanted platinum electrodes in the Rhesus macaque motor cortex. Neurosci Lett 2006; 406: 81–86.
Hirshler YK, Polat U, Biegon A . Intracranial electrode implantation produces regional neuroinflammation and memory deficits in rats. Exp Neurol 2010; 222: 42–50.
Kraev IV, Godukhin OV, Patrushev IV, Davies HA, Popov VI, Stewart MG . Partial kindling induces neurogenesis, activates astrocytes and alters synaptic morphology in the dentate gyrus of freely moving adult rats. Neuroscience 2009; 162: 254–267.
Ortinski PI, Dong J, Mungenast A, Yue C, Takano H, Watson DJ et al. Selective induction of astrocytic gliosis generates deficits in neuronal inhibition. Nat Neurosci 2010; 13: 584–591.
Jeong SH, Jun SB, Song JK, Kim SJ . Activity-dependent neuronal cell migration induced by electrical stimulation. Med Biol Eng Comput 2009; 47: 93–99.
Steindler DA, Laywell ED . Astrocytes as stem cells: nomenclature, phenotype, and translation. Glia 2003; 43: 62–69.
Middeldorp J, Boer K, Sluijs JA, De FL, Encha-Razavi F, Vescovi AL et al. GFAPdelta in radial glia and subventricular zone progenitors in the developing human cortex. Development 2010; 137: 313–321.
Toda H, Hamani C, Fawcett AP, Hutchison WD, Lozano AM . The regulation of adult rodent hippocampal neurogenesis by deep brain stimulation. J Neurosurg 2008; 108: 132–138.
Becker D, Gary DS, Rosenzweig ES, Grill WM, McDonald JW . Functional electrical stimulation helps replenish progenitor cells in the injured spinal cord of adult rats. Exp Neurol 2010; 222: 211–218.
Encinas JM, Hamani C, Lozano AM, Enikolopov G . Neurogenic hippocampal targets of deep brain stimulation. J Comp Neurol 2011; 519: 6–20.
Hodge RD, Kowalczyk TD, Wolf SA, Encinas JM, Rippey C, Enikolopov G et al. Intermediate progenitors in adult hippocampal neurogenesis: Tbr2 expression and coordinate regulation of neuronal output. J Neurosci 2008; 28: 3707–3717.
Encinas JM, Vaahtokari A, Enikolopov G . Fluoxetine targets early progenitor cells in the adult brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 8233–8238.
Khaindrava V, Salin P, Melon C, Ugrumov M, Kerkerian-Le-Goff L, Daszuta A . High frequency stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus impacts adult neurogenesis in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis 2011; 42: 284–291.
Bekar LK, He W, Nedergaard M . Locus coeruleus alpha-adrenergic-mediated activation of cortical astrocytes in vivo. Cereb Cortex 2008; 18: 2789–2795.
Lucassen PJ, Meerlo P, Naylor AS, van Dam AM, Dayer AG, Fuchs E et al. Regulation of adult neurogenesis by stress, sleep disruption, exercise and inflammation: implications for depression and antidepressant action. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2010; 20: 1–17.
Mamber C, Verhaagen J, Hol EM . In vivo targeting of subventricular zone astrocytes. Prog Neurobiol 2010; 92: 19–32.
Halassa MM, Florian C, Fellin T, Munoz JR, Lee SY, Abel T et al. Astrocytic modulation of sleep homeostasis and cognitive consequences of sleep loss. Neuron 2009; 61: 213–219.
Agulhon C, Fiacco TA, McCarthy KD . Hippocampal short- and long-term plasticity are not modulated by astrocyte Ca2+ signaling. Science 2010; 327: 1250–1254.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the financial support for our research by the Netherlands Organisation of Scientific Research—NWO (ALW-Vici 865.09.003 to EMH and ZON-MW VENI 916.66.095 to DD), International Parkinson Foundation-IPF (to EMH), International Alzheimer Foundation (ISAO 08504 to EMH and WK), Overstreet foundation and Brain and Spinal Cord Injury Trust Fund of Florida (to BR) and NIH, NPF, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, the Parkinson Alliance, Medtronic peer reviewed fellowship training grants and the UF Foundation (to MSO). Information from the UF National Deep Brain Stimulation Brain Tissue Network was utilized for the writing of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
MSO serves as a consultant for the National Parkinson Foundation. He has in the past received honoraria for DBS educational talks prior to 2010, but currently receives no support (since July 2009). He also has received royalties for publications with Demos, Manson, and Cambridge (movement disorders books). And he has potential royalty interest in the COMPRESS tool for DBS. MSO has participated in CME activities on movement disorders sponsored by the USF CME office. VV-M, EYB, WK, MGPF, DD, BAR and EMH declare no potential conflict of interest.
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vedam-Mai, V., van Battum, E., Kamphuis, W. et al. Deep brain stimulation and the role of astrocytes. Mol Psychiatry 17, 124–131 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2011.61
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2011.61