Abstract
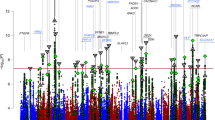
Meta-analyses of bipolar disorder (BD) genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified several genome-wide significant signals in European-ancestry samples, but so far account for little of the inherited risk. We performed a meta-analysis of ∼750 000 high-quality genetic markers on a combined sample of ∼14 000 subjects of European and Asian-ancestry (phase I). The most significant findings were further tested in an extended sample of ∼17 700 cases and controls (phase II). The results suggest novel association findings near the genes TRANK1 (LBA1), LMAN2L and PTGFR. In phase I, the most significant single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), rs9834970 near TRANK1, was significant at the P=2.4 × 10−11 level, with no heterogeneity. Supportive evidence for prior association findings near ANK3 and a locus on chromosome 3p21.1 was also observed. The phase II results were similar, although the heterogeneity test became significant for several SNPs. On the basis of these results and other established risk loci, we used the method developed by Park et al. to estimate the number, and the effect size distribution, of BD risk loci that could still be found by GWAS methods. We estimate that >63 000 case–control samples would be needed to identify the ∼105 BD risk loci discoverable by GWAS, and that these will together explain <6% of the inherited risk. These results support previous GWAS findings and identify three new candidate genes for BD. Further studies are needed to replicate these findings and may potentially lead to identification of functional variants. Sample size will remain a limiting factor in the discovery of common alleles associated with BD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertelsen A, Harvald B, Hauge M . A Danish twin study of manic-depressive disorders. Br J Psychiatry 1977; 130: 330–351.
Kendler KS, Pedersen N, Johnson L, Neale MC, Mathe AA . A pilot Swedish twin study of affective illness, including hospitaland population-ascertained subsamples. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1993; 50: 699–700.
Kendler KS . Twin studies of psychiatric illness: an update. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2001; 58: 1005–1014.
Cardno AG, Marshall EJ, Coid B, Macdonald AM, Ribchester TR, Davies NJ et al. Heritability estimates for psychotic disorders: the Maudsley Twin Psychosis Series. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1999; 56: 162–168.
Edvardsen J, Torgersen S, Roysamb E, Lygren S, Skre I, Onstad S . Heritability of bipolar spectrum disorders. Unity or heterogeneity? J Affect Disord 2008; 106: 229–240.
Smoller JW, Finn CT . Family, twin, and adoption studies of bipolar disorder. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 2003; 123C: 48–58.
Wendland JR, McMahon FJ . Genetics of Bipolar Disorder. In: Manji HK and Zarate Jr CA (eds). Behavioral Neurobiology of Bipolar Disorder and its Treatment. Springer: London, UK, 2011 pp 19–31.
Gershon ES, Hamovit J, Guroff JJ, Dibble E, Leckman JF, Sceery W et al. A family study of schizoaffective, bipolar I, bipolar II, unipolar and normal control probands. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1982; 39: 1157–1167.
Kieseppä T, Partonen T, Haukka J, Kaprio J, Lönnqvist J . High concordance of bipolar I disorder in a nationwide sample of twins. Am J Psychiatry 2004; 161: 1814–1821.
Goodwin FK, Jamison K . Manic-Depressive Illness: Bipolar Disorders and Recurrent Depression, 2nd Edn. Oxford Univ Press: New York, USA, 2007.
Craddock N, Jones I . Genetics of bipolar disorder. J Med Genet 1999; 36: 585–594.
Ferreira MA, O'Donovan MC, Meng YA, Jones IR, Ruderfer DM et al. Collaborative genome-wide association analysis supports a role for ANK3 and CACNA1C in bipolar disorder. Nature Genet 2008; 40: 1056–1058.
Baum AE, Akula N, Cabanero M, Cardona I, Corona W, Klemens B et al. A genome-wide association study implicates diacylglycerol kinase eta (DGKH) and several other genes in the etiology of bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry 2007; 13: 197–207.
Schulze TG, Detera-Wadleigh SD, Akula N, Gupta A, Kassem L, Steele J et al. Two variants in Ankyrin 3 (ANK3) are independent genetic risk factors for bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry 2009; 14: 487–491.
Scott LJ, Muglia P, Kong XQ, Guan W, Flickinger M, Upmanyu R et al. Genome-wide association and meta-analysis of bipolar disorder in individuals of European ancestry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 7501–7506.
Sklar P, Smoller JW, Fan J, Ferreira MA, Perlis RH, Chambert K et al. Whole-genome association study of bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry 2008; 13: 558–569.
McMahon FJ, Akula N, Schulze TG, Pierandrea M, Tozzi F, Detera-Wadleigh SD et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association data detects a risk locus for major mood disorders on chromosome 3p21.1. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 128–131.
Zeggini E, Scott LJ, Saxena R, Voight BF, Marchini JL, Hu T et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association data and large-scale replication identifies additional susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 638–645.
Zeggini E, Weedon MN, Lindgren CM, Frayling TM, Elliott KS, Lango H et al. Replication of genome-wide association signals in UK samples reveals risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Science 2007; 316: 1336–1341.
Weedon MN, Lango H, Lindgren CM, Wallace C, Evans DM, Mangino M et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies 20 loci that influence adult height. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 575–583.
Willer CJ, Sanna S, Jackson AU, Scuteri A, Bonnycastle LL, Clarke R et al. Newly identified loci that influence lipid concentrations and risk of coronary artery disease. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 161–169.
Houlston RS, Webb E, Broderick P, Pittman AM, Di Bernardo MC, Lubbe S et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association data identifies four new susceptibility loci for colorectal cancer. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 1426–1435.
Raychaudhuri S, Remmers EF, Lee AT, Hackett R, Guiducci C, Burtt NP et al. Common variants at CD40 and other loci confer risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 1216–1223.
Pereira TV, Patsopoulos NA, Salanti G, Ioannidis JP . Discovery properties of genome-wide association signals from cumulatively combined data sets. Am J Epidemiol 2009; 170: 1197–1206.
Moreno C, Laje G, Blanco C, Jiang H, Schmidt AB, Olfson M . National trends in the outpatient diagnosis and treatment of bipolar disorder in youth. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2007; 64: 1032–1039.
Pritchard JK, Coop G, Pickrell JK, Novembre J, Kudaravalli S, Li J et al. The role of geography in human adaptation. PLoS Genet 2009; 5: 1–16.
de Bakker PI, Neale BM, Daly MJ . Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2010; doi:10.1101/pdb.top81; http://cshprotocols.cshlp.org/content/2010/6/pdb.top81.full.
de Bakker PI, Ferreira MA, Jia X, Neale BM, Raychaudhuri S, Voight BF . Practical aspects of imputation-driven meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Hum Mol Genet 2008; 17: R122–R128.
Smith EN, Bloss CS, Badner JA, Barrett T, Belmonte PL, Berrettini W et al. Genome-wide association study of bipolar disorder in European American and African American individuals. Mol Psychiatry 2009; 14: 755–763.
Lee MTM, Chen CH, Lee CH, Chen CC, Chong MY, Ouyang WC et al. Genome-wide association study of bipolar I disorder in Han Chinese Population. Mol Psychiatry 2010; 16: 548–556.
Etain B, Dumaine A, Mathieu F, Chevalier F, Henry C, Kahn JP et al. A SNAP25 promoter variant is associated with early-onset bipolar disorder and a high expression level in brain. Mol Psychiatry 2010; 15: 748–755.
Sebastiani P, Solovieff N, Puca A, Hartley SW, Melista E, Andersen S et al. Genetic signatures of exceptional longevity in humans. Science 2010; e-pub ahead of print 11 November 2010; doi:10.1126/science.1190532.
Li Y, Abecasis GR . MACH 1.0: Rapid haplotype reconstruction and missing genotype inference. Am J Hum Genet 2006; S79: 2290.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Browning BL, Browning SR . A unified approach to genotype imputation and haplotype phase inference for large data sets of trios and unrelated individuals. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 84: 210–223.
Devlin B, Roeder K . Genomic control for association studies. Biometrics 1999; 55: 997–1004.
Ustun TB, Ayuso-Mateos JL, Chatterji S, Mathers C, Murray CJ . Global burden of depressive disorders in the year 2000. Br J Psychiatry 2004; 184: 386–392.
Han B, Eskin E . Random-effects model aimed at discovering associations in meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Am J Hum Genet 2011; 88: 586–598.
Metasoft vo3.1 [Internet]. [cited 2011 July 7] [Place Unknown] UCLA, Available from: http://genetics.cs.ucla.edu/meta 2011.
Pe'er I, Yelensky R, Altshuler D, Daly MJ . Estimation of the multiple testing burden for genome-wide association studies of nearly all common variants. Genet Epidemiol 2008; 32: 381–385.
Dudbridge F, Gusnanto A . Estimation of significance thresholds for genome-wide association scans. Genet Epidemiol 2008; 32: 227–234.
Manolio TA, Brooks LD, Collins FS . A HapMap harvest of insights into the genetics of common disease. J Clin Invest 2008; 118: 1590–1605.
Ioannidis JP . Interpretation of tests of heterogeneity and bias in meta-analysis. J Eval Clin Pract 2008; 14: 951–957.
Skol AD, Scott LJ, Abecasis GR, Boehnke M . Joint analysis is more efficient than replication-based analysis for two-stage genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 209–213.
Purcell S, Cherny SS, Sham PC . Genetic Power Calculator: design of linkage and association genetic mapping studies of complex traits. Bioinformatics 2003; 19: 149–150.
Phiel CJ, Zhang F, Huang EY, Guenther MG, Lazar MA, Klein PS et al. Histone deacetylase is a direct target of valproic acid, a potent anticonvulsant, mood stabilizer, and teratogen. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 36734–36741.
Schüle C, Baghai TC, Eser D, Häfner S, Born C, Herrmann S et al. 2009) The combined dexamethasone/CRH test (DEX/CRH test) and prediction of acute treatment response in major depression. PLoS ONE 2009; 4: e4324.
Barbier E, Wang JB . Anti-depressant and anxiolytic like behaviors in PKCI/HINT1 knockout mice associated with elevated plasma corticosterone level. BMC Neurosci 2009; 10: 132.
Gilmor ML, Skelton KH, Nemeroff CB, Owens MJ . The effects of chronic treatment with the mood stabilizers valproic acid and lithium on corticotropin-releasing factor neuronal systems. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2003; 305: 434–439.
Gibbs JR, van der Brug MP, Hernandez DG, Travnor BJ, Nalls MA, Lai SL et al. Abundant quantitative trait loci exist for DNA methylation and gene expression in human brain. PLoS Genet 2010; 6: e1000952.
Heinzen E, Ge D, Cronin KD, Maia J, Shianna KV, Gabriel W et al. Tissue specific genetic control of gene expression and alternative splicing: Implications for the study of human complex traits. PLoS Biol 2008; 6: e1.
SNPExpress [Internet]. Duke University 2011. Available from: http://people.genome.duke.edu/~dg48/SNPExpress/.
Kent WJ, Sugnet CW, Furey TS, Roskin KM, Pringle TH, Zahler AM et al. The human genome browser at UCSC. Genome Res 2002; 12: 996–1006.
David AS, Fleminger S, Kopelman MD, Lovestone S, Mellers JDC (eds). Lishman's Organic Psychiatry: A Textbook of Neuropsychiatry, 4th edn. Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, 2009.
Cichon S, Mühleisen TW, Degenhardt FA, Mattheisen M, Miró X, Strohmaier J et al. Genome-wide association study identifies genetic variation in neurocan as a susceptibility factor for bipolar disorder. Am J Hum Genet 2011; 88: 372–381.
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genome-wide association study of 14 000 cases of seven common diseases and 3000 shared controls. Nature 2007; 447: 661–678.
O'Donovan MC, Craddock N, Norton N, Williams H, Peirc T, Moskvina V et al. Identification of loci associated with schizophrenia by genome-wide association and follow-up. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 1053–1055.
Psychiatric GWAS Consortium Bipolar Working Group, Sklar P, Ripke S, Scott L, Andreassen OA, Cichon S et al. Large-scale genome-wide association analysis of bipolar disorder identifies a new susceptibility locus near ODZ4. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 977–983.
Park JH, Wacholder S, Gail MH, Peters U, Jacobs KB, Chanock SJ et al. Estimation of effect size distribution from genome-wide association studies and implications for future discoveries. Nature Genet 2010; 42: 570–575.
Ghosh A, Zou F, Wright FA . Estimating odds ratios in genome scans: an approximate conditional likelihood approach. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 82: 1064–1074.
Wray NR, Pergadia ML, Blackwood DHR, Penninx BWJH, Gordon SD, Nyholt DR et al. Genome-wide association study of major depressive disorder: New results, meta-analysis, and lessons learned. Mol Psychiatry 2010; e-pub ahead of print 2 November 2010. doi: 10.1038/mp.2010.109.
Green EK, Grozeva D, Jones I, Jones L, Kirov G, Caesar S et al. The bipolar disorder risk allele at CACNA1C also confers risk of recurrent major depression and of schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2010; 15: 1016–1022.
Yang J, Wray NR, Visscher PM . Comparing apples and oranges: equating the power of case–control and quantitative trait association studies. Genet Epidemiol 2010; 34: 254–257.
Pritchard JK, Pickrell JK, Coop G . The genetics of human adaptation: hard sweeps, soft sweeps, and polygenic adaptation. Curr Biol 2010; 20: R208–R215.
Kraeplin E . Comparative Psychiatry. In: Hirsch SR (eds). Themes and Variations in European Psychiatry. The University Press of Virginia: Charlottesville, pp 3–30.
Secolin R, Banzato CEM, Oliveira MCM, Bittar MFR, Santos ML, Dalgalarrondo P et al. Family-based association study for bipolar affective disorder. Psychiatr Genet 2010; 20: 126–129.
Yanai I, Benjamin H, Shmoish M, Chalifa-Caspi V, Shklar M, Ophir R et al. Genome-wide midrange transcription profiles reveal expression level relationships in human tissue specification. Bioinformatics 2005; 5: 650–659.
GeneCards [Internet]. [cited 11 May 2011] Weizmann Institute of Science 2011. Available from: http://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=TRANK1.
Lee SH, Wray NR, Goddard ME, Visscher PM . Estimating missing heritability for disease from genome-wide association studies. Am J Hum Genet 2011; 88: 294–305.
Littell JH, Corcoran J, Pillai VK . Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis. Oxford University Press: New York, USA, 2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Supplementary information
Appendix
Appendix
The Bipolar Genome Study (BiGS) Authorship List
University California, San Diego: John R. Kelsoe, Tiffany A. Greenwood, Caroline M. Nievergelt, Rebecca McKinney, Paul D. Shilling; Scripps Translational Science Institute: Nicholas J. Schork, Erin N. Smith, Cinnamon S. Bloss; Indiana University: John I. Nurnberger, Jr., Howard J. Edenberg, Tatiana Foroud, Daniel L. Koller; University of Chicago: Elliot S. Gershon, Chunyu Liu, Judith A. Badner; Rush University Medical Center: William A. Scheftner; Howard University: William B. Lawson, Evaristus A. Nwulia, Maria Hipolito; University of Iowa: William Coryell; Washington University: John Rice; University California, San Francisco: William Byerley; National Institute Mental Health: Francis J. McMahon, David T Chen; University of Pennsylvania: Wade H. Berrettini; Johns Hopkins: James B. Potash, Peter P. Zandi, Pamela B. Mahon; University of Michigan: Melvin G. McInnis, Sebastian Zöllner, Peng Zhang; The Translational Genomics Research Institute: David W. Craig, Szabolcs Szelinger; Portland Veterans Affairs Medical Center: Thomas B. Barrett; Georg-August-University Göttingen: Thomas G. Schulze.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, D., Jiang, X., Akula, N. et al. Genome-wide association study meta-analysis of European and Asian-ancestry samples identifies three novel loci associated with bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry 18, 195–205 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2011.157
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2011.157
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Sleep Disorder Kleine–Levin Syndrome (KLS) Joins the List of Polygenic Brain Disorders Associated with Obstetric Complications
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Multi-ancestry meta-analysis and fine-mapping in Alzheimer’s disease
Molecular Psychiatry (2023)
-
Zika virus-induced TNF-α signaling dysregulates expression of neurologic genes associated with psychiatric disorders
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2022)
-
CADPS functional mutations in patients with bipolar disorder increase the sensitivity to stress
Molecular Psychiatry (2022)
-
Genetic and functional analyses implicate microRNA 499A in bipolar disorder development
Translational Psychiatry (2022)