Abstract
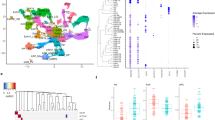
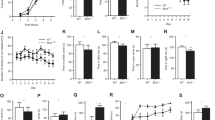
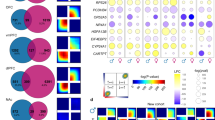
Women are twice as likely as men to develop major depressive disorder (MDD) and are more prone to recurring episodes. Hence, we tested the hypothesis that the illness may associate with robust molecular changes in female subjects, and investigated large-scale gene expression in the post-mortem brain of MDD subjects paired with matched controls (n=21 pairs). We focused on the lateral/basolateral/basomedian complex of the amygdala as a neural hub of mood regulation affected in MDD. Among the most robust findings were downregulated transcripts for genes coding for γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) interneuron-related peptides, including somatostatin (SST), tachykinin, neuropeptide Y (NPY) and cortistatin, in a pattern reminiscent to that previously reported in mice with low brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Changes were confirmed by quantitative PCR and not explained by demographic, technical or known clinical parameters. BDNF itself was significantly downregulated at the RNA and protein levels in MDD subjects. Investigating putative mechanisms, we show that this core MDD-related gene profile (including SST, NPY, TAC1, RGS4 and CORT) is recapitulated by complementary patterns in mice with constitutive (BDNF-heterozygous) or activity-dependent (exon IV knockout) decreases in BDNF function, with a common effect on SST and NPY. Together, these results provide both direct (low RNA/protein) and indirect (low BDNF-dependent gene pattern) evidence for reduced BDNF function in the amygdala of female subjects with MDD. Supporting studies in mutant mice models suggest a complex mechanism of low constitutive and activity-dependent BDNF function in MDD, particularly affecting SST/NPY-related GABA neurons, thus linking the neurotrophic and GABA hypotheses of depression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cotter D, Mackay D, Landau S, Kerwin R, Everall I . Reduced glial cell density and neuronal size in the anterior cingulate cortex in major depressive disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2001; 58: 545–553.
Rajkowska G, Halaris A, Selemon LD . Reductions in neuronal and glial density characterize the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in bipolar disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2001; 49: 741–752.
Bowley MP, Drevets WC, Ongur D, Price JL . Low glial numbers in the amygdala in major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2002; 52: 404–412.
Hamidi M, Drevets WC, Price JL . Glial reduction in amygdala in major depressive disorder is due to oligodendrocytes. Biol Psychiatry 2004; 55: 563–569.
Videbech P, Ravnkilde B . Hippocampal volume and depression: a meta-analysis of MRI studies. Am J Psychiatry 2004; 161: 1957–1966.
Campbell S, Marriott M, Nahmias C, MacQueen GM . Lower hippocampal volume in patients suffering from depression: a meta-analysis. Am J Psychiatry 2004; 161: 598–607.
Shirayama Y, Chen AC, Nakagawa S, Russell DS, Duman RS . Brain-derived neurotrophic factor produces antidepressant effects in behavioral models of depression. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 3251–3261.
Deltheil T, Tanaka K, Reperant C, Hen R, David DJ, Gardier AM . Synergistic neurochemical and behavioural effects of acute intrahippocampal injection of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and antidepressants in adult mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2009; 12: 905–915.
Monteggia LM, Barrot M, Powell CM, Berton O, Galanis V, Gemelli T et al. Essential role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in adult hippocampal function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 10827–10832.
Saarelainen T, Hendolin P, Lucas G, Koponen E, Sairanen M, MacDonald E et al. Activation of the TrkB neurotrophin receptor is induced by antidepressant drugs and is required for antidepressant-induced behavioral effects. J Neurosci 2003; 23: 349–357.
Molendijk ML, Bus BA, Spinhoven P, Penninx BW, Kenis G, Prickaerts J et al. Serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in major depressive disorder: state-trait issues, clinical features and pharmacological treatment. Mol Psychiatry 2010 (in press).
Sen S, Duman R, Sanacora G . Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor, depression, and antidepressant medications: meta-analyses and implications. Biol Psychiatry 2008; 64: 527–532.
Dunham JS, Deakin JF, Miyajima F, Payton A, Toro CT . Expression of hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its receptors in Stanley consortium brains. J Psychiatr Res 2009; 43: 1175–1184.
Thompson Ray M, Weickert CS, Wyatt E, Webster MJ . Decreased BDNF, trkB-TK+ and GAD(67) mRNA expression in the hippocampus of individuals with schizophrenia and mood disorders. J Psychiatry Neurosci 2011; 36: 100048.
Chen B, Dowlatshahi D, MacQueen GM, Wang JF, Young LT . Increased hippocampal BDNF immunoreactivity in subjects treated with antidepressant medication. Biol Psychiatry 2001; 50: 260–265.
Dwivedi Y, Rizavi HS, Conley RR, Roberts RC, Tamminga CA, Pandey GN . Altered gene expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and receptor tyrosine kinase B in postmortem brain of suicide subjects. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2003; 60: 804–815.
Karege F, Vaudan G, Schwald M, Perroud N, La Harpe R . Neurotrophin levels in postmortem brains of suicide victims and the effects of antemortem diagnosis and psychotropic drugs. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2005; 136: 29–37.
Kozicz T, Tilburg-Ouwens D, Faludi G, Palkovits M, Roubos E . Gender-related urocortin 1 and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in the adult human midbrain of suicide victims with major depression. Neuroscience 2008; 152: 1015–1023.
Ernst C, Deleva V, Deng X, Sequeira A, Pomarenski A, Klempan T et al. Alternative splicing, methylation state, and expression profile of tropomyosin-related kinase B in the frontal cortex of suicide completers. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2009; 66: 22–32.
Keller S, Sarchiapone M, Zarrilli F, Videtic A, Ferraro A, Carli V et al. Increased BDNF promoter methylation in the Wernicke area of suicide subjects. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2010; 67: 258–267.
Pregelj P, Nedic G, Paska AV, Zupanc T, Nikolac M, Balazic J et al. The association between brain-derived neurotrophic factor polymorphism (BDNF Val66Met) and suicide. J Affect Disord 2011; 128: 287–290.
Sequeira A, Mamdani F, Ernst C, Vawter MP, Bunney WE, Lebel V et al. Global brain gene expression analysis links glutamatergic and GABAergic alterations to suicide and major depression. PLoS One 2009; 4: e6585.
Sanacora G, Gueorguieva R, Epperson CN, Wu YT, Appel M, Rothman DL et al. Subtype-specific alterations of gamma-aminobutyric acid and glutamate in patients with major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2004; 61: 705–713.
Sanacora G, Mason GF, Rothman DL, Behar KL, Hyder F, Petroff OA et al. Reduced cortical gamma-aminobutyric acid levels in depressed patients determined by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1999; 56: 1043–1047.
Levinson AJ, Fitzgerald PB, Favalli G, Blumberger DM, Daigle M, Daskalakis ZJ . Evidence of cortical inhibitory deficits in major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2010; 67: 458–464.
Sibille E, Morris HM, Kota RS, Lewis DA . GABA-related transcripts in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in mood disorders. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2011; 14: 721–734.
Tripp A, Kota RS, Lewis DA, Sibille E . Reduced somatostatin in subgenual anterior cingulate cortex in major depression. Neurobiol Dis 2011; 42: 116–124.
Glorioso C, Sabatini M, Unger T, Hashimoto T, Monteggia LM, Lewis DA et al. Specificity and timing of neocortical transcriptome changes in response to BDNF gene ablation during embryogenesis or adulthood. Mol Psychiatry 2006; 11: 633–648.
Muller JF, Mascagni F, McDonald AJ . Postsynaptic targets of somatostatin-containing interneurons in the rat basolateral amygdala. J Comp Neurol 2007; 500: 513–529.
Seminowicz DA, Mayberg HS, McIntosh AR, Goldapple K, Kennedy S, Segal Z et al. Limbic-frontal circuitry in major depression: a path modeling metanalysis. Neuroimage 2004; 22: 409–418.
Pezawas L, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Goldman AL, Verchinski BA, Chen G, Kolachana BS et al. Evidence of biologic epistasis between BDNF and SLC6A4 and implications for depression. Mol Psychiatry 2008; 13: 709–716.
Hamilton JP, Gotlib IH . Neural substrates of increased memory sensitivity for negative stimuli in major depression. Biol Psychiatry 2008; 63: 1155–1162.
Glantz LA, Lewis DA . Reduction of synaptophysin immunoreactivity in the prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia. Regional and diagnostic specificity. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1997; 54: 943–952.
Sibille E, Wang Y, Joeyen-Waldorf J, Gaiteri C, Surget A, Oh S et al. A molecular signature of depression in the amygdala. Am J Psychiatry 2009; 166: 1011–1024.
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y . Controlling the false discovery rate - a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J Roy Stat Soc B Met 1995; 57: 289–300.
Morris HM, Hashimoto T, Lewis DA . Alterations in somatostatin mRNA expression in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Cereb Cortex 2008; 18: 1575–1587.
Korte M, Carroll P, Wolf E, Brem G, Thoenen H, Bonhoeffer T . Hippocampal long-term potentiation is impaired in mice lacking brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 8856–8860.
Sakata K, Woo NH, Martinowich K, Greene JS, Schloesser RJ, Shen L et al. Critical role of promoter IV-driven BDNF transcription in GABAergic transmission and synaptic plasticity in the prefrontal cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 5942–5947.
Franklin KBJ, Paxinos G . The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 3rd edn. Academic Press: New York, 2008, xxv, 1 v. pp (various pagings).
Sibille E, Arango V, Joeyen-Waldorf J, Wang Y, Leman S, Surget A et al. Large-scale estimates of cellular origins of mRNAs: enhancing the yield of transcriptome analyses. J Neurosci Methods 2008; 167: 198–206.
Bloom FE, Morales M . The central 5-HT3 receptor in CNS disorders. Neurochem Res 1998; 23: 653–659.
Pruunsild P, Kazantseva A, Aid T, Palm K, Timmusk T . Dissecting the human BDNF locus: bidirectional transcription, complex splicing, and multiple promoters. Genomics 2007; 90: 397–406.
Erraji-BenChekroun L, Underwood MD, Arango V, Galfalvy HC, Pavlidis P, Smyrniotopoulos P et al. Molecular aging in human prefrontal cortex is selective and continuous throughout adult life. Biological Psychiatry 2005; 57: 549–558.
Guilloux JP, Seney M, Edgar N, Sibille E . Integrated behavioral z-scoring increases the sensitivity and reliability of behavioral phenotyping in mice: relevance to emotionality and sex. J Neurosci Methods 2011; 197: 21–31.
van Disseldorp J, Faddy MJ, Themmen AP, de Jong FH, Peeters PH, van der Schouw YT et al. Relationship of serum antimullerian hormone concentration to age at menopause. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008; 93: 2129–2134.
Takei N, Sasaoka K, Inoue K, Takahashi M, Endo Y, Hatanaka H . Brain-derived neurotrophic factor increases the stimulation-evoked release of glutamate and the levels of exocytosis-associated proteins in cultured cortical neurons from embryonic rats. J Neurochem 1997; 68: 370–375.
Fatemi SH, Earle JA, Stary JM, Lee S, Sedgewick J . Altered levels of the synaptosomal associated protein SNAP-25 in hippocampus of subjects with mood disorders and schizophrenia. Neuroreport 2001; 12: 3257–3262.
Lewis DA, Campbell MJ, Morrison JH . An immunohistochemical characterization of somatostatin-28 and somatostatin-281-12 in monkey prefrontal cortex. J Comp Neurol 1986; 248: 1–18.
Glorioso C, Oh S, Douillard GG, Sibille E . Brain molecular aging, promotion of neurological disease and modulation by Sirtuin5 longevity gene polymorphism. Neurobiol Dis 2011; 41: 279–290.
Russo-Neustadt A, Beard RC, Cotman CW . Exercise, antidepressant medications, and enhanced brain derived neurotrophic factor expression. Neuropsychopharmacology 1999; 21: 679–682.
Duman RS, Monteggia LM . A neurotrophic model for stress-related mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry 2006; 59: 1116–1127.
Mattson MP, Maudsley S, Martin B . A neural signaling triumvirate that influences ageing and age-related disease: insulin/IGF-1, BDNF and serotonin. Ageing Res Rev 2004; 3: 445–464.
Buckley PF, Mahadik S, Pillai A, Terry Jr A . Neurotrophins and schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2007; 94: 1–11.
Zuccato C, Cattaneo E . Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurol 2009; 5: 311–322.
Gahete MD, Rubio A, Duran-Prado M, Avila J, Luque RM, Castano JP . Expression of Somatostatin, cortistatin, and their receptors, as well as dopamine receptors, but not of neprilysin, are reduced in the temporal lobe of Alzheimer's disease patients. J Alzheimers Dis 2010; 20: 465–475.
Fino E, Yuste R . Dense inhibitory connectivity in neocortex. Neuron 2011; 69: 1188–1203.
Hashimoto T, Volk DW, Eggan SM, Mirnics K, Pierri JN, Sun Z et al. Gene expression deficits in a subclass of GABA neurons in the prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia. J Neurosci 2003; 23: 6315–6326.
Siegle GJ, Thompson W, Carter CS, Steinhauer SR, Thase ME . Increased amygdala and decreased dorsolateral prefrontal BOLD responses in unipolar depression: related and independent features. Biol Psychiatry 2007; 61: 198–209.
Tsankova NM, Berton O, Renthal W, Kumar A, Neve RL, Nestler EJ . Sustained hippocampal chromatin regulation in a mouse model of depression and antidepressant action. Nat Neurosci 2006; 9: 519–525.
Surget A, Wang Y, Leman S, Ibarguen-Vargas Y, Edgar N, Griebel G et al. Corticolimbic transcriptome changes are state-dependent and region-specific in a rodent model of depression and of antidepressant reversal. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009; 34: 1363–1380.
Chourbaji S, Hellweg R, Brandis D, Zorner B, Zacher C, Lang UE et al. Mice with reduced brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression show decreased choline acetyltransferase activity, but regular brain monoamine levels and unaltered emotional behavior. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2004; 121: 28–36.
Ibarguen-Vargas Y, Surget A, Vourc’h P, Leman S, Andres CR, Gardier AM et al. Deficit in BDNF does not increase vulnerability to stress but dampens antidepressant-like effects in the unpredictable chronic mild stress. Behav Brain Res 2009; 202: 245–251.
Berton O, McClung CA, DiLeone RJ, Krishnan V, Renthal W, Russo SJ et al. Essential role of BDNF in the mesolimbic dopamine pathway in social defeat stress. Science 2006; 311: 864–868.
Autry AE, Adachi M, Cheng P, Monteggia LM . Gender-specific impact of brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling on stress-induced depression-like behavior. Biol Psychiatry 2009; 66: 84–90.
Monteggia LM, Luikart B, Barrot M, Theobold D, Malkovska I, Nef S et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor conditional knockouts show gender differences in depression-related behaviors. Biol Psychiatry 2007; 61: 187–197.
Advani T, Koek W, Hensler JG . Gender differences in the enhanced vulnerability of BDNF+/− mice to mild stress. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2009; 12: 583–588.
Sakata K, Jin L, Jha S . Lack of promoter IV-driven BDNF transcription results in depression-like behavior. Genes Brain Behav 2010; 9: 712–721.
Zeyda T, Diehl N, Paylor R, Brennan MB, Hochgeschwender U . Impairment in motor learning of somatostatin null mutant mice. Brain Res 2001; 906: 107–114.
Engin E, Stellbrink J, Treit D, Dickson CT . Anxiolytic and antidepressant effects of intracerebroventricularly administered somatostatin: behavioral and neurophysiological evidence. Neuroscience 2008; 157: 666–676.
Gatt JM, Nemeroff CB, Dobson-Stone C, Paul RH, Bryant RA, Schofield PR et al. Interactions between BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and early life stress predict brain and arousal pathways to syndromal depression and anxiety. Mol Psychiatry 2009; 14: 681–695.
Lau JY, Goldman D, Buzas B, Hodgkinson C, Leibenluft E, Nelson E et al. BDNF gene polymorphism (Val66Met) predicts amygdala and anterior hippocampus responses to emotional faces in anxious and depressed adolescents. Neuroimage 2010; 53: 952–961.
Mickey BJ, Zhou Z, Heitzeg MM, Heinz E, Hodgkinson CA, Hsu DT et al. Emotion processing, major depression, and functional genetic variation of neuropeptide Y. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2011; 68: 158–166.
Zhou Z, Zhu G, Hariri AR, Enoch MA, Scott D, Sinha R et al. Genetic variation in human NPY expression affects stress response and emotion. Nature 2008; 452: 997–1001.
Ogden CA, Rich ME, Schork NJ, Paulus MP, Geyer MA, Lohr JB et al. Candidate genes, pathways and mechanisms for bipolar (manic-depressive) and related disorders: an expanded convergent functional genomics approach. Mol Psychiatry 2004; 9: 1007–1029.
Mirnics K, Middleton FA, Stanwood GD, Lewis DA, Levitt P . Disease-specific changes in regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4) expression in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2001; 6: 293–301.
Rethelyi JM, Bakker SC, Polgar P, Czobor P, Strengman E, Pasztor PI et al. Association study of NRG1, DTNBP1, RGS4, G72/G30, and PIP5K2A with schizophrenia and symptom severity in a Hungarian sample. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2010; 153B: 792–801.
Etain B, Dumaine A, Mathieu F, Chevalier F, Henry C, Kahn JP et al. A SNAP25 promoter variant is associated with early-onset bipolar disorder and a high expression level in brain. Mol Psychiatry 2010; 15: 748–755.
Mai JK, Assheuer J, Paxinos G . Atlas of the Human Brain, 2nd edn. Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, Boston, 2004, viii, 246 p.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) MH084060 (ES), MH085111 (ES) and MH084053 (DAL). The funding agency had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish and preparation of the paper. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIMH or the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
David A Lewis currently receives investigator-initiated research support from the BMS Foundation, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Curridium and Pfizer and in 2008–2010 served as a consultant in the areas of target identification and validation and new compound development to AstraZeneca, BioLine RX, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Neurogen and SK Life Science.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guilloux, JP., Douillard-Guilloux, G., Kota, R. et al. Molecular evidence for BDNF- and GABA-related dysfunctions in the amygdala of female subjects with major depression. Mol Psychiatry 17, 1130–1142 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2011.113
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2011.113
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Interrogation of the human cortical peptidome uncovers cell-type specific signatures of cognitive resilience against Alzheimer’s disease
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Upregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor by Shiikuwasha (Citrus depressa Hayata)
Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Care and Sciences (2023)
-
Brain-specific Pd1 deficiency leads to cortical neurogenesis defects and depressive-like behaviors in mice
Cell Death & Differentiation (2023)
-
Maternal separation and its developmental consequences on anxiety and parvalbumin interneurons in the amygdala
Journal of Neural Transmission (2023)
-
The role of GPR39 zinc receptor in the modulation of glutamatergic and GABAergic transmission
Pharmacological Reports (2023)