Abstract
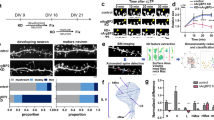
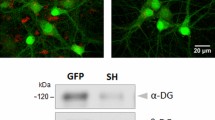
Genetic variations in dysbindin-1 (dystrobrevin-binding protein-1) are one of the most commonly reported variations associated with schizophrenia. As schizophrenia could be regarded as a neurodevelopmental disorder resulting from abnormalities of synaptic connectivity, we attempted to clarify the function of dysbindin-1 in neuronal development. We examined the developmental change of dysbindin-1 in rat brain by western blotting and found that a 50 kDa isoform is highly expressed during the embryonic stage, whereas a 40 kDa one is detected at postnatal day 11 and increased thereafter. Immunofluorescent analyses revealed that dysbindin-1 is enriched at the spine-like structure of primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons. We identified WAVE2, but not N-WASP, as a binding partner for dysbindin-1. We also found that Abi-1, a binding molecule for WAVE2 involved in spine morphogenesis, interacts with dysbindin-1. Although dysbindin-1, WAVE2 and Abi-1 form a ternary complex, dysbindin-1 promoted the binding of WAVE2 to Abi-1. RNA interference-mediated knockdown of dysbindin-1 led to the generation of abnormally elongated immature dendritic protrusions. The present results indicate possible functions of dysbindin-1 at the postsynapse in the regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis through the interaction with WAVE2 and Abi-1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others

References
Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, Perkins DO . Textbook of Schizophrenia. The American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.: Arlington, VA, 2006.
O’Donovan MC, Williams NM, Owen MJ . Recent advances in the genetics of schizophrenia. Hum Mol Genet 2003; 12: R125–R133.
Bellon A . New genes associated with schizophrenia in neurite formation: a review of cell culture experiments. Mol Psychiatry 2007; 12: 620–629.
Harrison PJ, Weinberger DR . Schizophrenia genes, gene expression, and neuropathology: on the matter of their convergence. Mol Psychiatry 2005; 10: 40–68.
Kamiya A, Kubo K, Tomoda T, Takaki M, Youn R, Ozeki Y et al. A schizophrenia-associated mutation of DISC1 perturbs cerebral cortex development. Nat Cell Biol 2005; 7: 1167–1178.
Ozeki Y, Tomoda T, Kleiderlein J, Kamiya A, Bord L, Fujii K et al. Disrupted-in-schizophrenia-1 (DISC-1): mutant truncation prevents binding to NudE-like (NUDEL) and inhibits neurite outgrowth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 289–294.
Miyoshi K, Honda A, Baba K, Taniguchi M, Oono K, Fujita T et al. Disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1, a candidate gene for schizophrenia, participates in neurite outgrowth. Mol Psychiatry 2003; 8: 685–694.
Straub RE, MacLean CJ, O’Neill FA, Burke J, Murphy B, Duke F et al. A potential vulnerability locus for schizophrenia on chromosome 6p24-22: evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Nat Genet 1995; 11: 287–293.
Schizophrenia Linkage Collaborative Group for Chromosomes 3 a. Additional support for schizophrenia linkage on chromosomes 6 and 8: a multicenter study. Am J Med Genet 1996; 67: 580–594.
Schwab SG, Hallmayer J, Albus M, Lerer B, Eckstein GN, Borrmann M et al. A genome-wide autosomal screen for schizophrenia susceptibility loci in 71 families with affected siblings: support for loci on chromosome 10p and 6. Mol Psychiatry 2000; 5: 638–649.
Straub RE, Jiang Y, MacLean CJ, Ma Y, Webb BT, Myakishev MV et al. Genetic variation in the 6p22.3 gene DTNBP1, the human ortholog of the mouse dysbindin gene, is associated with schizophrenia. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 337–348.
Schwab SG, Knapp M, Mondabon S, Hallmayer J, Borrmann-Hassenbach M, Albus M et al. Support for association of schizophrenia with genetic variation in the 6p22.3 gene, dysbindin, in sib-pair families with linkage and in an additional sample of triad families. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 72: 185–190.
Van Den Bogaert A, Schumacher J, Schulze TG, Otte AC, Ohlraun S, Kovalenko S et al. The DTNBP1 (dysbindin) gene contributes to schizophrenia, depending on family history of the disease. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 1438–1443.
Tang JX, Zhou J, Fan JB, Li XW, Shi YY, Gu NF et al. Family-based association study of DTNBP1 in 6p22.3 and schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2003; 8: 717–718.
Kirov G, Ivanov D, Williams NM, Preece A, Nikolov I, Milev R et al. Strong evidence for association between the dystrobrevin binding protein 1 gene (DTNBP1) and schizophrenia in 488 parent-offspring trios from Bulgaria. Biol Psychiatry 2004; 55: 971–975.
Williams NM, Preece A, Morris DW, Spurlock G, Bray NJ, Stephens M et al. Identification in 2 independent samples of a novel schizophrenia risk haplotype of the dystrobrevin binding protein gene (DTNBP1). Arch Gen Psychiatry 2004; 61: 336–344.
Funke B, Finn CT, Plocik AM, Lake S, DeRosse P, Kane JM et al. Association of the DTNBP1 locus with schizophrenia in a US population. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 75: 891–898.
Numakawa T, Yagasaki Y, Ishimoto T, Okada T, Suzuki T, Iwata N et al. Evidence of novel neuronal functions of dysbindin, a susceptibility gene for schizophrenia. Hum Mol Genet 2004; 13: 2699–2708.
Weickert CS, Straub RE, McClintock BW, Matsumoto M, Hashimoto R, Hyde TM et al. Human dysbindin (DTNBP1) gene expression in normal brain and in schizophrenic prefrontal cortex and midbrain. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2004; 61: 544–555.
Talbot K, Eidem WL, Tinsley CL, Benson MA, Thompson EW, Smith RJ et al. Dysbindin-1 is reduced in intrinsic, glutamatergic terminals of the hippocampal formation in schizophrenia. J Clin Invest 2004; 113: 1353–1363.
Benson MA, Newey SE, Martin-Rendon E, Hawkes R, Blake DJ . Dysbindin, a novel coiled-coil-containing protein that interacts with the dystrobrevins in muscle and brain. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 24232–24241.
Blake DJ, Weir A, Newey SE, Davies KE . Function and genetics of dystrophin and dystrophin-related proteins in muscle. Physiol Rev 2002; 82: 291–329.
Blake DJ, Hawkes R, Benson MA, Beesley PW . Different dystrophin-like complexes are expressed in neurons and glia. J Cell Biol 1999; 147: 645–658.
Marchand S, Stetzkowski-Marden F, Cartaud J . Differential targeting of components of the dystrophin complex to the postsynaptic membrane. Eur J Neurosci 2001; 13: 221–229.
Brunig I, Suter A, Knuesel I, Luscher B, Fritschy JM . GABAergic terminals are required for postsynaptic clustering of dystrophin but not of GABAA receptors and gephyrin. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 4805–4813.
Talbot K, Cho DS, Ong WY, Benson MA, Han LY, Kazi HA et al. Dysbindin-1 is a synaptic and microtubular protein that binds brain snapin. Hum Mol Genet 2006; 15: 3041–3054.
Kumamoto N, Matsuzaki S, Inoue K, Hattori T, Shimizu S, Hashimoto R et al. Hyperactivation of midbrain dopaminergic system in schizophrenia could be attributed to the down-regulation of dysbindin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 345: 904–909.
Iizuka Y, Sei Y, Weinberger DR, Straub RE . Evidence that the BLOC-1 protein dysbindin modulates dopamine D2 receptor internalization and signaling but not D1 internalization. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 12390–12395.
Chen XW, Feng YQ, Hao CJ, Guo XL, He X, Zhou ZY et al. DTNBP1, a schizophrenia susceptibility gene, affects kinetics of transmitter release. J Cell Biol 2008; 181: 791–801.
Ghiani CA, Starcevic M, Rodriguez-Fernandez IA, Nazarian R, Cheli VT, Chan LN et al. The dysbindin-containing complex (BLOC-1) in brain: developmental regulation, interaction with SNARE proteins and role in neurite outgrowth. Mol Psychiatry 2010; 15: 115, 204–215.
Bishop AL, Hall A . Rho GTPases and their effector proteins. Biochem J 2000; 348 (Part 2): 241–255.
Govek EE, Newey SE, Van Aelst L . The role of the Rho GTPases in neuronal development. Genes Dev 2005; 19: 1–49.
Bonhoeffer T, Yuste R . Spine motility. Phenomenology, mechanisms, and function. Neuron 2002; 35: 1019–1027.
Lisman J . Actin's actions in LTP-induced synapse growth. Neuron 2003; 38: 361–362.
Choi J, Ko J, Racz B, Burette A, Lee JR, Kim S et al. Regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis by insulin receptor substrate 53, a downstream effector of Rac1 and Cdc42 small GTPases. J Neurosci 2005; 25: 869–879.
Takenawa T, Miki H . WASP and WAVE family proteins: key molecules for rapid rearrangement of cortical actin filaments and cell movement. J Cell Sci 2001; 114: 1801–1809.
Proepper C, Johannsen S, Liebau S, Dahl J, Vaida B, Bockmann J et al. Abelson interacting protein 1 (Abi-1) is essential for dendrite morphogenesis and synapse formation. EMBO J 2007; 26: 1397–1409.
Shinohara H, Asano T, Kato K, Kameshima T, Semba R . Localization of a G protein Gi2 in the cilia of rat ependyma, oviduct and trachea. Eur J Neurosci 1998; 10: 699–707.
Nagata K, Asano T, Nozawa Y, Inagaki M . Biochemical and cell biological analyses of a mammalian septin complex, Sept7/9b/11. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 55895–55904.
Nagata K, Puls A, Futter C, Aspenstrom P, Schaefer E, Nakata T et al. The MAP kinase kinase kinase MLK2 co-localizes with activated JNK along microtubules and associates with kinesin superfamily motor KIF3. EMBO J 1998; 17: 149–158.
Nagata K, Inagaki M . Cytoskeletal modification of Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor activity: identification of a Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor as a binding partner for Sept9b, a mammalian septin. Oncogene 2005; 24: 65–76.
Kawabata I, Umeda T, Yamamoto K, Okabe S . Electroporation-mediated gene transfer system applied to cultured CNS neurons. Neuroreport 2004; 15: 971–975.
Nishimura T, Yamaguchi T, Tokunaga A, Hara A, Hamaguchi T, Kato K et al. Role of numb in dendritic spine development with a Cdc42 GEF intersectin and EphB2. Mol Biol Cell 2006; 17: 1273–1285.
Tada T, Simonetta A, Batterton M, Kinoshita M, Edbauer D, Sheng M . Role of septin cytoskeleton in spine morphogenesis and dendrite development in neurons. Curr Biol 2007; 17: 1752–1758.
Hering H, Sheng M . Dendritic spines: structure, dynamics and regulation. Nat Rev Neurosci 2001; 2: 880–888.
Haeckel A, Ahuja R, Gundelfinger ED, Qualmann B, Kessels MM . The actin-binding protein Abp1 controls dendritic spine morphology and is important for spine head and synapse formation. J Neurosci 2008; 28: 10031–10044.
Miki H, Takenawa T . Regulation of actin dynamics by WASP family proteins. J Biochem (Tokyo) 2003; 134: 309–313.
Pilpel Y, Segal M . Rapid WAVE dynamics in dendritic spines of cultured hippocampal neurons is mediated by actin polymerization. J Neurochem 2005; 95: 1401–1410.
Soderling SH, Guire ES, Kaech S, White J, Zhang F, Schutz K et al. A WAVE-1 and WRP signaling complex regulates spine density, synaptic plasticity, and memory. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 355–365.
Leng Y, Zhang J, Badour K, Arpaia E, Freeman S, Cheung P et al. Abelson-interactor-1 promotes WAVE2 membrane translocation and abelson-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation required for WAVE2 activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 1098–1103.
Miki H, Takenawa T . WAVE2 serves a functional partner of IRSp53 by regulating its interaction with Rac. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002; 293: 93–99.
Stuart JR, Gonzalez FH, Kawai H, Yuan ZM . c-Abl interacts with the WAVE2 signaling complex to induce membrane ruffling and cell spreading. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 31290–31297.
Suetsugu S, Kurisu S, Oikawa T, Yamazaki D, Oda A, Takenawa T . Optimization of WAVE2 complex-induced actin polymerization by membrane-bound IRSp53, PIP(3), and Rac. J Cell Biol 2006; 173: 571–585.
Kheir WA, Gevrey JC, Yamaguchi H, Isaac B, Cox D . A WAVE2-Abi1 complex mediates CSF-1-induced F-actin-rich membrane protrusions and migration in macrophages. J Cell Sci 2005; 118: 5369–5379.
Calabrese B, Wilson MS, Halpain S . Development and regulation of dendritic spine synapses. Physiology (Bethesda) 2006; 21: 38–47.
Sung JY, Engmann O, Teylan MA, Nairn AC, Greengard P, Kim Y . WAVE1 controls neuronal activity-induced mitochondrial distribution in dendritic spines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 3112–3116.
Parnass Z, Tashiro A, Yuste R . Analysis of spine morphological plasticity in developing hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Hippocampus 2000; 10: 561–568.
Bourne J, Harris KM . Do thin spines learn to be mushroom spines that remember? Curr Opin Neurobiol 2007; 17: 381–386.
Nimchinsky EA, Sabatini BL, Svoboda K . Structure and function of dendritic spines. Annu Rev Physiol 2002; 64: 313–353.
Miki H, Yamaguchi H, Suetsugu S, Takenawa T . IRSp53 is an essential intermediate between Rac and WAVE in the regulation of membrane ruffling. Nature 2000; 408: 732–735.
Hattori S, Murotani T, Matsuzaki S, Ishizuka T, Kumamoto N, Takeda M et al. Behavioral abnormalities and dopamine reductions in sdy mutant mice with a deletion in Dtnbp1, a susceptibility gene for schizophrenia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008; 373: 298–302.
Rapoport JL, Addington AM, Frangou S, Psych MR . The neurodevelopmental model of schizophrenia: update 2005. Mol Psychiatry 2005; 10: 434–449.
Camargo LM, Collura V, Rain JC, Mizuguchi K, Hermjakob H, Kerrien S et al. Disrupted in schizophrenia 1 interactome: evidence for the close connectivity of risk genes and a potential synaptic basis for schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2007; 12: 74–86.
Hayashi-Takagi A, Takaki M, Graziane N, Seshadri S, Murdoch H, Dunlop AJ et al. Disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) regulates spines of the glutamate synapse via Rac1. Nat Neurosci 2010; 13: 327–332.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs T Takenawa, S Okabe and M Hoshino for kindly providing us various expression vectors. This work was supported in part by grant-in-aid for scientific research from Ministry of Education, Science, Technology, Sports and Culture of Japan and by a grant from Takeda Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, H., Morishita, R., Shinoda, T. et al. Dysbindin-1, WAVE2 and Abi-1 form a complex that regulates dendritic spine formation. Mol Psychiatry 15, 976–986 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2010.69
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2010.69
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Orchestration of synaptic functions by WAVE regulatory complex-mediated actin reorganization
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2023)
-
Schizophrenia-associated dysbindin modulates axonal mitochondrial movement in cooperation with p150glued
Molecular Brain (2021)
-
Expression analyses of PLEKHG2, a Rho family-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor, during mouse brain development
Medical Molecular Morphology (2021)
-
A psychiatric disease-related circular RNA controls synaptic gene expression and cognition
Molecular Psychiatry (2020)
-
Biochemical and morphological characterization of SEPT1 in mouse brain
Medical Molecular Morphology (2020)