Abstract
Expression of claudin-2, a tight junction protein, is highly upregulated during inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and, due to its association with epithelial permeability, has been postulated to promote inflammation. Notably, claudin-2 has also been implicated in the regulation of intestinal epithelial proliferation. However, precise role of claudin-2 in regulating colonic homeostasis remains unclear. Here, we demonstrate, using Villin-Claudin-2 transgenic mice, that increased colonic claudin-2 expression augments mucosal permeability as well as colon and crypt length. Most notably, despite leaky colon, Cl-2TG mice were significantly protected against experimental colitis. Importantly, claudin-2 expression increased colonocyte proliferation and provided protection against colitis-induced colonocyte death in a PI-3Kinase/Bcl-2-dependent manner. However, Cl-2TG mice also demonstrated marked suppression of colitis-induced increases in immune activation and associated signaling, suggesting immune tolerance. Accordingly, colons from naive Cl-2TG mice harbored significantly increased numbers of regulatory (CD4+Foxp3+) T cells than WT littermates. Furthermore, macrophages isolated from Cl-2TG mouse colon exhibited immune anergy. Importantly, these immunosuppressive changes were associated with increased synthesis of the immunoregulatory cytokine TGF-β by colonic epithelial cells in Cl-2TG mice compared with WT littermates. Taken together, our findings reveal a critical albeit complex role of claudin-2 in intestinal homeostasis by regulating epithelial permeability, inflammation and proliferation and suggest novel therapeutic opportunities.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), including ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, are chronic inflammatory conditions of the gastrointestinal tract caused by dysregulated immune responses. Earlier studies have indicated that the intestinal epithelium of IBD patients exhibits increased permeability compared with normal subjects.1 Increased mucosal permeability has also been reported in mouse models of experimental colitis.2 These findings have led to the hypothesis that the intact epithelium represents a barrier against the development of gastrointestinal inflammation and that impaired barrier function is a potential cause of mucosal inflammation. However, the normal epithelium permits limited exposure of mucosal immune elements to antigens in the commensal microflora. One potential explanation for this apparent subversion of epithelial barrier function may be the need of the mucosal immune system to develop tolerance toward antigens of the commensal microflora, because in its absence mucosal inflammation is likely to occur. However, a dearth of experimental models where the intestinal epithelial barrier is targeted directly without affecting other cellular functions has impeded progress in this research area.
Members of the claudin family of proteins are the principal constituents of the tight junctions, which regulate paracellular permeability in an intact epithelium.3 Consequently, recent studies have examined potential alterations in the status of claudin family members in IBD patients and demonstrated a robust increase in claudin-2 expression in IBD.4, 5, 6, 7 Claudin-2 is unique among claudin family members as its normal expression is restricted to leaky epithelia in vivo.8, 9 In cultured epithelial cells, claudin-2 expression correlates inversely with the transepithelial resistance (TER) and serves as a paracellular transport channel for Na+ and Ca++ ions.8, 10, 11 In addition, claudin-2 is a target for Wnt/β-catenin signaling and, compared with other claudins, is uniquely expressed by undifferentiated and proliferative colonocytes at the crypt base.12, 13 We have further demonstrated that activation of EGFR, a key regulator of colonocyte proliferation, induces colonic claudin-2 expression.13 Taken together, these findings have suggested an important role of claudin-2 in regulating colonic physiology and pathology.
In the present study, we demonstrate, based upon extensive analysis using mouse models of colitis, cultured colonic epithelial cells subjected to colitis-inducing agents and novel transgenic mice with targeted intestinal epithelial claudin-2 overexpression that claudin-2 expression protects against experimentally induced colitis. This protection is mediated by resistance to dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-dependent epithelial injury and immune tolerance in the face of increased colonic epithelial permeability. Taken together, our findings suggest a critical role of claudin-2 in regulating colonic epithelial homeostasis, immune activation, and inflammation.
Results
Villin-Claudin-2 transgenic (Cl-2TG) mice exhibit increased colon length and permeability
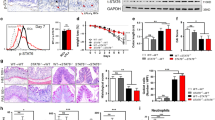
To understand the clinical significance of claudin-2 expression during intestinal inflammation, we generated Cl-2TG mice using the villin promoter (Supplementary Figure S1A online) to achieve intestine-specific overexpression. Immunoblot analysis using colon lysates and immunohistochemistry confirmed a robust increase in claudin-2 expression in the colonic epithelial cells of Cl-2TG mice vs. WT littermates, similar to IBD (Figure 1a and b and Supplementary Figure S1B). Claudin-2 overexpression was also observed in the small intestine and to a minor extent in the kidney, organs known to express Villin protein (Supplementary Figure S1C and D). Colonic expression of other TJ-proteins, claudin-3, occludin, and ZO-1, remained largely unaffected in Cl-2TG mice (Figure 1a). Notably, further analyses revealed unexpected increases in the colon and crypt lengths of Cl-2TG vs. WT mice (P<0.01; Figure 1ci,ii). A similar increase in intestine length was also noted (P<0.05; Supplementary Figure S1E). To understand the physiological basis for this phenotype, we investigated potential changes in colonocyte proliferation and/or apoptosis. Colonic epithelial cells were isolated from BrdU-injected Cl-2TG and WT mice, stained with anti-cytokeratin, -BrdU, and -caspase-3 (cleaved/activated) antibodies and subjected to flow cytometry analysis. Results demonstrated a significant increase in BrdU-positive colonocytes in Cl-2TG vs. WT mice (P<0.05; Figure 1d), although numbers of caspase-3-positive cells were not significantly different (data not shown). These findings supported a role of claudin-2 in the regulation of colonocyte proliferation.
Villin-Claudin-2 transgenic mice exhibit increased colon length and permeability. (ai) Immunoblot analysis using mouse colon lysates and antigen-specific antibodies and (aii) quantitative analysis of protein expression relative to the expression in WT mice. (b) Immunohistochemical analysis of endogenous and exogenous colonic claudin-2 expression. (ci) Colon length (N# 10, **P<0.01) and (cii) crypt height. (d) BrdU-positive colonocytes in Cl-2TG vs. WT mice. Cytokeratin-positive cells were isolated from the colons and subjected to fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS)-analysis following staining with an anti-BrdU antibody. (e) Transepithelial resistance (TER) (N# 5, *P<0.05). (fi) Transmucosal permeability using Ussing chamber (N#5, *P<0.05, **P<0.01) and (fii) transmucosal permeability using intrarectal delivery of FITC-dextran (4 kDa) (N#5, *P<0.05).
We further determined the effect of claudin-2 overexpression on transmucosal resistance and paracellular Na+ passes. Results using the Ussing chamber showed a significant decrease in transmucosal resistance (P<0.05; Figure 1e) and an increase in paracellular Na+ permeability (P<0.05; Supplementary Figure S1F) in transgenic vs. WT mice. Further analysis using the Ussing chamber or intrarectal delivery of FITC-dextran into the colon demonstrated that the colonic epithelium of Cl-2TG mice was also permeable to non-charged molecules (Figure 1fi,ii and Supplementary Figure S1G). Nevertheless, the TJ-ultrastructure remained largely unaltered in Cl-2TG mice (Supplementary Figure S1H). Taken together, our data suggested that claudin-2 overexpression promotes mucosal permeability.
Cl-2TG mice are protected from acute and chronic colitis
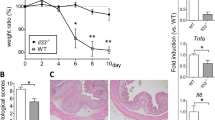
Despite increased mucosal permeability, Cl-2TG mice did not have signs of mucosal inflammation. To examine whether Cl-2TG mice are more susceptible to colitis, Cl-2TG and WT mice were subjected to chemically induced colitis by providing drinking water containing DSS. As expected, DSS-treated WT mice demonstrated significant body weight loss (P<0.01; Figure 2a). However, the DSS-induced weight loss was inhibited in Cl-2TG mice. The cumulative clinical disease index further supported protection of Cl-2TG mice against DSS colitis (Figure 2b). Consistent with these findings, colon length in DSS-treated WT mice was significantly decreased (P<0.001) compared with control mice (Figure 2ci–iii), whereas this parameter was not significantly different between DSS-treated and control Cl-2TG mice. Independent evaluation by a gastrointestinal pathologist confirmed a significantly lower injury score (P<0.001) in DSS-treated Cl-2TG vs. WT mice (Figure 2d). Importantly, depth of inflammation, crypt damage, and % involved by crypt damage were all significantly different between DSS-treated WT and Cl-2TG mice (Supplementary Figure S2). Histological analysis further demonstrated marked preservation of the crypt architecture and decreased inflammation in DSS-treated Cl-2TG mice, as compared with WT mice where crypt architecture was largely disrupted and the severe loss of epithelia was accompanied by massive inflammation (Figure 2e). A marked decrease in myeloperoxidase activity in DSS-treated Cl-2TG mice further suggested decreased neutrophil infiltration in the colon (Figure 2f). Because our animals were generated on a B6D2F1/J background, and because colitis is influenced by the genetic background of the animals employed, we performed similar experiments with claudin-2 transgenic animals that were backcrossed more than 10 times with C57BL/6 mice, which demonstrated similar differences as those observed for the mixed background animals (Supplementary Figure S3A–E). Taken together, these data showed that Cl-2TG mice were, contrary to expectation, protected against experimentally induced colitis.
Cl-2TG mice are protected from dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced acute colitis. To induce colitis, mice received DSS (4% w/v) in the drinking water (10 days). (a) Weight loss during the course of DSS administration. (b) Disease activity index (DAI) changes among DSS-treated groups. (ci) Colon length (cm) in control and DSS-treated mice. (cii) Representative colon images and (ciii) Colon weight/cm. (d) Cumulative injury scores. Control mice did not show inflammation and associated injury. (e) Representative H&E staining of the colonic tissues from control and DSS-treated mice. (f) Representative photomicrographs demonstrating immunostaining to determine colonic myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity from control and DSS-treated mice. Values are presented as mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Bars=500 or 50 μm.
Considering that IBD is a chronic inflammatory condition, we further examined whether Cl-2TG mice are also resistant to chronic colitis. For this purpose, we subjected Cl-2TG and WT mice to three cycles of DSS administration (5 days/cycle) followed by regular drinking water (16 days/cycle). As shown in Figure 3, we found significant decreases in the body weight of DSS-treated WT mice but not Cl-2TG mice (Figure 3a). This protection was also revealed by the colon length, cumulative injury score, and histopathology (Figure 3b–d) and was evident at both the levels of mucosal inflammation and crypt injury (Supplementary Figure S4).
Cl-2TG mice are protected from chronic colitis. Mice were subjected to three cycles of dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) (4% w/v) drinking water (5 days/cycle) followed by regular drinking water (16 days/cycle). (a) Weight loss during the treatment course. Body weight did not differ significantly among control groups. (bi) Mean colon length (cm) in control and DSS-treated mice, (bii) representative images, and (biii) colon weight/cm of colon length. (c) Cumulative injury score. Control mice did not show inflammation and associated injury. (d) Representative H&E staining of colonic tissues from control and DSS-treated mice. Values are presented as mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Bars=500 or 50 μm.
Cl-2TG mice demonstrate upregulation of proliferation-associated genes and downregulation of inflammation-associated genes
To investigate mechanisms by which claudin-2 overexpression influences colonic epithelial integrity and inflammation, we performed a global comparative transcriptome analysis to determine differentially expressed genes in DSS-treated WT and Cl-2TG mice. The DSS-treated WT mice were compared with control WT mice, and the DSS-challenged Cl-2TG mice were compared with DSS-treated WT mice. Analysis was stringent, and only genes that were changed significantly (P<0.05, upregulated or downregulated) in two group comparisons were considered. A total of 195 upregulated and 293 downregulated genes constituted the differentially expressed genes when comparing DSS-treated vs. control WT mice. Pathway analysis revealed that genes associated with proliferation and colon stem cells, including Ki67, LGR5, Sox9, and Foxa2, and key regulators of cell cycle and mitosis such as Aurkb, Kif-11, Nek2, and CDC25b were downregulated in DSS-treated vs. control WT mice (Supplementary Figure S5A). In contrast, these genes were significantly upregulated in DSS-treated Cl-2TG mice compared with DSS-treated WT mice (Supplementary Figure S5A). The top genes upregulated in DSS-treated vs. control WT mice included known key regulators of mucosal inflammation such as IL-1, TNF-α, Ptgs2, Cxcl2, CCL3, MMP-10, MMP-13, S100a8, and S100a9 (Supplementary Figure S5B). Importantly, expression of these inflammation-associated genes was sharply downregulated in DSS-treated Cl-2TG vs. WT mice. Taken together, these data suggested a role for epithelial integrity and suppressed immune activation in the protection of Cl-2TG mice from colitis.
Increased proliferation and decreased apoptosis in DSS-treated Cl-2TG mice
On the basis of the above gene expression data, we examined potential differences in proliferation and/or apoptosis between DSS-treated Cl-2TG and WT mice. Mice were injected with BrdU before killing, and the BrdU-positive cells were examined by immunohistochemistry and fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis. We found a significant increase in BrdU-positive epithelial cells in DSS-treated CL-2TG vs. WT mice (P<0.01, Figure 4ai and ii). Also, DSS colitis caused a marked decrease in cyclin-D1 expression in DSS-treated vs. control WT mice (P<0.05), which was largely prevented in CL-2TG mice (Figure 4aiii). In contrast, caspase-3-positive cells and expression of cleaved caspase-3 were more abundant in DSS-treated WT vs. Cl-2TG mice (P<0.01, Figure 4bi–iii).
Claudin-2 modulates colonic epithelial cell homeostasis. (ai) Representative images showing BrdU-positive cells in control and dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-treated animals. Please note that crypts in DSS-treated WT mice are BrdU-negative, but that adjoining infiltrating immune cells are positive and (aii) Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis of colonic epithelial cells coimmunostained for BrdU and cleaved-caspase-3, and (aiii) immunoblot analysis to determine cyclin-D1 expression. (bi) Representative images showing cleaved caspase-3-positive cells in control and DSS-treated animals, (bii) FACS analysis using colonic epithelial cells co-immunostained for BrdU and cleaved-caspase-3, and (biii) immunoblot analysis to determine cleaved caspase-3 expression in control and DSS-treated mice: N# 3-6. Values are mean+s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. Bars=500 μm.
In Caco-2 cells, claudin-2 overexpression protects against DSS-dependent cell death
Because of the preserved epithelial integrity and increased epithelial cell proliferation in DSS-challenged CL-2TG mice, we investigated a causal association of claudin-2 with epithelial restitution and protection from cell death during colitis. Polarized Caco-2 cells were exposed to increasing concentrations of DSS, and effects on cell viability and claudin-2 expression were determined. MTT assays demonstrated a decrease in cell viability of DSS-treated cells (Figure 5a). Notably, claudin-2 expression also decreased in a dose-dependent manner in DSS-treated cells, whereas E-cadherin and claudin-4 expression remained unaltered (Figure 5bi). Similar findings were observed for another CEC line, HT-29 (Figure 5bii).
In Caco-2 cells, claudin-2 overexpression protects against dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-dependent decrease in cell viability. (a) Effect of DSS treatment on cell viability. (bi,ii) Immunoblot analysis to determine expression of claudin-2, claudin-4, and E-cadherin in Caco-2 (i) or HT-29 (ii) cells exposed to different concentrations of DSS for 24 h. (ci) Immunoblot analysis demonstrating stable overexpression of an untagged claudin-2 or an HA-tagged claudin-2 cDNA construct in Caco-2 cells. (cii) Effect of claudin-2 expression on cell viability in DSS-treated Caco-2 cells. (di) Immunoblot analysis using total cell lysate from unchallenged control and Caco-2Cl-2HA cells. (dii) qRT–PCR analysis to determine Bcl-2 expression in colonic epithelial cells isolated from Cl-2TG mice and WT-littermates (n#4/group). (diii) Effect of DSS-treatment upon Bcl-2 expression in control and Caco-2Cl-2HA cells with or without pretreatment with LY-294002. (div) Effect of DSS treatment upon cell viability in control and Caco-2Cl-2HA cells with or without pretreatment with LY-294002. Data are presented as mean±s.e.m. from at least three independent experiments. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001.
To further determine whether claudin-2 expression can protect CECs from DSS-dependent cell death, we stably overexpressed CMV promoter-driven claudin-2 with (Caco-2Cl-2HA) or without (Caco-2Cl-2) a C-terminal HA-tag in Caco-2 cells and subjected the resultant cell lines to DSS treatment. As shown in Figure 5ci, endogenous claudin-2 expression sharply decreased, whereas exogenously expressed claudin-2 remained largely unaffected. Claudin-4 expression was also unaltered by claudin-2 overexpression or DSS treatment. MTT assays showed that claudin-2-overexpressing cells resisted the DSS-dependent decrease in cell viability (P<0.001; Figure 5cii). Notably, Caco-2Cl-2HA cells also demonstrated marked upregulation of Phospho-Akt and the cell survival protein Bcl-2 (vs. control cells; Figure 5di). The colonic epithelial cells from Cl-2TG mice similarly demonstrated increased Bcl-2 expression (Figure 5dii). DSS stimulation led to a further increase in Bcl-2 expression in Caco-2Cl-2HA cells, but LY-294002, a PI-3 kinase inhibitor, prevented this increase (Figure 5diii). Notably, LY-294002 treatment also inhibited the protection of Caco-2Cl-2HA cells from DSS-dependent death (Figure 5div). Taken together, our data supported a causal role of claudin-2 expression in protection against cell death of CECs treated with colitis-inducing agents.
Inflammation-associated gene expression and signaling is suppressed in DSS-treated Cl-2TG mice
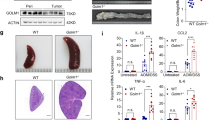
Disruption of the normal balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory immune responses is associated with mucosal inflammation. Notably, real-time RT–PCR analysis of colon mRNA expression showed increased expression of inflammatory proteins TNF-α, IFN- γ, and KC in DSS-treated WT mice but not in Cl-2TG mice compared with their respective controls (Figure 6ai–iii), thus supporting our microarray analysis (Supplementary Figure S5B). We further performed an extensive comparative analysis of colon tissue protein expression of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Results showed increased expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 along with TNF-α, IL-1α, IL-12(p40), and G-CSF, the Th1-related cytokine IFN-γ, IL-15, the Th17-associated cytokine IL-17, and the chemokines KC/CXCL1, IP-10/CXCL10, MCP-1/CCL2 and MIP-2 (P<0.001) in total colon lysates from DSS-treated vs. control WT mice and DSS-treated Cl-2TG mice (Figure 6bi–xiii).
Expression of inflammatory cytokines/chemokines is sharply down-regulated in DSS-treated Cl-2TG mice. Mice were subjected to DSS colitis as described in the legend to Figure 2. (a) Cytokine/chemokine levels as determined by quantitative real-time RT–PCR and (b) cytokine/chemokine levels as determined by Luminex analysis (N#5/group). Values are presented as mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
Importantly, IL-6 and TNF-α help induce NF-κB signaling, the key regulator of mucosal inflammation.14, 15 Therefore, we investigated whether suppressed NF-κB signaling underlies the resistance to colitis in Cl-2TG mice. Immunoblot analysis of RelA/p65 phosphorylation in colon lysates from mice subjected to DSS colitis revealed undetectable levels of phospho(p)-p65 in control WT and Cl-2TG mice, and a robust increase in p-p65 expression in DSS-treated WT but not Cl-2TG mice (P<0.001, Figure 7ai). Immunohistochemistry analysis further demonstrated intense nuclear p65 expression, predominantly in immune cells, in DSS-treated WT vs. Cl-2TG mice (Figure 7aii). IL-6 also regulates STAT3 signaling, which helps regulate mucosal inflammation and epithelial homeostasis.16, 17 Importantly, robust STAT3 expression was detected in samples obtained from all control and experimental groups. In contrast, we found minimal p-STAT3 expression in control samples, increased levels in DSS-treated WT mice (P<0.01, Figure 7bi), and suppressed levels in DSS-treated Cl-2TG mice. Immunohistochemistry using an anti-p-STAT3 antibody showed nuclear localization in epithelial cells and infiltrating immune cells (Figure 7bii). Taken together, our data suggested that immune activation in response to DSS-treatment was suppressed in Cl-2TG mice.
The dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced activation of NF-κB and STAT3-signaling is attenuated in Cl-2TG mice. Samples from mice subjected to DSS colitis were used. (ai) Immunoblot analysis using anti-phospho-p65, p65 antibodies and representative densitometric analyses and (aii) immunohistochemical analysis to determine cellular localization of p65 protein. (bi) Immunoblot analysis using anti-phospho-STAT3 and -STAT3 antibodies and representative densitometric analyses and (bii) immunohistochemical analysis to determine the tissue distribution and cellular localization of phospho-STAT3; n#3-6, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Bars=50 μm.
Colonic macrophages in Cl-2TG mice demonstrate inflammatory anergy
Our additional analysis further showed marked decreases in infiltrating F4/80+ cells in the colon of DSS-treated Cl-2TG vs. WT mice. Expression of iNOS by F4/80+ cells supported their proinflammatory M1-phenotype (Figure 8a). Importantly, resistance to colitis and immune tolerance/adaptation in mice harboring a leakier colon similar to Cl-2TG mice has been reported.18 Therefore, we asked whether this is also the case in Cl-2TG mice. Considering the primary role of macrophages in innate immune responses, we therefore analyzed whether immune responses of colonic macrophages in Cl-2TG mice are compromised. As claudin-2 overexpression in Cl-2TG mice was restricted to the gut epithelium, immune function of peritoneal macrophages was not expected to be affected, and therefore peritoneal macrophages isolated from the same animals were used as positive control (Supplementary Figure S6). The colonic and peritoneal macrophages from naive WT and Cl-2TG mice were then stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 1 μg ml−1) and IFN-γ (100 IU ml−1). As shown in Figure 8bi–ii, IL-6 and TNF-α mRNA expressions were upregulated significantly in activated peritoneal macrophages isolated from WT and Cl-2TG mice. Interestingly, however, expression of these mRNAs was upregulated only in the colonic macrophages from WT but not Cl-2TG mice. ELISA analysis demonstrated similar upregulation of inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, IL-1β, and KC, only in WT colonic macrophages (Figure 8biii). Thus, our data suggested inflammatory anergy among macrophages residing in the colonic submucosa of Cl-2TG mice.
Colonic macrophages in Cl-2TG mice exhibit inflammatory anergy. (a) Representative images demonstrating macrophage (F4/80) infiltration in the colonic mucosa in control and DSS-treated WT and Cl-2TG mice. F4/80+ cells were co-immunostained with an anti-iNOS antibody. (bi,ii) Colonic or peritoneal macrophages were isolated from naive WT and Cl-2TG mice and were subjected to immune activation using LPS and IFN- γ for 24 h. mRNA expression of TNF-α and IL-6 was determined using qRT–PCR. (biii) Supernatant from in vitro activated macrophages isolated from Cl-2TG and WT-mice was subjected to ELISA analysis using an antigen-specific antibody. Values are presented as mean±s.e.m. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Bars=50 μm.
The Treg-cell population and TGF-β synthesis are upregulated in Cl-2TG mice
On the basis of our data that macrophages residing in the colonic mucosa of Cl-2TG mice exhibit immune anergy, and because CL-2TG mice have increased mucosal permeability, we investigated the possibility that resistance to colitis induction in Cl-2TG mice was mediated in part by bacterial translocation and induction of adaptive immune tolerance. Indeed, PCR analysis, using genomic DNA from the colon of naive WT and Cl-2TG mice and primers based on highly conserved bacterial sequences, demonstrated a significant increase in bacteria in the colonic mucosa of Cl-2TG mice compared with WT mice (P<0.05; Figure 9a). Of note, it has been previously shown that regulatory CD4+Foxp3+ T cells are upregulated in mice harboring leaky gut, and that these cells help promote immune tolerance.18, 19 To examine similar responses in Cl-2TG mice, we immune-phenotyped leukocytes isolated from the lamina propria of Cl-2TG and WT mice. Notably, no major differences were observed in CD4+ cells between naive Cl-2TG and WT mice (5.47% vs. 5.68%, respectively; data not shown). In contrast, CD4+Foxp3+ cells were significantly increased in Cl-2TG vs. WT mice (P<0.03; Figure 9bi). Interestingly, however, the CD11b+CD11c− cell population was sharply decreased in the colon of Cl-2TG mice (P<0.001; Figure 9bii). Previous studies have shown that the immunoregulatory cytokine TGF-β protects from DSS colitis and induces immune tolerance by inhibiting IL-6/NF-κB signaling.20, 21, 22 Therefore, we determined whether increased TGF-β production underlies the observed immune suppression in Cl-2TG mice. Immunoblot analysis demonstrated an upward trend in TGF-β expression in control Cl-2TG vs. WT mice. Furthermore, DSS treatment led to a significant decrease in TGF-β levels in DSS-treated WT mice but not Cl-2TG mice, as compared with their respective controls (Figure 9ci). As immunoblot analysis represents total tissue expression, we further examined whether TGF-β synthesis differs between specific cell types in naive mice. For this purpose, we isolated E-cadherin+, F480+, and CD4+ cells from naive Cl-2TG and WT mice. Real-time RT–PCR using mRNA from these cell populations demonstrated a specific and significant increase in TGF-β expression in colonic epithelial cells of Cl-2TG vs. WT mice (Figure 9cii). Taken together, our data suggested that claudin-2-expression upregulates TGF-β synthesis in colonic epithelial cells, which, in turn, may help regulate immune tolerance and protection of Cl-2TG mice from experimental colitis.
Regulatory T cells and expression of the immunoregulatory cytokine TGF-β are significantly upregulated in the colon of naive Cl-2TG mice. Samples from unchallenged Cl-2TG mice and WT littermates were used. (a) Genomic DNA isolated from the colon was subjected to PCR using primers based on universal bacterial sequence. (bi,ii) Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis using an antigen-specific antibody was performed using cells isolated from the lamina propria of naive Cl-2TG mice and WT littermates. (ci) Immunoblot analysis to determine TGF-β expression and representative densitometric analysis. Total tissue lysate from control and dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-treated mice was used. (cii) TGF-β expression analysis using mRNA isolated from specific cell populations isolated from the colon of unchallenged Cl-2TG mice and WT-littermates. n#3-6, *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
Discussion
Claudin-2 is one of the highly regulated claudin family members, as its expression is regulated by immune regulators, such as IL-2, TNF-α, IL-13, IL-15, and IL-17, and regulators of growth factor signaling, including EGF-, HGF-, ERK1/2- and PI-3-signaling, thus highlighting its biological importance.4, 13, 23, 24, 25 In the present studies, we have demonstrated a critical role of claudin-2 in regulating colonic epithelial homeostasis, immune responses, and mucosal inflammation. Our finding that claudin-2 overexpression leads to a significant decrease in transepithelial resistance while increasing the paracellular Na+ permeability of the colonic epithelium supports a key role of claudin-2 in regulating colonic epithelial barrier function and is supported by data from claudin-2-deficient mice.26, 27
Claudin-2 expression led to increased colonocyte proliferation and increased colon and crypt lengths, suggesting an additional role for claudin-2 beside static cell–cell adhesion. Decreased apoptosis and increased proliferation in DSS-challenged Cl-2TG vs. WT mice further supported a role of claudin-2 in the regulation of colonic epithelial cell homeostasis and its contribution to protection against DSS-colitis. These changes were accompanied by corresponding changes in the expression of genes regulating proliferation and cell cycle progression and genes encoding intestinal stem cell markers. As noted previously, among claudins, claudin-2 expression is uniquely restricted to the proliferative zone at the crypt base.13, 28, 29 As already mentioned, others and we have previously reported a role of Wnt/β-catenin, EGFR-ERK1/2, and PI-3 kinase signaling in the regulation of colonic claudin-2 expression.12, 13, 30 Notably, similar to claudin-2 overexpression, EGF or TGF-α administration to mice protects from DSS colitis.31, 32 Further, proliferative changes in intestinal epithelial cells in response to manipulation of cell adhesion proteins, cingulin and symplekin, were associated with changes in claudin-2 expression.33, 34 In addition, intestinal claudin-2 expression is required for efficient paracellular Na+-transport and intestinal nutrient absorption, as shown in mice lacking claudin-2 and claudin-15.35 Consistent with this conclusion, EGF-dependent potentiation of colonic Na+-transport, despite decreased sodium channel expression, protects against DSS colitis.36 Furthermore, IL-13 and IL-17, cytokines associated with adaptive immunity, upregulate claudin-2 expression in colonic epithelial cells.4, 25 Thus, epithelial restitution might be a critical component of the protection of Cl-2TG mice from mucosal inflammation. Our data that claudin-2-overexpressing Caco-2 cells are protected from DSS-dependent decreases in cell viability in a PI-3Kinase-Bcl2-dependent manner strongly support this possibility. Of note, a protective role of PI-3 kinase and/or Bcl-2 in colitis has been previously reported.37 Our data from Caco-2 cells also excludes the possibility that the observed epithelial integrity in DSS-treated Cl-2TG mice may simply be due to decreased exposure to DSS.
Our data also suggest a role of immune tolerance in the protection of Cl-2TG mice from experimental colitis. Notably, as the sole physical separation between the gut microbiota and the immune system, the mucosal epithelium is under constant challenge to balance the need of the immune system to mount efficient immune responses against pathogens while maintaining tolerance toward commensal microorganisms. Mucosal epithelial permeability associates with and is thought to augment mucosal inflammation. However, recent studies have demonstrated that sustained increases in mucosal permeability preceding an inflammatory insult, either using pharmacological means or genetic manipulation, instead protects from colitis.18, 38 Our findings that Cl-2TG mice are protected from colitis despite increased mucosal permeability is consistent with the above reports. Furthermore, a recent report that claudin-2 knockout (KO) mice suffer from severe colitis when subjected to DSS colitis strengthens our findings.39 Yet another commonality among mice demonstrating increased mucosal permeability is the immune tolerance/adaptation.18, 19 Importantly, our immune-phenotyping analyses confirmed significant suppression of DSS-induced proinflammatory molecules in DSS-treated Cl-2TG vs. WT mice. The significant increases in regulatory CD4+Foxp3+ cells in the colonic mucosa of unchallenged Cl-2TG mice and decreases in immune cell infiltration in the colons of DSS-challenged Cl-2TG mice further suggest that immune adaptation potentially helps protect Cl-2TG mice from DSS colitis. Of note, significant decreases in IL-6 expression, NF-κB activation, and STAT3 signaling in Cl-2TG mice support potential desensitization of IL-6/NF-κB/STAT3 signaling in these animals. Consistent with this possibility, TGF-β expression was increased in the colon of naive Cl-2TG mice, whereas macrophages isolated from the lamina propria of these mice exhibited inflammatory anergy. Importantly, TGF-β induces macrophage immune anergy as well as regulatory T-cell differentiation.19, 20, 40 Thus, our findings suggest a complex and context-dependent effect of claudin-2 expression on mucosal homeostasis. We postulate that the constitutively increased epithelial permeability in Cl-2TG mice facilitates the interaction of mucosal immune elements and luminal antigens to promote tolerance/adaptation. Our data showing increased bacterial translocation in Cl-2TG mice supports this notion. Notably, a recent study has suggested that claudin-2 assists in the uptake of mucosal antigens.41 Furthermore, we cannot rule out the possibility that modulation of intraepithelial lymphocytes contributes to colitis protection in CL-2TG mice. Of note, Occludin, a tight junction protein, helps regulate the migration of γδ intraepithelial lymphocytes, which protect from DSS colitis.42 Further studies will be needed to determine the cellular and molecular details underlying claudin-2-dependent regulation of immune anergy.
In summary, we here report a critical role of claudin-2 in the regulation of colonic epithelial homeostasis and barrier function, which in turn regulates mucosal immune activation and inflammation. The key finding of our study is that claudin-2 helps regulate colonocyte proliferation/integrity and increases colonic epithelial permeability to potentially induce immune tolerance/adaptation rather than increased sensitization, as has been generally assumed. This paradoxical finding gains support from similar results obtained by other groups where increased mucosal permeability leads to immune tolerance and protection from colitis.18, 38 The contrasting disease outcome in claudin-2 KO mice subjected to DSS colitis further supports our findings. These findings emphasize a dynamic rather than static role of the epithelial barrier in regulating antigen–immune cell communication and mucosal inflammation. Taken together, we here report a novel and important role of claudin-2 in the regulation of colonic epithelial and immune homeostasis. We predict our findings to affect current understanding of the role of epithelial permeability in general and of claudin-2, in particular, in the regulation of intestinal homeostasis and immune regulation and to open potential therapeutic opportunities.
Materials and Methods
Cell culture, transfection, and reagents. The procurement and culture conditions for Caco-2 and HT-29 cells have been previously described.13 All cell culture reagents were from Invitrogen (San Francisco, CA). A pcDNA-4 expression plasmid (Invitrogen) containing claudin-2 coding sequences with or without C-terminal HA-tag was used for overexpression. Caco-2 cells overexpressing untagged or HA-tagged claudin-2 cDNA were selected using Zeocin (100 μg ml−1). All antibodies and chemicals used in this study are described in Supplementary Table 1.
Generation of Villin-Claudin-2 transgenic (Cl-2TG) mice. A mammalian expression construct with the Villin-promoter (a gift from Dr Sylvie Robine, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, France) was used to insert the human claudin-2 coding sequence downstream of the Villin-promoter. Extensive sequencing confirmed the correct sequence and orientation of the transgene. Transgenic mice were generated at the Vanderbilt Mouse Genomic Core facility using the B6D2F1/J-strain of mice. Integration of the transgene into the host chromosome was confirmed by PCR amplification. Transgenic animals were backcrossed with C57BL/6 WT mice for at least 10 generations to generate the Cl-2TG mice on the C57BL/6 strain background.
Ethics Statement. Throughout the study, recommendations in the Guideline for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health were followed. The animal use protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Vanderbilt University (Protocol # M/09/244).
Transepithelial Resistance and paracellular Na+ permeability. Distal colon mucosal sheets were collected and mounted in the dual channel Ussing Chamber system (Physiologic Instrument, San Diego, CA) using the manufacturer’s guidelines. The NaCl dilution potential was measured as described previously.27 For analysis of transepithelial conductance, each chamber was filled with 5.0 ml of buffer solution (150 mM NaCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgCl2, 10 mM mannitol, 10 mM glucose, and 10 mM Tris-HEPES, pH 7.4). Throughout the experimental procedure, chamber temperature was maintained at 37 °C, and 100% O2 was bubbled through the solution. The transmucosal potential was measured using 3 M KCl agar bridges connected to the electrodes, using a voltage-clamping device. To estimate the NaCl dilution potential, the apical solution was replaced with one containing 75 mM NaCl instead of 150 mM NaCl (osmolarity was maintained with mannitol). The paracellular Na+ permeability was calculated using the Kimizuka-Koketsu equation.
Colon permeability measurements. To determine the potential changes in colonic permeability, FITC-dextran (4 kDa) was used, as described.43 Presence of the dye in the blood was assessed in samples collected before (0 h) and 30 min after FITC-dextran administration. Colons were removed and processed to visualize the FITC-dextran in the colonic epithelium using a Carl-Zeiss fluorescent microscope.
Determination of FITC-dextran permeability by using the Ussing chamber. To complement the in vivo permeability assay, we determined FITC-dextran permeability using the Ussing chamber system. FITC-dextran (4-kDa) was added to the mucosal side to achieve a final concentration of 0.02 mM, and the presence of dye in the serosal compartment was determined using samples collected at different time points. Fluorescence in collected samples was determined using a microplate fluorescence reader (Synergy-2; Bio-tek, Winooski, VT; excitation wavelength of 485 nm and emission wavelength of 528 nm).
Induction of mouse colitis and collection of colonic tissue. Male mice (8–10 weeks old) were provided regular drinking water (control) or 4% (w/v) DSS (MW=36–50 kDa, MP Biomedicals, Solon, OH, USA), as described with minor modifications.44 For chronic colitis, mice (8–10 weeks old) were provided DSS (2.5% w/v) in the drinking water for 5 days followed by regular drinking water for 16 days. Mice underwent three consecutive treatment cycles before killing.44 The DSS/water consumption was monitored, and mice were weighed daily and visually inspected for diarrhea and/or rectal bleeding. Animals were killed by CO2 narcosis on study termination. Colons were removed and assessed for weight, length, and histology. The disease activity index was evaluated by combining scores of (i) weight loss, (ii) stool consistency, and (iii) bleeding (divided by 3). Each score was evaluated as follows: change in weight (0: <1%, 1: 1–5%, 2: 5–10%, 4: >15%); stool blood (0: negative, 2: positive or 4: gross bleeding); and stool consistency (0: normal, 2: loose stools, 4: diarrhea), as previously described.45 Body weight loss was calculated as percent difference between the original body weight and the actual body weight on a given day. Histological slides were evaluated independently by a University GI-pathologist (M.K.W.) in a blinded manner. The cumulative injury score was calculated according to Supplementary Table 2.
FACS analysis to determine BrdU or cleaved caspase-3-positive colonic epithelial cells. BrdU (5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine) was injected intraperitoneally (12.0 mg g−1 of body weight) 2 h before killing the mice. Colonic epithelial cells were isolated as described above and were fixed with 0.1% paraformaldehyde. These cells were then incubated with an anti-pan cytokeratin antibody conjugated with phycoerythrin (PE; dilution 1:50), anti-active caspase-3 antibody conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC; dilution 1:50) and anti-BrdU antibodies conjugated with allophycocyanin (APC; dilution 1:100) for 30 min at 4 °C. Cells were acquired using an LSR II flow cytometer (BD Biosciences), and pan cytokeratin-positive cells were analyzed for levels of active caspase-3 and BrdU by Flowjo (TreeStar, Ashland, OR).
Luminex multiple cytokine assay. After mice were killed, colons were removed and snap-frozen or processed to prepare total protein lysates. These lysates were then used to determine multiple cytokines using the MILLIPLEX MAP Mouse Cytokine/Chemokine Magnetic Bead Panel (Millipore, Billerica, MA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions using a Luminex FLEXMAP 3D instrument.
Macrophage isolation and activation. Colonic and peritoneal macrophages were isolated using the biotin-labeled anti-mouse F4/80 antibody (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) and streptavidin magnetic beads (Invitrogen), as described.46 For activation, the F4/80+ cells were incubated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 1 μg ml−1) and IFN-γ (100 IU ml−1) in complete RPMI 1640 medium.
Genomic DNA extraction and determination of bacterial translocation. Genomic DNA from colon tissue was extracted by tissue lysis buffer (50 mM Tris–HCl-pH 8.0; 100 mM EDTA; 100 mM NaCl; 1% SDS; 0.4 mg ml−1 proteinase K), and bacterial translocation in CL-2TG mice was evaluated with real-time PCR. Universal primers, specific for the conserved regions of the bacterial 16S2 rDNA gene, were used (forward, 5′-TCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAGT-3′; reverse, 5′-GGACTACCAGGGTATCTAATCCTGTT-3′). For the quantification of 16 S rDNA in colonic tissues, a pair of primers specific to the mouse Selp gene (forward, 5′-ATGATTAGCAAATTCTAGCTCCTGTTT-3′; reverse, 5′-TAGGTCTCTTAGGATCTCCCTTCAAT-3′) was used in a separate reaction as the endogenous control to normalize the DNA loading between samples.47
MTT assay. The CellTiter assay (MTT assay; Promega, Madison, WI) was conducted as described previously.13 In brief, 20,000 cells were plated in 96-well plates. Twenty-four hours post-plating, cells were exposed to DSS in regular culture medium for the desired duration. The CellTiter reagent was added 3 h before collecting samples at 24 h post-DSS treatment.
RNA isolation and qRT–PCR analysis. RNA was extracted from tissue samples using the RNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA). Reverse transcription was performed using iScript cDNA synthesis kit (Bio-Rad). The real-time PCR reactions were performed with 20 ng of cDNA per reaction and 2 × iQTM SYBR Green Supermix (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA). Primer sequences are described in Supplementary Table 3.
Immunoblot analysis. This was performed as previously described.13 Signals were detected using an enhanced chemiluminescence detection kit (Amersham Biosciences, Piscataway, NJ). Equal protein loading was assessed by re-probing with an anti-β actin antibody (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO) after stripping the respective membrane.
Immunostaining. Immunofluorescent and/or immunohistochemical staining were performed as described previously.13 Imaging was performed at the Vanderbilt University Medical Center Cell Imaging Core.
Statistical analysis. Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test to determine significance in two group comparisons. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test was employed where analysis involved more than two groups. Results were plotted using GraphPad Prism 5.0 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA). A P value <0.05 was defined as statistically significant. All data presented are representative of at least three repeat experiments and are presented as mean±s.e.m.
References
Hollander, D. Intestinal permeability, leaky gut, and intestinal disorders. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 1, 410–416 (1999).
Arrieta, M.C., Madsen, K, Doyle, J & Meddings, J. Reducing small intestinal permeability attenuates colitis in the IL10 gene-deficient mouse. Gut 58, 41–48 (2009).
Tsukita, S & Furuse, M. Occludin and claudins in tight-junction strands: leading or supporting players? Trends Cell Biol. 9, 268–273 (1999).
Heller, F. et al. Interleukin-13 is the key effector Th2 cytokine in ulcerative colitis that affects epithelial tight junctions, apoptosis, and cell restitution. Gastroenterology 129, 550–564 (2005).
Zeissig, S. et al. Changes in expression and distribution of claudin 2, 5 and 8 lead to discontinuous tight junctions and barrier dysfunction in active Crohn's disease. Gut 56, 61–72 (2007).
Ridyard, A.E., Brown, J.K., Rhind, S.M., Else, R.W., Simpson, J.W. & Miller, H.R. Apical junction complex protein expression in the canine colon: differential expression of claudin-2 in the colonic mucosa in dogs with idiopathic colitis. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 55, 1049–1058 (2007).
Weber, C.R., Nalle, S.C., Tretiakova, M, Rubin, D.T. & Turner, J.R. Claudin-1 and claudin-2 expression is elevated in inflammatory bowel disease and may contribute to early neoplastic transformation. Lab. Investig. 88, 1110–1120 (2008).
Furuse, M, Furuse, K, Sasaki, H & Tsukita, S. Conversion of zonulae occludentes from tight to leaky strand type by introducing claudin-2 into Madin-Darby canine kidney I cells. J Cell Biol. 153, 263–272 (2001).
Enck, A.H., Berger, U.V. & Yu, A.S. Claudin-2 is selectively expressed in proximal nephron in mouse kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 281, F966–F974 (2001).
Yu, A.S., Cheng, M.H. & Coalson, R.D. Calcium inhibits paracellular sodium conductance through claudin-2 by competitive binding. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 37060–37069 (2010).
Fujita, H. et al. Tight junction proteins claudin-2 and -12 are critical for vitamin D-dependent Ca2+ absorption between enterocytes. Mol. Biol. Cell 19, 1912–1921 (2008).
Mankertz, J, Hillenbrand, B, Tavalali, S, Huber, O, Fromm, M & Schulzke, J.D. Functional crosstalk between Wnt signaling and Cdx-related transcriptional activation in the regulation of the claudin-2 promoter activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 314, 1001–1007 (2004).
Dhawan, P. et al. Claudin-2 expression increases tumorigenicity of colon cancer cells: role of epidermal growth factor receptor activation. Oncogene 30, 3234–3247 (2011).
Claud, E.C., Zhang, X, Petrof, E.O. & Sun, J. Developmentally regulated tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced nuclear factor-kappaB activation in intestinal epithelium. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 292, G1411–G1419 (2007).
Wang, L, Walia, B, Evans, J & Gewirtz, A.T. Merlin D, Sitaraman SV. IL-6 induces NF-kappa B activation in the intestinal epithelia. J Immunol. 171, 3194–3201 (2003).
Han, X, Sosnowska, D, Bonkowski, E.L. & Denson, L.A. Growth hormone inhibits signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation and reduces disease activity in murine colitis. Gastroenterology 129, 185–203 (2005).
Atreya, R & Neurath, M.F. Signaling molecules: the pathogenic role of the IL-6/STAT-3 trans signaling pathway in intestinal inflammation and in colonic cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 9, 369–374 (2008).
Boirivant, M. et al. A transient breach in the epithelial barrier leads to regulatory T-cell generation and resistance to experimental colitis. Gastroenterology 135, 1612–1623, e1615 (2008).
Khounlotham, M, Kim, W, Peatman, E, Nava, P & Medina-Contreras, O. Addis C et al. Compromised intestinal epithelial barrier induces adaptive immune compensation that protects from colitis. Immunity 37, 563–573 (2012).
Smythies, L.E. et al. Inflammation anergy in human intestinal macrophages is due to Smad-induced IkappaBalpha expression and NF-kappaB inactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 19593–19604 (2010).
Bassaganya-Riera, J. et al. Activation of PPAR gamma and delta by conjugated linoleic acid mediates protection from experimental inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 127, 777–791 (2004).
Marafini, I, Zorzi, F, Codazza, S, Pallone, F & Monteleone, G. TGF-beta signaling manipulation as potential therapy for IBD. Curr. Drug Targets 14, 1400–1404 (2013).
Nishiyama, R. et al. Interleukin-2 receptor beta subunit-dependent and -independent regulation of intestinal epithelial tight junctions. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 35571–35580 (2001).
Amasheh, M. et al. TNFalpha-induced and berberine-antagonized tight junction barrier impairment via tyrosine kinase, Akt and NFkappaB signaling. J. Cell Sci. 123 (Pt 23), 4145–4155 (2010).
Kinugasa, T, Sakaguchi, T, Gu, X & Reinecker, H.C. Claudins regulate the intestinal barrier in response to immune mediators. Gastroenterology 118, 1001–1011 (2000).
Muto, S. et al. Claudin-2-deficient mice are defective in the leaky and cation-selective paracellular permeability properties of renal proximal tubules. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. US A 107, 8011–8016 (2010).
Tamura, A. et al. Loss of claudin-15, but not claudin-2, causes Na+ deficiency and glucose malabsorption in mouse small intestine. Gastroenterology 140, 913–923 (2011).
Holmes, J.L., Van Itallie, C.M., Rasmussen, J.E. & Anderson, J.M. Claudin profiling in the mouse during postnatal intestinal development and along the gastrointestinal tract reveals complex expression patterns. Gene Exp. Patterns 6, 581–588 (2006).
Humphries, A & Wright, N.A. Colonic crypt organization and tumorigenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 8, 415–424 (2008).
Prasad, S. et al. Inflammatory processes have differential effects on claudins 2, 3 and 4 in colonic epithelial cells. Lab. Investig. 85, 1139–1162 (2005).
Egger, B. et al. Mice lacking transforming growth factor alpha have an increased susceptibility to dextran sulfate-induced colitis. Gastroenterology 113, 825–832 (1997).
Krishnan, K, Arnone, B & Buchman, A. Intestinal growth factors: potential use in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease and their role in mucosal healing. Inflamm Bowel Dis.eases 17, 410–422 (2011).
Guillemot, L & Citi, S. Cingulin regulates claudin-2 expression and cell proliferation through the small GTPase RhoA. Mol. Biol. Cell 17, 3569–3577 (2006).
Buchert, M. et al. Symplekin promotes tumorigenicity by up-regulating claudin-2 expression. Proc. Natl Acad Sci. USA 107, 2628–2633 (2010).
Wada, M, Tamura, A, Takahashi, N & Tsukita, S. Loss of Claudins 2 and 15 from mice causes defects in paracellular Na(+) flow and nutrient transport in gut and leads to death from malnutrition. Gastroenterology 144, 369–380 (2012).
McCole, D.F., Rogler, G, Varki, N & Barrett, K.E. Epidermal growth factor partially restores colonic ion transport responses in mouse models of chronic colitis. Gastroenterology 129, 591–608 (2005).
Huang, X.L. et al. PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is involved in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis. Inflamm. Res. 60, 727–734 (2011).
Laukoetter, M.G. et al. JAM-A regulates permeability and inflammation in the intestine in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 204, 3067–3076 (2007).
Nishida, M, Yoshida, M, Nishiumi, S, Furuse, M & Azuma, T. Claudin-2 regulates colorectal inflammation via myosin light chain kinase-dependent signaling. Dig. Dis. Sci. 58, 1546–1559 (2013).
Smythies, L.E. et al. Human intestinal macrophages display profound inflammatory anergy despite avid phagocytic and bacteriocidal activity. J. Clin. Investig. 115, 66–75 (2005).
Liu, X. et al. Microbial products induce claudin-2 to compromise gut epithelial barrier function. PloS ONE 8, e68547 (2013).
Edelblum, K.L. et al. Dynamic migration of gammadelta intraepithelial lymphocytes requires occludin. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, 7097–7102 (2012).
Garrett, W.S. et al. Communicable ulcerative colitis induced by T-bet deficiency in the innate immune system. Cell 131, 33–45 (2007).
Wirtz, S, Neufert, C, Weigmann, B & Neurath, M.F. Chemically induced mouse models of intestinal inflammation. Nat. Protocols 2, 541–546 (2007).
Cooper, H.S., Murthy, S.N., Shah, R.S. & Sedergran, D.J. Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium experimental murine colitis. Lab. Investig. 69, 238–249 (1993).
Lewis, N.D. et al. Immune evasion by Helicobacter pylori is mediated by induction of macrophage arginase II. J. Immunol. 186, 3632–3641 (2011).
Fu, J. et al. Loss of intestinal core 1-derived O-glycans causes spontaneous colitis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 121, 1657–1666 (2011).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by DK088902 (A.B.S.), CA124977 (P.D.), VA-merit BX002086 (P.D.), the Vanderbilt DDRC P30DK058404, the VICC P30CA68485, and StarBRITE funds (#VR730).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL is linked to the online version of the paper
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, R., Chaturvedi, R., Olivares-Villagómez, D. et al. Targeted colonic claudin-2 expression renders resistance to epithelial injury, induces immune suppression, and protects from colitis. Mucosal Immunol 7, 1340–1353 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/mi.2014.21
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mi.2014.21
This article is cited by
-
Akkermansia muciniphila and its membrane protein ameliorates intestinal inflammatory stress and promotes epithelial wound healing via CREBH and miR-143/145
Journal of Biomedical Science (2023)
-
Paracellular permeability and tight junction regulation in gut health and disease
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (2023)
-
Claudin-23 reshapes epithelial tight junction architecture to regulate barrier function
Nature Communications (2023)
-
5-Aminosalicylic acid alters the gut microbiota and altered microbiota transmitted vertically to offspring have protective effects against colitis
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist GTS-21 attenuates DSS-induced intestinal colitis by improving intestinal mucosal barrier function
Molecular Medicine (2022)