Abstract
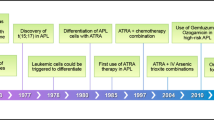
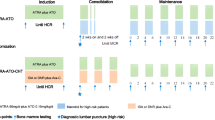
Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) is a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia characterized by t(15;17) and a life-threatening coagulopathy. Once highly fatal, nowadays standard treatment approaches with all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) along with chemotherapy allows curing up to 80–85% of cases. In the past decade, arsenic trioxide used alone or in combination with ATRA has demonstrated high efficacy in APL, and is currently regarded as the gold standard for treatment of relapsed cases. Chemotherapy-free approaches based on the combination of arsenic trioxide and ATRA are currently being tested against standard ATRA and chemotherapy in randomized clinical trials for frontline therapy of APL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
We are sorry, but there is no personal subscription option available for your country.
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernard J . History of promyelocytic leukaemia. Leukemia 1994; 8 (Suppl 2): S1–S5.
Wang ZY, Chen Z . Acute promyelocytic leukemia: from highly fatal to highly curable. Blood 2008; 111: 2505–2515.
Sanz MA, Montesinos P, Vellenga E, Rayón C, de la Serna J, Parody R et al. Risk-adapted treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with all-trans retinoic acid and anthracycline monochemotherapy: long-term outcome of the LPA 99 multicenter study by the PETHEMA Group. Blood 2008; 112: 3130–3134.
Lo-Coco F, Avvisati G, Vignetti M, Breccia M, Gallo E, Rambaldi A, et al., Italian GIMEMA Cooperative Group. Front-line treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with AIDA induction followed by risk-adapted consolidation for adults younger than 61 years: results of the AIDA-2000 trial of the GIMEMA Group. Blood 2010; 116: 3171–3179.
Zhang P, Wang SY, Hu LH . Arsenic trioxide treated 72 cases of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Chin J Hematol 1996; 17: 58–62.
Shen ZX, Shi ZZ, Fang J, Gu BW, Li JM, Zhu YM et al. All-trans retinoic acid/As2O3 combination yields a high quality remission and survival in newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 5328–5335.
Estey E, Garcia-Manero G, Ferrajoli A, Faderl S, Verstovsek S, Jones D et al. Use of all-trans retinoic acid plus arsenic trioxide as an alternative to chemotherapy in untreated acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood 2006; 107: 3469–3473.
Sanz MA, Lo-Coco F . Modern approaches to treating acute promyelocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 495–503.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
FL-C received speaker's honoraria from Cephalon. LC declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This article was published as part of a supplement that was supported by Novartis, MSD Italia, Roche, Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi, Gilead, Adienne, Italfarmaco, Pierre Fabre Pharmaceuticals with an unrestricted educational contribution to AREO—Associazione Ricerche Emato-Oncologiche (Genoa) and AMS—Associazione Malattie del Sangue (Milan) for the purpose of advancing research in acute and chronic leukemia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lo-Coco, F., Cicconi, L. Novel strategies in treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Leukemia Suppl 1 (Suppl 2), S18–S19 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/leusup.2012.12
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leusup.2012.12