Abstract
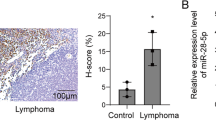
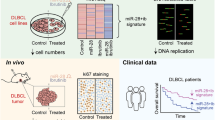
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) is frequently altered in DLBCL and inhibition of HDAC6 has potent anti-tumor effects in vitro and in vivo. We profiled miRNAs that altered in the HDAC6 knockdown DLBCL cells with NanoString nCounter assay and identified microRNA-27b (miR-27b) as the most significantly increased miRNA. We validated decreased expression of miR-27b in DLBCL tissues, and we found that low expression of miR-27b was associated with poor overall survival of patients with DLBCL. In addition, forced expression of miR-27b suppressed DLBCL cell viability and proliferation in vitro, and inhibited tumor growth in vivo. Mechanistically, Rel A/p65 is found to negatively regulate miR-27b expression, and its acetylation and block of nuclear translocalization caused by HDAC6 inhibition significantly elevates miR-27b expression. Furthermore, miR-27b targets MET and thus represses the MET/PI3K/AKT pathway. These findings highlight an important role of miR-27b in the development of DLBCL and uncover a HDAC6-Rel A/p65-miR-27b-MET signaling pathway. Elevating miR-27b through HDAC6 inhibition would be a promising strategy for DLBCL treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campo E, Swerdlow SH, Harris NL, Pileri S, Stein H, Jaffe ES . The 2008 WHO classification of lymphoid neoplasms and beyond: evolving concepts and practical applications. Blood 2011; 117: 5019–5032.
Lossos IS, Morgensztern D . Prognostic biomarkers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 995–1007.
Olsen EA, Kim YH, Kuzel TM, Pacheco TR, Foss FM, Parker S et al. Phase IIb multicenter trial of vorinostat in patients with persistent, progressive, or treatment refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 3109–3115.
Piekarz RL, Frye R, Turner M, Wright JJ, Allen SL, Kirschbaum MH et al. Phase II multi-institutional trial of the histone deacetylase inhibitor romidepsin as monotherapy for patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 5410–5417.
McDermott J, Jimeno A . Belinostat for the treatment of peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Drugs Today 2014; 50: 337–345.
Gloghini A, Buglio D, Khaskhely NM, Georgakis G, Orlowski RZ, Neelapu SS et al. Expression of histone deacetylases in lymphoma: implication for the development of selective inhibitors. Br J Haematol 2009; 147: 515–525.
Marquard L, Poulsen CB, Gjerdrum LM, de Nully Brown P, Christensen IJ, Jensen PB et al. Histone deacetylase 1, 2, 6 and acetylated histone H4 in B- and T-cell lymphomas. Histopathology 2009; 54: 688–698.
Santo L, Hideshima T, Kung AL, Tseng JC, Tamang D, Yang M et al. Preclinical activity, pharmacodynamic, and pharmacokinetic properties of a selective HDAC6 inhibitor, ACY-1215, in combination with bortezomib in multiple myeloma. Blood 2012; 119: 2579–2589.
Mishima Y, Santo L, Eda H, Cirstea D, Nemani N, Yee AJ et al. Recolinostat (ACY-1215) induced inhibition of aggresome formation accelerates carfilzomib-induced multiple myeloma cell death. Br J Heamatol 2015; 169: 423–434.
Amengual JE, Johannet P, Lombardo M, Zullo K, Hoehn D, Bhagat G et al. Dual targeting of protein degradation pathways with the selective HDAC6 inhibitor ACY-1215 and Bortezomib is synergistic in lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 2015; 21: 4663–4675.
Dasmahapatra G, Patel H, Friedberg J, Quayle SN, Jones SS, Grant S . in vitro and in vivo interactions between the HDAC6 inhibitor ricolinostat (ACY1215) and the irreversible proteasome inhibitor carfilzomib in non-Hodgkin lymphoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther 2014; 13: 2886–2897.
Bartel DP . MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004; 116: 281–297.
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N . Mechanisms of posttranscriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet 2008; 9: 102–114.
Wang S, Huang J, Lyu H, Lee CK, Tan J, Wang J et al. Functional cooperation of miR-125a, miR-125b, and miR-205 in entinostat-induced downregulation of erbB2/erbB3 and apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 2013; 4: e556.
Scott GK, Mattie MD, Berger CE, Benz SC, Benz CC . Rapid alteration of microRNA levels by histone deacetylase inhibition. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 1277–1281.
Li C, Zhou Y, Loberg A, Tahara SM, Malik P, Kalra VK . Activated transcription factor 3 in association with histone deacetylase 6 negatively regulates microRNA 199a2 transcription by chromatin remodeling and reduces endothelin-1 expression. Mol Cell Biol 2016; 36: 2838–2854.
Wang JH, Shih KS, Wu YW, Wang AW, Yang CR . Histone deacetylase inhibitors increase microRNA-146a expression and enhance negative regulation of interleukin-1βsignaling in osteoarthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2013; 21: 1987–1996.
Matsuyama R, Okuzaki D, Okada M, Oneyama C . microRNA-27b suppresses tumor progression by regulating ARFGEF1 and focal adhesion signaling. Cancer Sci 2016; 107: 28–35.
Tao J, Zhi X, Zhang X, Fu M, Huang H, Fan Y et al. miR-27b-3p suppresses cell proliferation through targeting receptor tyrosine kinase like orphan receptor 1 in gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2015; 34: 1–13.
Takahashi R-U, Miyazaki H, Takeshita F, Yamamoto Y, Minoura K, Ono M et al. Loss of microRNA-27b contributes to breast cancer stem cell generation by activating ENPP1. Nat Commun 2015; 6: 7318.
Fukumoto I, Koshizuka K, Hanazawa T, Kikkawa N, Matsushita R, Kurozumi A et al. The tumor-suppressive microRNA-23b/27b cluster regulates the MET oncogene in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol 2016; 49: 1119–1129.
Geng Y, Lu X, Wu X, Xue L, Wang X, Xu J . microRNA-27b suppresses Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric tumorigenesis through negatively regulating Frizzled 7. Oncol Rep 2016; 35: 2441–2450.
He S, Zhang J, Lin J, Zhang C, Sun S . Expression and function of microRNA-27b in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med Rep 2016; 13: 2801–2808.
Sun XF, Sun JP, Hou HT, Li K, Liu X, Ge QX . microRNA-27b exerts an oncogenic function by targeting Fbxw7 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol 2016; 37: 15325–15332.
Cai Y, Cui W, Chen W, Wei P, Chi YY, Zhang P et al. The effects of a histone deacetylase inhibitor on biological behavior of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell lines and insights into the underlying mechanisms. Cancer Cell Int 2013; 13: 57.
Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Gascoyne RD, Delabie J, Ott G et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 2004; 103: 275–282.
Sinha S, Singh RK, Alam N, Roy A, Roychoudhury S, Panda CK et al. Alterations in candidate genes PHF2, FANCC, PTCH1 and XPA at chromosomal 9q22.3 region: pathological significance in early- and late-onset breast carcinoma. Mol Cancer 2008; 7: 84.
Odqvist L, Montes-Moreno S, Sanchez-Pacheco RE, Young KH, Esperanza Martin-Sanchez, Laura Cereceda et al. NFκB expression is a feature of both activated B-cell-like and germinal center B-cell-like subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Mod Pathol 2014; 27: 1331–1337.
Campbell KJ, Rocha S, Perkins ND . Active repression of antiapoptotic gene expression by Rel A (p65) NF-kappa B. Mol Cell 2004; 13: 853–865.
Li ZY, Li QZ, Chen L, Chen BD, Wang B, Zhang XJ et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor RGFP109 overcomes temozolomide resistance by blocking NF-κB-dependent transcription in glioblastoma cell lines. Neurochem Res 2016; 41: 3192–3205.
Mabb AM, SMiyamoto S . SUMO and NF-kappaB ties. Cell Mol Life Sci 2007; 64: 1979–1996.
Chen LF, Mu Y, Greene WC . Acetylation of RelA at discrete sites regulates distinct nuclear functions of NF-kappaB. EMBO J 2002; 21: 6539–6548.
Kiernan R, Bres V, Ng RW, Coudart MP, EI Messaoudi S, Sardet C et al. Postactivation turn-off of NF-kappa B-dependent transcription is regulated by acetylation of p65. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 2758–2766.
Bolden JE, Peart MJ, Johnstone RW . Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2006; 5: 769–784.
Lim EL, Trinh DL, Scott DW, Chu A, Krzywinski M, Zhao Y et al. Comprehensive miRNA sequence analysis reveals survival differences in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. Genome Biol 2015; 16: 18.
Zhang Z, Cao Y, Zhao W, Guo L, Liu W . HDAC6 serves as a biomarker for the prognosis of patients with renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark 2016; 19: 169–175.
Saji S, Kawakami M, Hayashi S-I, Yoshida N, Hirose M, Horiguchi S et al. Significance of HDAC6 regulation via estrogen signaling for cell motility and prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Oncogene 2005; 24: 4531–4539.
Ding N, Ping L, Feng L, Zheng X, Song Y, Zhu J . Histone deacetylase 6 activity is critical for the metastasis of Burkitt’s lymphoma cells. Cancer Cell Int 2014; 14: 139.
Ha SY, Lee J, Kang SY, Do IG, Ahn S, Park JO et al. MET overexpression assessed by new interpretation method predicts gene amplification and poor survival in advanced gastric carcinomas. Mod Pathol 2013; 26: 1632–1641.
Cheng Hl Trink B, Ts Tzai, Liu HS, Chan SH, Ho CL et al. Overexpression of MET as a prognostic indicator for transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder: a comparison with p53 nuclear accumulation. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 1544–1550.
Miyata Y, Sagara Y, Kanda S, Hayashi T, Kanetake H . Phosphorylated hepatocyte growth factor receptor/c-met is associated with tumor growth and prognosis in patients with bladder cancer: correlation with matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -7 and e-cadherin. Hum Pathol 2009; 40: 496–504.
Liu Z, Wei P, Yang Y, Cui W, Cao B, Tan C et al. BATF2 deficiency promotes progression in human colorectal cancer via activation of HGF/MET signaling: a potential rationale for combining MET inhibitors with IFNs. Clin Cancer Res 2015; 21: 1752–1763.
Mahtouk K, Tjin EP, Spaargaren M, Pals ST . The HGF/MET pathway as target for the treatment of multiple myeloma and B-cell lymphomas. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010; 1806: 208–219.
Huang WT, Chuang SS . High MET gene copy number predicted poor prognosis in primary intestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Diagn Pathol 2013; 8: 16.
Tjin EP, Groen RW, Vogelzang I, Derksen PW, Klok MD, Meijer HP et al. Functional analysis of HGF/MET signaling and aberrant HGF-activator expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2006; 107: 760–768.
Kawano R, Ohshima K, Karube K, Yamaquchi T, Kohno S, Suzumiya J et al. Prognostic significance of hepatocyte growth factor and MET expression in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2004; 127: 305–307.
Engelman JA . Targeting PI3K signalling in cancer: opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 550–62.
Slomovitz BM, Coleman RL . The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway as a therapeutic target in endometrial cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2012; 18: 5856–5864.
Chow LM, Baker SJ . PTEN function in normal and neoplastic growth. Cancer Lett 2006; 241: 184–196.
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81470353, 81272630, XYZ), Science and Technology commission of Shanghai Municipality (15495810300), Shanghai hospital development center Emerging advanced technology joint research project (SHDC 12014105) and Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (2015ZB0204). This work was also supported by the Sister Institution Network Funds of UT MD Anderson Cancer Center to MJY, and matching fund from Shanghai Cancer Center to XYZ. MJY was partially supported by NIH/NCI R01 CA164346, and R01 CA200703, Developmental Research Awards in Leukemia SPORE CA100632 and CPRIT RP140402. We would like to thank Dr Emilia L Lim and Dr Marco A Marra at University of British Columbia for kindly providing their original data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Y., Liu, Z., Wang, W. et al. HDAC6 regulates microRNA-27b that suppresses proliferation, promotes apoptosis and target MET in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 32, 703–711 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.299
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.299
This article is cited by
-
microRNA sequencing for biomarker detection in the diagnosis, classification and prognosis of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Clinicopathologic features and abnormal signaling pathways in plasmablastic lymphoma: a multicenter study in China
BMC Medicine (2022)
-
Effect of miR-27b on the proliferation and apoptosis of diffuse large b-cell lymphoma cells by targeting the regulation of MET/PI3K/AKT pathway
Discover Oncology (2022)
-
Long non-coding RNA ZNFX1-AS1 promotes the tumor progression and metastasis of colorectal cancer by acting as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-144 to regulate EZH2 expression
Cell Death & Disease (2019)
-
MicroRNA transcriptome analysis of poly I:C-stimulated and PRRSV-infected porcine alveolar macrophages
Journal of Applied Genetics (2019)