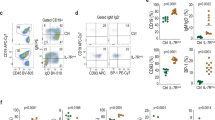
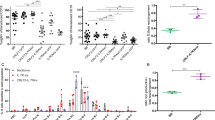
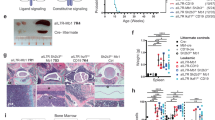
Abstract
The chimeric fusion oncogene early B-cell factor 1–platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β (EBF1-PDGFRB) is a recurrent lesion observed in Philadelphia-like B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) and is associated with particularly poor prognosis. While it is understood that this fusion activates tyrosine kinase signaling, the mechanisms of transformation and importance of perturbation of EBF1 activity remain unknown. EBF1 is a nuclear transcription factor required for normal B-lineage specification, commitment and development. Conversely, PDGFRB is a receptor tyrosine kinase that is normally repressed in lymphocytes, yet PDGFRB remains a common fusion partner in leukemias. Here, we demonstrate that the EBF1-PDGFRB fusion results in loss of EBF1 function, multimerization and autophosphorylation of the fusion protein, activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) signaling and gain of interleukin-7 (IL-7)-independent cell proliferation. Deregulation and loss of EBF1 function is critically dependent on the nuclear export activity of the transmembrane (TM) domain of PDGFRB. Deletion of the TM domain partially rescues EBF1 function and restores IL-7 dependence, without requiring kinase inhibition. Moreover, we demonstrate that EBF1-PDGFRB synergizes with loss of IKAROS function in a fully penetrant B-ALL in vivo. Thus, we establish that EBF1-PDGFRB is sufficient to drive leukemogenesis through TM-dependent loss of transcription factor function, increased proliferation and synergy with additional genetic insults including loss of IKAROS function.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 2016; 66: 7–30.
Iacobucci I, Mullighan CG . Genetic Basis of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2017; 35: 975–983.
Roberts KG, Morin RD, Zhang J, Hirst M, Zhao Y, Su X et al. Genetic alterations activating kinase and cytokine receptor signaling in high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell 2012; 22: 153–166.
Jain N, Roberts KG, Jabbour E, Patel K, Eterovic AK, Chen K et al. Ph-like acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a high-risk subtype in adults. Blood 2017; 129: 572–581.
Schwab C, Ryan SL, Chilton L, Elliott A, Murray J, Richardson S et al. EBF1-PDGFRB fusion in paediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (BCP-ALL): genetic profile and clinical implications. Blood 2016; 127: 2214–2218.
Demoulin JB, Montano-Almendras CP . Platelet-derived growth factors and their receptors in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Am J Blood Res 2012; 2: 44–56.
Demoulin JB, Essaghir A . PDGF receptor signaling networks in normal and cancer cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2014; 25: 273–283.
Ishibashi T, Yaguchi A, Terada K, Ueno-Yokohata H, Tomita O, Iijima K et al. Ph-like ALL-related novel fusion kinase ATF7IP-PDGFRB exhibits high sensitivity to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in murine cells. Exp Hematol 2016; 44: 177–188.e5.
O'Connor D, Moorman AV, Wade R, Hancock J, Tan RM, Bartram J et al. Use of minimal residual disease assessment to redefine induction failure in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2017; 35: 660–667.
Vilagos B, Hoffmann M, Souabni A, Sun Q, Werner B, Medvedovic J et al. Essential role of EBF1 in the generation and function of distinct mature B cell types. J Exp Med 2012; 209: 775–792.
Pongubala JM, Northrup DL, Lancki DW, Medina KL, Treiber T, Bertolino E et al. Transcription factor EBF restricts alternative lineage options and promotes B cell fate commitment independently of Pax5. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 203–215.
Treiber T, Mandel EM, Pott S, Györy I, Firner S, Liu ET et al. Early B cell factor 1 regulates B cell gene networks by activation, repression, and transcription- independent poising of chromatin. Immunity 2010; 32: 714–725.
Lin H, Grosschedl R . Failure of B-cell differentiation in mice lacking the transcription factor EBF. Nature 1995; 376: 263–267.
Györy I, Boller S, Nechanitzky R, Mandel E, Pott S, Liu E et al. Transcription factor Ebf1 regulates differentiation stage-specific signaling, proliferation, and survival of B cells. Genes Dev 2012; 26: 668–682.
Lukin K, Fields S, Lopez D, Cherrier M, Ternyak K, Ramirez J et al. Compound haploinsufficiencies of Ebf1 and Runx1 genes impede B cell lineage progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 7869–7874.
Heltemes-Harris LM, Willette MJ, Ramsey LB, Qiu YH, Neeley ES, Zhang N et al. Ebf1 or Pax5 haploinsufficiency synergizes with STAT5 activation to initiate acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Exp Med 2011; 208: 1135–1149.
Heckl D, Schwarzer A, Haemmerle R, Steinemann D, Rudolph C, Skawran B et al. Lentiviral vector induced insertional haploinsufficiency of Ebf1 causes murine leukemia. Mol Ther 2012; 20: 1187–1195.
Mullighan CG, Goorha S, Radtke I, Miller CB, Coustan-Smith E, Dalton JD et al. Genome-wide analysis of genetic alterations in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature 2007; 446: 758–764.
Yang JJ, Bhojwani D, Yang W, Cai X, Stocco G, Crews K et al. Genome-wide copy number profiling reveals molecular evolution from diagnosis to relapse in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2008; 112: 4178–4183.
Roberts KG, Li Y, Payne-Turner D, Harvey RC, Yang Y-L, Pei D et al. Targetable kinase-activating lesions in Ph-like acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2014; 371: 1005–1015.
Williams RT, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ . Arf gene loss enhances oncogenicity and limits imatinib response in mouse models of Bcr-Abl-induced acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 6688–6693.
Sorkin A, Westermark B, Heldin CH, Claesson-Welsh L . Effect of receptor kinase inactivation on the rate of internalization and degradation of PDGF and the PDGF beta-receptor. J Cell Biol 1991; 112: 469–478.
Toffalini F, Hellberg C, Demoulin JB . Critical role of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) beta transmembrane domain in the TEL-PDGFRbeta cytosolic oncoprotein. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 12268–12278.
Gao H, Lukin K, Ramirez J, Fields S, Lopez D, Hagman J . Opposing effects of SWI/SNF and Mi-2/NuRD chromatin remodeling complexes on epigenetic reprogramming by EBF and Pax5. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 11258–11263.
Boller S, Ramamoorthy S, Akbas D, Nechanitzky R, Burger L, Murr R et al. Pioneering activity of the C-terminal domain of EBF1 shapes the chromatin landscape for B cell programming. Immunity 2016; 44: 527–541.
la Cour T, Gupta R, Rapacki K, Skriver K, Poulsen FM, Brunak S . NESbase version 1.0: a database of nuclear export signals. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31: 393–396.
Claesson-Welsh L . Signal transduction by the PDGF receptors. Prog Growth Factor Res 1994; 5: 37–54.
Pahara J, Shi H, Chen X, Wang Z . Dimerization drives PDGF receptor endocytosis through a C-terminal hydrophobic motif shared by EGF receptor. Exp Cell Res 2010; 316: 2237–2250.
Mori S, Tanaka K, Omura S, Saito Y . Degradation process of ligand-stimulated platelet-derived growth factor beta-receptor involves ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 29447–29452.
Stein EM . Molecularly targeted therapies for acute myeloid leukemia. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Prog 2015; 2015: 579–583.
Katoh M . FGFR inhibitors: effects on cancer cells, tumor microenvironment and whole-body homeostasis. Int J Mol Med 2016; 38: 3–15.
Zimmerman EI, Turner DC, Buaboonnam J, Hu S, Orwick S, Roberts MS et al. Crenolanib is active against models of drug-resistant FLT3-ITD-positive acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2013; 122: 3607–3615.
Churchman ML, Low J, Qu C, Paietta EM, Kasper LH, Chang Y et al. Efficacy of retinoids in IKZF1-mutated BCR-ABL1 acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell 2015; 28: 343–356.
Toffalini F, Hellberg C, Demoulin JB . Critical role of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) beta transmembrane domain in the TEL-PDGFRBbeta cytosolic oncoprotein. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 12268–12278.
De Keersmaecker K, Rocnik JL, Bernad R, Lee BH, Leeman D, Gielen O et al. Kinase activation and transformation by NUP214-ABL1 is dependent on the context of the nuclear pore. Mol Cell 2008; 31: 134–142.
Toffalini F, Kallin A, Vandenberghe P, Pierre P, Michaux L, Cools J et al. The fusion proteins TEL-PDGFRbeta and FIP1L1-PDGFRalpha escape ubiquitination and degradation. Haematologica 2009; 94: 1085–1093.
Kasyapa CS, Kunapuli P, Cowell JK . HSPA1A is an important regulator of the stability and function of ZNF198 and its oncogenic derivative, ZNF198-FGFR1. J Cell Biochem 2007; 102: 1308–1317.
Schwab C, Ryan SL, Chilton L, Elliott A, Murray J, Richardson S et al. EBF1-PDGFRB fusion in pediatric B-Cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL): genetic profile and clinical implications. Blood 2016; 127: 2214–2218.
Mullighan CG, Su X, Zhang J, Radtke I, Phillips LA, Miller CB et al. Deletion of IKZF1 and prognosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2009; 360: 470–480.
Petti LM, Talbert-Slagle K, Hochstrasser ML, DiMaio D . A single amino acid substitution converts a transmembrane protein activator of the platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor into an inhibitor. J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 27273–27286.
Harvey RC, Mullighan CG, Wang X, Dobbin KK, Davidson GS, Bedrick EJ et al. Identification of novel cluster groups in pediatric high-risk B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia with gene expression profiling: correlation with genome-wide DNA copy number alterations, clinical characteristics, and outcome. Blood 2010; 116: 4874–4884.
Hunger SP, Mullighan CG . Redefining ALL classification: toward detecting high-risk ALL and implementing precision medicine. Blood 2015; 125: 3977–3987.
Schwickert TA, Tagoh H, Gültekin S, Dakic A, Axelsson E, Minnich M et al. Stage-specific control of early B cell development by the transcription factor Ikaros. Nat Immunol 2014; 15: 283–293.
Churchman ML, Mullighan CG . Ikaros: exploiting and targeting the hematopoietic stem cell niche in B-progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Exp Hematol 2017; 46: 1–8.
Joshi I, Yoshida T, Jena N, Qi X, Zhang J, Van Etten RA et al. Loss of Ikaros DNA-binding function confers integrin-dependent survival on pre-B cells and progression to acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat Immunol 2014; 15: 294–304.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Jay Hesselberth, John Cambier, Mark Johnston, Laurent Gapin, Aaron M Johnson, Hua Huang and Mikael Sigvardsson for helpful suggestions and reagents. We also thank the National Jewish Health Flow Cytometry Core and Josh Loomis for support and technical assistance, the St Jude Children’s Research Hospital Flow Cytometry and Cell Sorting Shared Resource and Cell and Tissue Imaging Center. This work was funded by grants to JH from the National Institutes of Health R01 AI081878 and AI098417, The Wendy Siegel Fund for Leukemia and Cancer Research and the Cancer League of Colorado. The Victor W Bolie and Earleen D Bolie Graduate Scholarship Fund supported SJW. This work was supported by the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities of St Jude Children’s Research Hospital. CGM was supported by a St Baldrick’s Foundation Scholar Award, a St Baldrick’s Foundation Robert J Arceci Innovation Award, a Specialized Center of Research Award from the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society and an Outstanding Investigator Award (R35 CA197695) from the National Cancer Institute.
Author contributions
Conceptualization and methodology: SJW, MLC, MT, CGM and JH; investigation: SJW, MLC and MT; writing: SJW, MLC, CGM and JH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Welsh, S., Churchman, M., Togni, M. et al. Deregulation of kinase signaling and lymphoid development in EBF1-PDGFRB ALL leukemogenesis. Leukemia 32, 38–48 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.166
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.166
This article is cited by
-
Unusual PDGFRB fusion reveals novel mechanism of kinase activation in Ph-like B-ALL
Leukemia (2023)
-
EBF1–JAK2 inhibits the PAX5 function through physical interaction with PAX5 and kinase activity
International Journal of Hematology (2023)
-
Effective treatment with imatinib for acute B-lymphoblastic leukaemia with EBF1-PDGFRB fusion
Annals of Hematology (2021)
-
Keeping PACE with Ph Positive to Ph-Like Detection in B-Lineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Practical and Cost Effective (PACE) Approach in a Resource Constrained Setting
Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion (2018)