Abstract
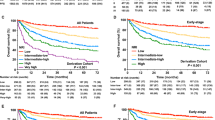
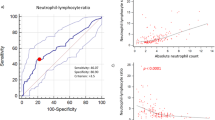
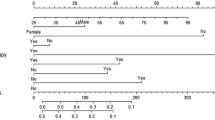
The aim of this study was to develop a widely accepted prognostic nomogram for extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type (NKTCL). The clinical data from 1383 patients with NKTCL treated at 10 participating institutions between 2000 and 2011 were reviewed. A nomogram was developed that predicted overall survival (OS) based on the Cox proportional hazards model. To contrast the utility of the nomogram against the widely used Ann Arbor staging system, the International Prognostic Index (IPI) and the Korean Prognostic Index (KPI), we used the concordance index (C-index) and a calibration curve to determine its predictive and discriminatory capacity. The 5-year OS rate was 60.3% for the entire group. The nomogram included five important variables based on a multivariate analysis of the primary cohort: stage; age; Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; lactate dehydrogenase; and primary tumor invasion. The calibration curve showed that the nomogram was able to predict 5-year OS accurately. The C-index of the nomogram for OS prediction was 0.72 for both cohorts, which was superior to the predictive power (range, 0.56–0.64) of the Ann Arbor stage, IPI and KPI in the primary and validation cohorts. The proposed nomogram provides an individualized risk estimate of OS in patients with NKTCL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai WZ, Chang ET, Fish K, Fu K, Weisenburger DD, Keegan TH . Racial patterns of extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type, in California: a population-based study. Br J Haematol 2012; 156: 626–632.
Au WY, Weisenburger DD, Intragumtornchai T, Nakamura S, Kim WS, Sng I et al. International Peripheral TCLP: clinical differences between nasal and extranasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: a study of 136 cases from the International Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Project. Blood 2009; 113: 3931–3937.
Suzuki R, Suzumiya J, Yamaguchi M, Nakamura S, Kameoka J, Kojima H et al. Prognostic factors for mature natural killer (NK) cell neoplasms: aggressive NK cell leukemia and extranodal NK cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann Oncol 2010; 21: 1032–1040.
Kim TM, Lee SY, Jeon YK, Ryoo BY, Cho GJ, Hong YS et al. Clinical heterogeneity of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: a national survey of the Korean Cancer Study Group. Ann Oncol 2008; 19: 1477–1484.
Vazquez A, Khan MN, Blake DM, Sanghvi S, Baredes S, Eloy JA . Extranodal natural killer/T-Cell lymphoma: a population-based comparison of sinonasal and extranasal disease. Laryngoscope 2014; 124: 888–895.
Sun J, Yang Q, Lu Z, He M, Gao L, Zhu M et al. Distribution of lymphoid neoplasms in China: analysis of 4,638 cases according to the World Health Organization classification. Am J Clin Pathol 2012; 138: 429–434.
Li YX, Yao B, Jin J, Wang WH, Liu YP, Song YW et al. Radiotherapy as primary treatment for stage IE and IIE nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 181–189.
Lee J, Suh C, Park YH, Ko YH, Bang SM, Lee JH et al. Extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type: a prognostic model from a retrospective multicenter study. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 612–618.
Li YX, Wang H, Jin J, Wang WH, Liu QF, Song YW et al. Radiotherapy alone with curative intent in patients with stage I extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2012; 82: 1809–1815.
Kwong YL, Kim WS, Lim ST, Kim SJ, Tang T, Tse E et al. SMILE for natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: analysis of safety and efficacy from the Asia Lymphoma Study Group. Blood 2012; 120: 2973–2980.
Li YX, Liu QF, Wang WH, Jin J, Song YW, Wang SL et al. Failure patterns and clinical implications in early stage nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma treated with primary radiotherapy. Cancer 2011; 117: 5203–5211.
Kim TM, Park YH, Lee SY, Kim JH, Kim DW, Im SA et al. Local tumor invasiveness is more predictive of survival than International Prognostic Index in stage I(E)/II(E) extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Blood 2005; 106: 3785–3790.
Huang JJ, Zhu YJ, Xia Y, Zhao W, Lin TY, Jiang WQ et al. A novel prognostic model for extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Med Oncol 2012; 29: 2183–2190.
Cai Q, Luo X, Zhang G, Huang H, Huang H, Lin T et al. New prognostic model for extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann Hematol 2014; 93: 1541–1549.
Jo JC, Yoon DH, Kim S, Lee BJ, Jang YJ, Park CS et al. Clinical features and prognostic model for extranasal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Eur J Haematol 2012; 89: 103–110.
A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The International Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. N Engl J Med 1993; 329: 987–994.
Albert JM, Liu DD, Shen Y, Pan IW, Shih YC, Hoffman KE et al. Nomogram to predict the benefit of radiation for older patients with breast cancer treated with conservative surgery. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 2837–2843.
Walz J, Gallina A, Saad F, Montorsi F, Perrotte P, Shariat SF et al. A nomogram predicting 10-year life expectancy in candidates for radical prostatectomy or radiotherapy for prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 3576–3581.
Han DS, Suh YS, Kong SH, Lee HJ, Choi Y, Aikou S et al. Nomogram predicting long-term survival after d2 gastrectomy for gastric cancer. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 3834–3840.
Chan JKC, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Ferry JA, Peh SC . Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. In Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, Thield J, Vardiman JW (eds). World Health Organization Classification of Tumours: Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2008; pp 285–288.
Fang H, Jin J, Wang WH, Wang SL, Zhou LQ, Li YX . Prognostic factors and treatment outcomes for patients with stage II extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma of the upper aerodigestive tract. Leuk Lymphom 2014; 55: 1832–1837.
Li YX, Fang H, Liu QF, Lu J, Qi SN, Wang H et al. Clinical features and treatment outcome of nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma of Waldeyer ring. Blood 2008; 112: 3057–3064.
Cheung MMC, Chan JKC, Lau W-h, RKC Ngan, WWL Foo . Early stage nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma: clinical outcome, prognostic factors, and the effect of treatment modality. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2002; 54: 182–190.
Li YX, Liu QF, Fang H, Qi SN, Wang H, Wang WH et al. Variable clinical presentations of nasal and waldeyer ring natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 2905–2912.
Lee J, Park YH, Kim WS, Lee SS, Ryoo BY, Yang SH et al. Extranodal nasal type NK/T-cell lymphoma: elucidating clinical prognostic factors for risk-based stratification of therapy. Eur J Cancer 2005; 41: 1402–1408.
Wang ZY, Li YX, Wang WH, Jin J, Wang H, Song YW et al. Primary radiotherapy showed favorable outcome in treating extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma in children and adolescents. Blood 2009; 114: 4771–4776.
Wang ZY, Li YX, Wang H, Wang WH, Jin J, Liu YP et al. Unfavorable prognosis of elderly patients with early-stage extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma. Ann Oncol 2011; 22: 390–396.
Na II, Kang HJ, Park YH, Lee SS, Yoo HJ, Choe DH et al. Prognostic factors for classifying extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma, nasal type, as lymphoid neoplasia. Eur J Haematol 2007; 79: 1–7.
Chim CS, Ma SY, Au WY, Choy C, Lie AKW, Liang R et al. Primary nasal natural killer cell lymphoma: long-term treatment outcome and relationship with the International Prognostic Index. Blood 2004; 103: 216–221.
Li YX, Coucke PA, Li JY, Gu DZ, Liu XF, Zhou LQ et al. Primary non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the nasal cavity: prognostic significance of paranasal extension and the role of radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Cancer 1998; 83: 449–456.
Iasonos A, Schrag D, Raj GV, Panageas KS . How to build and interpret a nomogram for cancer prognosis. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 1364–1370.
von Tresckow B, Plutschow A, Fuchs M, Klimm B, Markova J, Lohri A et al. Dose-intensification in early unfavorable Hodgkin's lymphoma: final analysis of the German Hodgkin Study Group HD14 trial. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 907–913.
Pfreundschuh M, Ho AD, Cavallin-Stahl E, Wolf M, Pettengell R, Vasova I et al. Prognostic significance of maximum tumour (bulk) diameter in young patients with good-prognosis diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma treated with CHOP-like chemotherapy with or without rituximab: an exploratory analysis of the MabThera International Trial Group (MInT) study. Lancet Oncol 2008; 9: 435–444.
Kim S, Kim B, Choi C, Choi J, Kim I, Lee YH et al. Ki-67 expression is predictive of prognosis in patients with stage I/II extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann Oncol 2007; 18: 1382–1387.
Shim SJ, Yang WI, Shin E, Koom WS, Kim YB, Cho JH et al. Clinical significance of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in extranodal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2007; 67: 31–38.
Wang ZY, Liu QF, Wang H, Jin J, Wang WH, Wang SL et al. Clinical implications of plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA in early-stage extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma patients receiving primary radiotherapy. Blood 2012; 120: 2003–2010.
Kwong YL, Pang AW, Leung AY, Chim CS, Tse E . Quantification of circulating Epstein-Barr virus DNA in NK/T-cell lymphoma treated with the SMILE protocol: diagnostic and prognostic significance. Leukemia 2014; 28: 865–870.
Liu QF, Wang WH, Wang SL, Liu YP, Huang WT, Lu N et al. Immunophenotypic and clinical differences between the nasal and extranasal subtypes of upper aerodigestive tract natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2014; 88: 806–813.
Moon SH, Cho SK, Kim WS, Kim SJ, Chan Ahn Y, Choe YS et al. The role of 18F-FDG PET/CT for initial staging of nasal type natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: a comparison with conventional staging methods. J Nucl Med 2013; 54: 1039–1044.
Wang H, Li YX, Wang WH, Jin J, Dai JR, Wang SL et al. Mild toxicity and favorable prognosis of high-dose and extended involved-field intensity-modulated radiotherapy for patients with early-stage nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2012; 82: 1115–1121.
Bi XW, Li YX, Fang H, Jin J, Wang WH, Wang SL et al. High-dose and extended-field intensity modulated radiation therapy for early-stage NK/T-cell lymphoma of Waldeyer's Ring: dosimetric analysis and clinical outcome. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2013; 87: 1086–1093.
Yamaguchi M, Tobinai K, Oguchi M, Ishizuka N, Kobayashi Y, Isobe Y et al. Phase I/II study of concurrent chemoradiotherapy for localized nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study JCOG0211. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 5594–5600.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Author Contributions
YXL designed the research; YXL, YY and QFL collected and analyzed the data; YJZ, YY and YXL wrote the paper; all authors provided study materials or patients and approved the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Zhang, YJ., Zhu, Y. et al. Prognostic nomogram for overall survival in previously untreated patients with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type: a multicenter study. Leukemia 29, 1571–1577 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.44
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.44
This article is cited by
-
Immunotyping of peripheral blood lymphocytes by flow cytometry reveals Th cell as a potential prognostic biomarker for extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma
Annals of Hematology (2024)
-
The prognostic value of controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score–based nomogram on extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma patients
Annals of Hematology (2023)
-
Central nervous system involvement at initial diagnosis of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma: a retrospective study of a consecutive 12-year case series
Annals of Hematology (2023)
-
Comparative analysis of upper aerodigestive tract and non-upper aerodigestive tract in NK/T-cell lymphoma
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2023)
-
Risk stratification and prognostic value of multi-modal MRI-based radiomics for extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma
BMC Cancer (2023)