Abstract
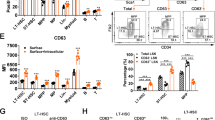
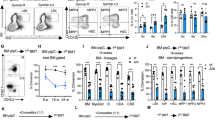
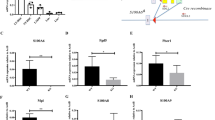
FHL2, a member of the four and one half LIM domain protein family, is a critical transcriptional modulator. Here, we identify FHL2 as a critical regulator of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) that is essential for maintaining HSC self-renewal under regenerative stress. We find that Fhl2 loss has limited effects on hematopoiesis under homeostatic conditions. In contrast, Fhl2-null chimeric mice reconstituted with Fhl2-null bone marrow cells developed abnormal hematopoiesis with significantly reduced numbers of HSCs, hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs), red blood cells and platelets as well as hemoglobin levels. In addition, HSCs displayed a significantly reduced self-renewal capacity and were skewed toward myeloid lineage differentiation. We find that Fhl2 loss reduces both HSC quiescence and survival in response to regenerative stress, probably as a consequence of Fhl2-loss-mediated downregulation of cyclin-dependent kinase-inhibitors, including p21(Cip) and p27(Kip1). Interestingly, FHL2 is regulated under the control of a tissue-specific promoter in hematopoietic cells and it is downregulated by DNA hypermethylation in the leukemia cell line and primary leukemia cells. Furthermore, we find that downregulation of FHL2 frequently occurs in myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia patients, raising a possibility that FHL2 downregulation has a role in the pathogenesis of myeloid malignancies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Genini M, Schwalbe P, Scholl FA, Remppis A, Mattei MG, Schafer BW . Subtractive cloning and characterization of DRAL, a novel LIM-domain protein down-regulated in rhabdomyosarcoma. DNA Cell Biol 1997; 16: 433–442.
Johannessen M, Moller S, Hansen T, Moens U, Van Ghelue M . The multifunctional roles of the four-and-a-half-LIM only protein FHL2. Cell Mol Life Sci 2006; 63: 268–284.
Chu PH, Ruiz-Lozano P, Zhou Q, Cai C, Chen J . Expression patterns of FHL/SLIM family members suggest important functional roles in skeletal muscle and cardiovascular system. Mech Dev 2000; 95: 259–265.
Morgan MJ, Madgwick AJ . The fourth member of the FHL family of LIM proteins is expressed exclusively in the testis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1999; 255: 251–255.
Morgan MJ, Madgwick AJ . The LIM proteins FHL1 and FHL3 are expressed differently in skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1999; 255: 245–250.
Tanahashi H, Tabira T . Alzheimer's disease-associated presenilin 2 interacts with DRAL, an LIM-domain protein. Hum Mol Genet 2000; 9: 2281–2289.
Amaar YG, Thompson GR, Linkhart TA, Chen ST, Baylink DJ, Mohan S . Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 (IGFBP-5) interacts with a four and a half LIM protein 2 (FHL2). J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 12053–12060.
Wixler V, Geerts D, Laplantine E, Westhoff D, Smyth N, Aumailley M et al. The LIM-only protein DRAL/FHL2 binds to the cytoplasmic domain of several alpha and beta integrin chains and is recruited to adhesion complexes. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 33669–33678.
Muller JM, Isele U, Metzger E, Rempel A, Moser M, Pscherer A et al. FHL2, a novel tissue-specific coactivator of the androgen receptor. EMBO J 2000; 19: 359–369.
Morlon A, Sassone-Corsi P . The LIM-only protein FHL2 is a serum-inducible transcriptional coactivator of AP-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 3977–3982.
Fimia GM, De Cesare D, Sassone-Corsi P . A family of LIM-only transcriptional coactivators: tissue-specific expression and selective activation of CREB and CREM. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 8613–8622.
McLoughlin P, Ehler E, Carlile G, Licht JD, Schafer BW . The LIM-only protein DRAL/FHL2 interacts with and is a corepressor for the promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger protein. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 37045–37053.
Chen D, Xu W, Bales E, Colmenares C, Conacci-Sorrell M, Ishii S et al. SKI activates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in human melanoma. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 6626–6634.
Martin B, Schneider R, Janetzky S, Waibler Z, Pandur P, Kuhl M et al. The LIM-only protein FHL2 interacts with beta-catenin and promotes differentiation of mouse myoblasts. J Cell Biol 2002; 159: 113–122.
Wei Y, Renard CA, Labalette C, Wu Y, Levy L, Neuveut C et al. Identification of the LIM protein FHL2 as a coactivator of beta-catenin. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 5188–5194.
Purcell NH, Darwis D, Bueno OF, Muller JM, Schule R, Molkentin JD . Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 interacts with and is negatively regulated by the LIM-only protein FHL2 in cardiomyocytes. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 1081–1095.
Ding L, Wang Z, Yan J, Yang X, Liu A, Qiu W et al. Human four-and-a-half LIM family members suppress tumor cell growth through a TGF-beta-like signaling pathway. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 349–361.
Shi X, Bowlin KM, Garry DJ . Fhl2 interacts with Foxk1 and corepresses Foxo4 activity in myogenic progenitors. Stem Cells 28: 462–469.
Du X, Hublitz P, Gunther T, Wilhelm D, Englert C, Schule R . The LIM-only coactivator FHL2 modulates WT1 transcriptional activity during gonadal differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta 2002; 1577: 93–101.
Bai S, Kitaura H, Zhao H, Chen J, Muller JM, Schule R et al. FHL2 inhibits the activated osteoclast in a TRAF6-dependent manner. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 2742–2751.
Gunther T, Poli C, Muller JM, Catala-Lehnen P, Schinke T, Yin N et al. Fhl2 deficiency results in osteopenia due to decreased activity of osteoblasts. EMBO J 2005; 24: 3049–3056.
Philippar U, Schratt G, Dieterich C, Muller JM, Galgoczy P, Engel FB et al. The SRF target gene Fhl2 antagonizes RhoA/MAL-dependent activation of SRF. Mol Cell 2004; 16: 867–880.
Stilo R, Leonardi A, Formisano L, Di Jeso B, Vito P, Liguoro D . TUCAN/CARDINAL and DRAL participate in a common pathway for modulation of NF-kappaB activation. FEBS Lett 2002; 521: 165–169.
Kinoshita M, Nakagawa T, Shimizu A, Katsuoka Y . Differently regulated androgen receptor transcriptional complex in prostate cancer compared with normal prostate. Int J Urol 2005; 12: 390–397.
Gabriel B, Mildenberger S, Weisser CW, Metzger E, Gitsch G, Schule R et al. Focal adhesion kinase interacts with the transcriptional coactivator FHL2 and both are overexpressed in epithelial ovarian cancer. Anticancer Res 2004; 24: 921–927.
Yan J, Zhu J, Zhong H, Lu Q, Huang C, Ye Q . BRCA1 interacts with FHL2 and enhances FHL2 transactivation function. FEBS Lett 2003; 553: 183–189.
Dahan J, Nouet Y, Jouvion G, Levillayer F, Adib-Conquy M, Cassard-Doulcier AM et al. LIM-only protein FHL2 activates NF-kappaB signaling in the control of liver regeneration and hepatocarcinogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 2013; 33: 3299–3308.
Qian Z, Mao L, Fernald AA, Yu H, Luo R, Jiang Y et al. Enhanced expression of FHL2 leads to abnormal myelopoiesis in vivo. Leukemia 2009; 23: 1650–1657.
Qian Z, Chen L, Fernald AA, Williams BO, Le Beau MM . A critical role for Apc in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell survival. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 2163–2175.
Foudi A, Jarrier P, Zhang Y, Wittner M, Geay JF, Lecluse Y et al. Reduced retention of radioprotective hematopoietic cells within the bone marrow microenvironment in CXCR4-/- chimeric mice. Blood 2006; 107: 2243–2251.
Qian Z, Fernald AA, Godley LA, Larson RA, Le Beau MM . Expression profiling of CD34+ hematopoietic stem/ progenitor cells reveals distinct subtypes of therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 14925–14930.
Chu PH, Bardwell WM, Gu Y, Ross J Jr., Chen J . FHL2 (SLIM3) is not essential for cardiac development and function. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 7460–7462.
Akashi K, Traver D, Miyamoto T, Weissman IL . A clonogenic common myeloid progenitor that gives rise to all myeloid lineages. Nature 2000; 404: 193–197.
Paul C, Lacroix M, Iankova I, Julien E, Schafer BW, Labalette C et al. The LIM-only protein FHL2 is a negative regulator of E4F1. Oncogene 2006; 25: 5475–5484.
Martin BT, Kleiber K, Wixler V, Raab M, Zimmer B, Kaufmann M et al. FHL2 regulates cell cycle-dependent and doxorubicin-induced p21Cip1/Waf1 expression in breast cancer cells. Cell Cycle 2007; 6: 1779–1788.
Labalette C, Nouet Y, Sobczak-Thepot J, Armengol C, Levillayer F, Gendron MC et al. The LIM-only protein FHL2 regulates cyclin D1 expression and cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 15201–15208.
Brun J, Fromigue O, Dieudonne FX, Marty C, Chen J, Dahan J et al. The LIM-only protein FHL2 controls mesenchymal cell osteogenic differentiation and bone formation through Wnt5a and Wnt10b. Bone 2013; 53: 6–12.
Ito K, Hirao A, Arai F, Takubo K, Matsuoka S, Miyamoto K et al. Reactive oxygen species act through p38 MAPK to limit the lifespan of hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Med 2006; 12: 446–451.
Harrison DE, Stone M, Astle CM . Effects of transplantation on the primitive immunohematopoietic stem cell. J Exp Med 1990; 172: 431–437.
Cheng T, Rodrigues N, Shen H, Yang Y, Dombkowski D, Sykes M et al. Hematopoietic stem cell quiescence maintained by p21cip1/waf1. Science 2000; 287: 1804–1808.
Tothova Z, Kollipara R, Huntly BJ, Lee BH, Castrillon DH, Cullen DE et al. FoxOs are critical mediators of hematopoietic stem cell resistance to physiologic oxidative stress. Cell 2007; 128: 325–339.
Miyamoto K, Araki KY, Naka K, Arai F, Takubo K, Yamazaki S et al. Foxo3a is essential for maintenance of the hematopoietic stem cell pool. Cell Stem Cell 2007; 1: 101–112.
Cheng T, Rodrigues N, Dombkowski D, Stier S, Scadden DT . Stem cell repopulation efficiency but not pool size is governed by p27(kip1). Nat Med 2000; 6: 1235–1240.
Matsumoto A, Takeishi S, Kanie T, Susaki E, Onoyama I, Tateishi Y et al. p57 is required for quiescence and maintenance of adult hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2011; 9: 262–271.
Zou P, Yoshihara H, Hosokawa K, Tai I, Shinmyozu K, Tsukahara F et al. p57(Kip2) and p27(Kip1) cooperate to maintain hematopoietic stem cell quiescence through interactions with Hsc70. Cell Stem Cell 2011; 9: 247–261.
Haferlach T, Kohlmann A, Wieczorek L, Basso G, Kronnie GT, Bene MC et al. Clinical utility of microarray-based gene expression profiling in the diagnosis and subclassification of leukemia: report from the International Microarray Innovations in Leukemia Study Group. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 2529–2537.
Bhalla KN . Epigenetic and chromatin modifiers as targeted therapy of hematologic malignancies. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 3971–3993.
Huang PH, Chen CY, Lin CP, Wang CH, Tsai HY, Lo WY et al. Deletion of FHL2 gene impaired ischemia-induced blood flow recovery by modulating circulating proangiogenic cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2013; 33: 709–717.
Shi X, Bowlin KM, Garry DJ . Fhl2 interacts with Foxk1 and corepresses Foxo4 activity in myogenic progenitors. Stem Cells 2010; 28: 462–469.
Kirfel J, Pantelis D, Kabba M, Kahl P, Roper A, Kalff JC et al. Impaired intestinal wound healing in Fhl2-deficient mice is due to disturbed collagen metabolism. Exp Cell Res 2008; 314: 3684–3691.
Wixler V, Hirner S, Muller JM, Gullotti L, Will C, Kirfel J et al. Deficiency in the LIM-only protein Fhl2 impairs skin wound healing. J Cell Biol 2007; 177: 163–172.
Pietras EM, Warr MR, Passegue E . Cell cycle regulation in hematopoietic stem cells. J Cell Biol 2011; 195: 709–720.
Kang CM, Park KP, Song JE, Jeoung DI, Cho CK, Kim TH et al. Possible biomarkers for ionizing radiation exposure in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Radiat Res 2003; 159: 312–319.
Paul S, Amundson SA . Gene expression signatures of radiation exposure in peripheral white blood cells of smokers and non-smokers. Int J Radiat Biol 2011; 87: 791–801.
Kong Y, Shelton JM, Rothermel B, Li X, Richardson JA, Bassel-Duby R et al. Cardiac-specific LIM protein FHL2 modifies the hypertrophic response to beta-adrenergic stimulation. Circulation 2001; 103: 2731–2738.
Denicourt C, Dowdy SF . Cip/Kip proteins: more than just CDKs inhibitors. Genes Dev 2004; 18: 851–855.
van Os R, Kamminga LM, Ausema A, Bystrykh LV, Draijer DP, van Pelt K et al. A Limited role for p21Cip1/Waf1 in maintaining normal hematopoietic stem cell functioning. Stem Cells 2007; 25: 836–843.
Foudi A, Hochedlinger K, Van Buren D, Schindler JW, Jaenisch R, Carey V et al. Analysis of histone 2B-GFP retention reveals slowly cycling hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 2009; 27: 84–90.
Scandura JM, Boccuni P, Massague J, Nimer SD . Transforming growth factor beta-induced cell cycle arrest of human hematopoietic cells requires p57KIP2 up-regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 15231–15236.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institute of Health grants RO1 CA140979 (to ZQ). We thank the staff in the UIC flow core facility for their assistance in cell sorting.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, Y., Wang, X., Li, L. et al. FHL2 regulates hematopoietic stem cell functions under stress conditions. Leukemia 29, 615–624 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.254
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.254
This article is cited by
-
Genome-wide profiling of 5-hydroxymethylcytosines in circulating cell-free DNA reveals population-specific pathways in the development of multiple myeloma
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2022)
-
FOXM1 regulates leukemia stem cell quiescence and survival in MLL-rearranged AML
Nature Communications (2020)
-
miR-340-FHL2 axis inhibits cell growth and metastasis in ovarian cancer
Cell Death & Disease (2019)