Abstract
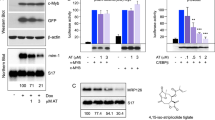
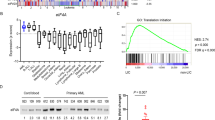
The eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E is a potent oncogene elevated in many cancers, including the M4 and M5 subtypes of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Although eIF4E RNA levels are elevated 3- to 10-fold in M4/M5 AML, the molecular underpinnings of this dysregulation were unknown. Here, we demonstrate that EIF4E is a direct transcriptional target of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) that is dysregulated preferentially in M4 and M5 AML. In primary hematopoietic cells and in cell lines, eIF4E levels are induced by NF-κB activating stimuli. Pharmacological or genetic inhibition of NF-κB represses this activation. The endogenous human EIF4E promoter recruits p65 and cRel to evolutionarily conserved κB sites in vitro and in vivo following NF-κB activation. Transcriptional activation is demonstrated by recruitment of p300 to the κB sites and phosphorylated Pol II to the coding region. In primary AML specimens, generally we observe that substantially more NF-κB complexes associate with eIF4E promoter elements in M4 and M5 AML specimens examined than in other subtypes or unstimulated normal primary hematopoietic cells. Consistently, genetic inhibition of NF-κB abrogates eIF4E RNA levels in this same population. These findings provide novel insights into the transcriptional control of eIF4E and a novel molecular basis for its dysregulation in at least a subset of M4/M5 AML specimens.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borden KL, Culjkovic-Kraljacic B . Ribavirin as an anti-cancer therapy: acute myeloid leukemia and beyond? Leuk Lymphoma 2010; 51: 1805–1815.
Lazaris-Karatzas A, Montine KS, Sonenberg N . Malignant transformation by a eukaryotic initiation factor subunit that binds to mRNA 5′ cap. Nature 1990; 345: 544–547.
Polunovsky VA, Rosenwald IB, Tan AT, White J, Chiang L, Sonenberg N et al. Translational control of programmed cell death: eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E blocks apoptosis in growth-factor-restricted fibroblasts with physiologically expressed or deregulated Myc. Mol Cell Biol 1996; 16: 6573–6581.
Graff JR, Boghaert ER, De Benedetti A, Tudor DL, Zimmer CC, Chan SK et al. Reduction of translation initiation factor 4E decreases the malignancy of ras-transformed cloned rat embryo fibroblasts. Int J Cancer 1995; 60: 255–263.
De Benedetti A, Rhoads RE . Overexpression of eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation factor 4E in HeLa cells results in aberrant growth and morphology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990; 87: 8212–8216.
Filipowicz W, Furuichi Y, Sierra JM, Muthukrishnan S, Shatkin AJ, Ochoa S . A protein binding the methylated 5′-terminal sequence, m7GpppN, of eukaryotic messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1976; 73: 1559–1563.
Culjkovic B, Topisirovic I, Borden KL . Controlling gene expression through RNA regulons: the role of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E. Cell Cycle 2007; 6: 65–69.
Gingras AC, Raught B, Sonenberg N . eIF4 initiation factors: effectors of mRNA recruitment to ribosomes and regulators of translation. Annu Rev Biochem 1999; 68: 913–963.
Culjkovic B, Topisirovic I, Skrabanek L, Ruiz-Gutierrez M, Borden KL . eIF4E is a central node of an RNA regulon that governs cellular proliferation. J Cell Biol 2006; 175: 415–426.
Assouline S, Culjkovic B, Cocolakis E, Rousseau C, Beslu N, Amri A et al. Molecular targeting of the oncogene eIF4E in acute myeloid leukemia (AML): a proof-of-principle clinical trial with ribavirin. Blood 2009; 114: 257–260.
Oridate N, Kim HJ, Xu X, Lotan R . Growth inhibition of head and neck squamous carcinoma cells by small interfering RNAs targeting eIF4E or cyclin D1 alone or combined with cisplatin. Cancer Biol Ther 2005; 4: 318–323.
Kentsis A, Topisirovic I, Culjkovic B, Shao L, Borden KL . Ribavirin suppresses eIF4E-mediated oncogenic transformation by physical mimicry of the 7-methyl guanosine mRNA cap. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 18105–18110.
Graff JR, Konicek BW, Vincent TM, Lynch RL, Monteith D, Weir SN et al. Therapeutic suppression of translation initiation factor eIF4E expression reduces tumor growth without toxicity. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 2638–2648.
Jones RM, Branda J, Johnston KA, Polymenis M, Gadd M, Rustgi A et al. An essential E box in the promoter of the gene encoding the mRNA cap-binding protein (eukaryotic initiation factor 4E) is a target for activation by c-myc. Mol Cell Biol 1996; 16: 4754–4764.
Mainwaring LA, Kenney AM . Divergent functions for eIF4E and S6 kinase by sonic hedgehog mitogenic signaling in the developing cerebellum. Oncogene 2011; 30: 1784–1797.
Zhu N, Gu L, Findley HW, Zhou M . Transcriptional repression of the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E gene by wild type p53. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 335: 1272–1279.
Bush A, Mateyak M, Dugan K, Obaya A, Adachi S, Sedivy J et al. c-myc null cells misregulate cad and gadd45 but not other proposed c-Myc targets. Genes Dev 1998; 12: 3797–3802.
Khanna-Gupta A, Abayasekara N, Levine M, Sun H, Virgilio M, Nia N et al. Up-regulation of translation eukaryotic initiation factor 4E in nucleophosmin 1 haploinsufficient cells results in changes in CCAAT enhancer-binding protein alpha activity: implications in myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 32728–32737.
Topisirovic I, Guzman ML, McConnell MJ, Licht JD, Culjkovic B, Neering SJ et al. Aberrant eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-dependent mRNA transport impedes hematopoietic differentiation and contributes to leukemogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 2003; 23: 8992–9002.
Gilmore TD . Introduction to NF-kappaB: players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene 2006; 25: 6680–6684.
Guzman ML, Neering SJ, Upchurch D, Grimes B, Howard DS, Rizzieri DA et al. Nuclear factor-kappaB is constitutively activated in primitive human acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Blood 2001; 98: 2301–2307.
Karin M . NF-kappaB as a critical link between inflammation and cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2009; 1: a000141.
Gerondakis S, Siebenlist U . Roles of the NF-kappaB pathway in lymphocyte development and function. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2010; 2: a000182.
Quandt K, Frech K, Karas H, Wingender E, T Werner . MatInd and MatInspector: new fast and versatile tools for detection of consensus matches in nucleotide sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res 1995; 23: 4878–4884.
Pfaffl MW . A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 2001; 29: e45.
Kraljacic BC, Arguello M, Amri A, Cormack G, Borden K . Inhibition of eIF4E with ribavirin cooperates with common chemotherapies in primary acute myeloid leukemia specimens. Leukemia 2011; 25: 1197–1200.
Chin M, Herscovitch M, Zhang N, Waxman DJ, Gilmore TD . Overexpression of an activated REL mutant enhances the transformed state of the human B-lymphoma BJAB cell line and alters its gene expression profile. Oncogene 2009; 28: 2100–2111.
Mori N, Yamada Y, Ikeda S, Yamasaki Y, Tsukasaki K, Tanaka Y et al. Bay 11-7082 inhibits transcription factor NF-kappaB and induces apoptosis of HTLV-I-infected T-cell lines and primary adult T-cell leukemia cells. Blood 2002; 100: 1828–1834.
Makhlouf AA, Namboodiri AM, McDermott PJ . Transcriptional regulation of the rat eIF4E gene in cardiac muscle cells: the role of specific elements in the promoter region. Gene 2001; 267: 1–12.
Sen R, Baltimore D . Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell 1986; 47: 921–928.
Chen LF, Mu Y, Greene WC . Acetylation of RelA at discrete sites regulates distinct nuclear functions of NF-kappaB. EMBO J. 2002; 21: 6539–6548.
Gruss HJ, Brach MA, Drexler HG, Bonifer R, Mertelsmann RH, Herrmann F . Expression of cytokine genes, cytokine receptor genes, and transcription factors in cultured Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. Cancer Res 1992; 52: 3353–3360.
Odero MD, Zeleznik-Le NJ, Chinwalla V, Rowley JD . Cytogenetic and molecular analysis of the acute monocytic leukemia cell line THP-1 with an MLL-AF9 translocation. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2000; 29: 333–338.
Mufson RA, Myers C, Turpin JA, Meltzer M . Phorbol ester reduces constitutive nuclear NF kappa B and inhibits HIV-1 production in mature human monocytic cells. J Leukoc Biol 1992; 52: 637–644.
Landry B, Aliabadi HM, Samuel A, Gul-Uludag H, Jiang X, Kutsch O et al. Effective non-viral delivery of siRNA to acute myeloid leukemia cells with lipid-substituted polyethylenimines. PLoS One 2012; 7: e44197.
Pettersson F, Yau C, Dobocan MC, Culjkovic-Kraljacic B, Retrouvay H, Puckett R et al. Ribavirin treatment effects on breast cancers overexpressing eif4e, a biomarker with prognostic specificity for luminal B-type breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 2874–2884.
Kentsis A, Volpon L, Topisirovic I, Soll CE, Culjkovic B, Shao L et al. Further evidence that ribavirin interacts with eIF4E. RNA 2005; 11: 1762–1766.
Cohen N, Sharma M, Kentsis A, Perez JM, Strudwick S, Borden KL . PML RING suppresses oncogenic transformation by reducing the affinity of eIF4E for mRNA. EMBO J 2001; 20: 4547–4559.
Wan F, Lenardo MJ . The nuclear signaling of NF-kappaB: current knowledge, new insights, and future perspectives. Cell Res 2010; 20: 24–33.
Acknowledgements
These studies were supported by grants from the NIH (RO1 98571) and Leukemia and Lymphoma Society Translational Research Program to KLBB, the Ride to Conquer Cancer and the Canadian Foundation for Innovation to KKM. FH is supported by PhD studentships from the Fonds de la recherche en santé du Québec (FRSQ) and the Cole Foundation. MA is a fellow of the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society. KKM is a Chercheur Boursier of the FRSQ. KLBB holds a Canada Research Chair. The Institute for Research in Immunology and Cancer receives infrastructure support from the CIHR and FRSQ. Clinical specimens were collected and analyzed by the BCLQ of the Reseau de recherche sur le cancer of the FRSQ, which is affiliated with the Canadian Tumor Repository Network.
Author contributions
FH, MA and KLBB designed research. FH, MA, LV and THN performed research. FH, MA, BCK and KLBB analyzed the data. KKM and JH contributed valuable reagents. FH and KLBB wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hariri, F., Arguello, M., Volpon, L. et al. The eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E is a direct transcriptional target of NF-κB and is aberrantly regulated in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 27, 2047–2055 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.73
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.73
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
eIF4E phosphorylation mediated LPS induced depressive-like behaviors via ameliorated neuroinflammation and dendritic loss
Translational Psychiatry (2023)
-
The polyphenol/saponin-rich Rhus tripartita extract has an apoptotic effect on THP-1 cells through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies (2021)
-
Eukaryotic initiating factor eIF4E is targeted by EBV-encoded miR-BART11-3p and regulates cell cycle and apoptosis in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma
Virus Genes (2021)
-
Mass cytometry analysis reveals hyperactive NF Kappa B signaling in myelofibrosis and secondary acute myeloid leukemia
Leukemia (2017)
-
miR-139-5p controls translation in myeloid leukemia through EIF4G2
Oncogene (2016)