Abstract
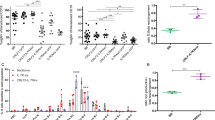
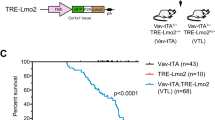
MLL-AF4 fusion is hallmark in high-risk infant pro-B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia (pro-B-ALL). Our limited understanding of MLL-AF4-mediated transformation reflects the absence of human models reproducing this leukemia. Hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPCs) constitute likely targets for transformation. We previously reported that MLL-AF4 enhanced hematopoietic engraftment and clonogenic potential in cord blood (CB)-derived CD34+ HSPCs but was not sufficient for leukemogenesis, suggesting that additional oncogenic lesions are required for MLL-AF4-mediated transformation. MLL-AF4+ pro-B-ALL display enormous levels of FLT3, and occasionally FLT3-activating mutations, thus representing a candidate cooperating event in MLL-AF4+ pro-B-ALL. We have explored whether FLT3.TKD (tyrosine kinase domain) mutation or increased expression of FLT3.WT (wild type) cooperates with MLL-AF4 to immortalize/transform CB-CD34+ HSPCs. In vivo, FLT3.TKD/FLT3.WT alone, or in combination with MLL-AF4, enhances hematopoietic repopulating function of CB-CD34+ HSPCs without impairing migration or hematopoietic differentiation. None of the animals transplanted with MLL-AF4+FLT3.TKD/WT-CD34+ HSPCs showed any sign of disease after 16 weeks. In vitro, enforced expression of FLT3.TKD/FLT3.WT conveys a transient overexpansion of MLL-AF4-expressing CD34+ HSPCs associated to higher proportion of cycling cells coupled to lower apoptotic levels, but does not augment clonogenic potential nor confer stable replating. Together, FLT3 activation does not suffice to immortalize/transform MLL-AF4-expressing CB-CD34+ HSPCs, suggesting the need of alternative (epi)-genetic cooperating oncogenic lesions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greaves MF . Infant leukaemia biology, aetiology and treatment. Leukemia 1996; 10: 372–377.
Meyer C, Kowarz E, Hofmann J, Renneville A, Zuna J, Trka J et al. New insights to the MLL recombinome of acute leukemias. Leukemia 2009; 23: 1490–1499.
Pui CH . Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. Curr Opin Oncol 2000; 12: 3–12.
Pui CH, Frankel LS, Carroll AJ, Raimondi SC, Shuster JJ, Head DR et al. Clinical characteristics and treatment outcome of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia with the t(4;11)(q21;q23): a collaborative study of 40 cases. Blood 1991; 77: 440–447.
Bueno C, Montes R, Catalina P, Rodriguez R, Menendez P . Insights into the cellular origin and etiology of the infant pro-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia with MLL-AF4 rearrangement. Leukemia 2011; 25: 400–410.
Ford AM, Ridge SA, Cabrera ME, Mahmoud H, Steel CM, Chan LC et al. In utero rearrangements in the trithorax-related oncogene in infant leukaemias. Nature 1993; 363: 358–360.
Greaves MF, Maia AT, Wiemels JL, Ford AM . Leukemia in twins: lessons in natural history. Blood 2003; 102: 2321–2333.
Greaves MF, Wiemels J . Origins of chromosome translocations in childhood leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 639–649.
Eguchi M, Eguchi-Ishimae M, Greaves M . Molecular pathogenesis of MLL-associated leukemias. Int J Hematol 2005; 82: 9–20.
Marschalek R . Mechanisms of leukemogenesis by MLL fusion proteins. Br J Haematol 2011; 152: 141–154.
Bursen A, Schwabe K, Ruster B, Henschler R, Ruthardt M, Dingermann T et al. The AF4.MLL fusion protein is capable of inducing ALL in mice without requirement of MLL.AF4. Blood 2010; 115: 3570–3579.
Chen W, Li Q, Hudson WA, Kumar A, Kirchhof N, Kersey JH . A murine Mll-AF4 knock-in model results in lymphoid and myeloid deregulation and hematologic malignancy. Blood 2006; 108: 669–677.
Krivtsov AV, Feng Z, Lemieux ME, Faber J, Vempati S, Sinha AU et al. H3K79 methylation profiles define murine and human MLL-AF4 leukemias. Cancer Cell 2008; 14: 355–368.
Metzler M, Forster A, Pannell R, Arends MJ, Daser A, Lobato MN et al. A conditional model of MLL-AF4 B-cell tumourigenesis using invertor technology. Oncogene 2006; 25: 3093–3103.
Montes R, Ayllon V, Gutierrez-Aranda I, Prat I, Hernandez-Lamas MC, Ponce L et al. Enforced expression of MLL-AF4 fusion in cord blood CD34+ cells enhances the hematopoietic repopulating cell function and clonogenic potential but is not sufficient to initiate leukemia. Blood 2011; 117: 4746–4758.
Bueno C, Montes R, Melen GJ, Ramos-Mejia V, Real PJ, Ayllon V et al. A human ESC model for MLL-AF4 leukemic fusion gene reveals an impaired early hematopoietic-endothelial specification. Cell Res 2012; 22: 986–1002.
Armstrong SA, Mabon ME, Silverman LB, Li A, Gribben JG, Fox EA et al. FLT3 mutations in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2004; 103: 3544–3546.
Taketani T, Taki T, Sugita K, Furuichi Y, Ishii E, Hanada R et al. FLT3 mutations in the activation loop of tyrosine kinase domain are frequently found in infant ALL with MLL rearrangements and pediatric ALL with hyperdiploidy. Blood 2004; 103: 1085–1088.
Yamaguchi H, Hanawa H, Uchida N, Inamai M, Sawaguchi K, Mitamura Y et al. Multistep pathogenesis of leukemia via the MLL-AF4 chimeric gene/Flt3 gene tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) mutation-related enhancement of S100A6 expression. Exp Hematol 2009; 37: 701–714.
Chillon MC, Gomez-Casares MT, Lopez-Jorge CE, Rodriguez-Medina C, Molines A, Sarasquete ME et al. Prognostic significance of FLT3 mutational status and expression levels in MLL-AF4+ and MLL-germline acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2012; 26: 2360–2366.
Guenther MG, Lawton LN, Rozovskaia T, Frampton GM, Levine SS, Volkert TL et al. Aberrant chromatin at genes encoding stem cell regulators in human mixed-lineage leukemia. Genes Dev 2008; 22: 3403–3408.
Stam RW, den Boer ML, Schneider P, Meier M, Beverloo HB, Pieters R . D-HPLC analysis of the entire FLT3 gene in MLL rearranged and hyperdiploid acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2007; 92: 1565–1568.
Stam RW, Schneider P, de Lorenzo P, Valsecchi MG, den Boer ML, Pieters R . Prognostic significance of high-level FLT3 expression in MLL-rearranged infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2007; 110: 2774–2775.
Bueno C, Ayllon V, Montes R, Navarro-Montero O, Ramos-Mejia V, Real JP et al. FLT3 activation cooperates with MLL-AF4 fusion protein to abrogate the hematopoietic specification of human ESCs. Blood 2013; 121: 3867–3878.
Bueno C, Catalina P, Melen GJ, Montes R, Sanchez L, Ligero G et al. Etoposide induces MLL rearrangements and other chromosomal abnormalities in human embryonic stem cells. Carcinogenesis 2009; 30: 1628–1637.
Bueno C, Montes R, Martin L, Prat I, Hernandez MC, Orfao A et al. NG2 antigen is expressed in CD34+ HPCs and plasmacytoid dendritic cell precursors: is NG2 expression in leukemia dependent on the target cell where leukemogenesis is triggered? Leukemia 2008; 22: 1475–1478.
Real PJ, Ligero G, Ayllon V, Ramos-Mejia V, Bueno C, Gutierrez-Aranda I et al. SCL/TAL1 regulates hematopoietic specification from human embryonic stem cells. Mol Ther 2012; 20: 1443–1453.
Bueno C, Montes R, de la Cueva T, Gutierrez-Aranda I, Menendez P . Intra-bone marrow transplantation of human CD34(+) cells into NOD/LtSz-scid IL-2rgamma(null) mice permits multilineage engraftment without previous irradiation. Cytotherapy 2010; 12: 45–49.
Navarro-Montero O, Romero-Moya D, Montes R, Ramos-Mejia V, Bueno C, Real PJ et al. Intrahepatic transplantation of cord blood CD34+ cells into newborn NOD/SCID-IL2Rgamma(null) mice allows efficient multi-organ and multi-lineage hematopoietic engraftment without accessory cells. Clin Immunol 2012; 145: 89–91.
Levac K, Menendez P, Bhatia M . Intra-bone marrow transplantation facilitates pauci-clonal human hematopoietic repopulation of NOD/SCID/beta2m(−/−) mice. Exp Hematol 2005; 33: 1417–1426.
Gutierrez-Aranda I, Ramos-Mejia V, Bueno C, Munoz-Lopez M, Real PJ, Macia A et al. Human induced pluripotent stem cells develop teratoma more efficiently and faster than human embryonic stem cells regardless the site of injection. Stem Cells 2010; 28: 1568–1570.
Romero-Moya D, Bueno C, Montes R, Navarro-Montero O, Iborra FJ, Lopez LC et al. Cord blood-derived CD34+ hematopoietic cells with low levels of mitochondrial mass are enriched in hematopoietic repopulating stem cell function. Haematologica 2013; 98: 102–1029.
Bueno C, Montes R, Menendez P . The ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 negatively affects the expansion/survival of both fresh and cryopreserved cord blood-derived CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells. Stem Cell Rev 2010; 6: 215–223.
Ji J, Vijayaragavan K, Bosse M, Menendez P, Weisel K, Bhatia M . OP9 stroma augments survival of hematopoietic precursors and progenitors during hematopoietic differentiation from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 2008; 26: 2485–2495.
Catalina P, Bueno C, Montes R, Nieto A, Ligero G, Sanchez L et al. Genetic stability of human embryonic stem cells: a first-step toward the development of potential hESC-based systems for modeling childhood leukemia. Leuk Res 2009; 33: 980–990.
Emerenciano M, Menezes J, Vasquez ML, Zalcberg I, Thuler LC, Pombo-de-Oliveira MS . Clinical relevance of FLT3 gene abnormalities in Brazilian patients with infant leukemia. Leuk Lymph 2008; 49: 2291–2297.
Bardini M, Galbiati M, Lettieri A, Bungaro S, Gorletta TA, Biondi A et al. Implementation of array based whole-genome high-resolution technologies confirms the absence of secondary copy-number alterations in MLL-AF4-positive infant ALL patients. Leukemia 2011; 25: 175–178.
Bardini M, Spinelli R, Bungaro S, Mangano E, Corral L, Cifola I et al. DNA copy-number abnormalities do not occur in infant ALL with t(4;11)/MLL-AF4. Leukemia 2010; 24: 169–176.
Menendez P, Caballero MD, Prosper F, Del Canizo MC, Perez-Simon JA, Mateos MV et al. The composition of leukapheresis products impacts on the hematopoietic recovery after autologous transplantation independently of the mobilization regimen. Transfusion 2002; 42: 1159–1172.
Menendez P, Vargas A, Bueno C, Barrena S, Almeida J, De Santiago M et al. Quantitative analysis of bcl-2 expression in normal and leukemic human B-cell differentiation. Leukemia 2004; 18: 491–498.
Prelle C, Bursen A, Dingermann T, Marschalek R . Secondary mutations in t(4;11) leukemia patients. Leukemia 2013; 27: 1425–1427.
Daser A, Rabbitts TH . The versatile mixed lineage leukaemia gene MLL and its many associations in leukaemogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol 2005; 15: 175–188.
Barabe F, Kennedy JA, Hope KJ, Dick JE . Modeling the initiation and progression of human acute leukemia in mice. Science 2007; 316: 600–604.
Hess JL, Yu BD, Li B, Hanson R, Korsmeyer SJ . Defects in yolk sac hematopoiesis in Mll-null embryos. Blood 1997; 90: 1799–1806.
Gubin AN, Njoroge JM, Bouffard GG, Miller JL . Gene expression in proliferating human erythroid cells. Genomics 1999; 59: 168–177.
Driessen EM, van Roon EH, Spijkers-Hagelstein JA, Schneider P, de Lorenzo P, Valsecchi MG et al. Frequencies and prognostic impact of RAS mutations in MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia in infants. Haematologica 2013; 98: 937–944.
Deshpande AJ, Chen L, Fazio M, Sinha AU, Bernt KM, Banka D et al. Leukemic transformation by the MLL-AF6 fusion oncogene requires the H3K79 methyltransferase Dot1l. Blood 2013; 121: 2533–2541.
Stumpel DJ, Schneider P, van Roon EH, Boer JM, de Lorenzo P, Valsecchi MG et al. Specific promoter methylation identifies different subgroups of MLL-rearranged infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia, influences clinical outcome, and provides therapeutic options. Blood 2009; 114: 5490–5498.
Stumpel DJ, Schneider P, van Roon EH, Pieters R, Stam RW . Absence of global hypomethylation in promoter hypermethylated Mixed Lineage Leukaemia-rearranged infant acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Eur J Cancer 2012; 49: 175–184.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by FIS/FEDER (PI10/00449 to PM and PI11/00119 to CB), The Spanish Association Against Cancer to PM. CB is supported by a ‘Miguel Servet’ Fellowship (CP07/0059). RMo is supported by The ISCIII (CA10/01332). DR-M and CPri are supported by PFIS scholarships. PM is an ICREA investigator. His research is supported by ISCIII Red de Terapia Celular (Tercel; RD12/0019/0006).
Author contributions
RMo, VA, CB and PM designed the research; RMo, VA, CB, AB, RMa, CC, PJR, DR-M, OM-N and CP performed the research and analyzed the data; and RMo, CB and PM wrote the paper. The manuscript has been seen and approved by all authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montes, R., Ayllón, V., Prieto, C. et al. Ligand-independent FLT3 activation does not cooperate with MLL-AF4 to immortalize/transform cord blood CD34+ cells. Leukemia 28, 666–674 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.346
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.346
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Increased baseline RASGRP1 signals enhance stem cell fitness during native hematopoiesis
Oncogene (2020)
-
Molecular processes involved in B cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2018)
-
NG2 antigen is involved in leukemia invasiveness and central nervous system infiltration in MLL-rearranged infant B-ALL
Leukemia (2018)