Abstract
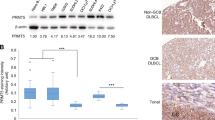
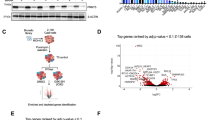
Protein tyrosine phosphatases such as PTPN6 can be downregulated in various neoplasms. PTPN6 expression by immunohistochemistry in 40 diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) tumors was lost or suppressed in 53% (21/40). To elucidate the molecular mechanisms of PTPN6 suppression, we performed a comprehensive epigenetic analysis of PTPN6 promoter 2 (P2). None of the DLBCL primary tumors (0/37) had PTPN6 hypermethylation on the CpG1 island using methylation-specific PCR, pyrosequencing, and high-resolution melting assays. However, hypermethylation in 57% (21/37) of cases was found in a novel CpG island (CpG2) in P2. PTPN6 gene suppression was reversed by 5-aza-deoxycytidine (5-Aza), a DNA methyltransferase inhibitor, and the histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi) LBH589. LBH589 and 5-Aza in combination inhibited DLBCL survival and PTPN6 hypermethylation at CpG2. The role of histone modifications was investigated with a chromatin-immunoprecipitation assay demonstrating that PTPN6 P2 is associated with silencing histone marks H3K27me3 and H3K9me3 in DLBCL cells but not normal B cells. 3-Deazaneplanocin A, a histone methyltransferase inhibitor, decreased the H3K27me3 mark, whereas HDACi LBH589 increased the H3K9Ac mark within P2 resulting in re-expression of PTPN6. These studies have uncovered novel epigenetic mechanisms of PTPN6 suppression and suggest that PTPN6 may be a potential target of epigenetic therapy in DLBCL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Habermann TM, Weller EA, Morrison VA, Gascoyne RD, Cassileth PA, Cohn JB et al. Rituximab-CHOP versus CHOP alone or with maintenance rituximab in older patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 3121–3127.
Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, Herbrecht R, Tilly H, Bouabdallah R et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 235–242.
Witzig TE, Reeder CB, LaPlant BR, Gupta M, Johnston PB, Micallef IN et al. A phase II trial of the oral mTOR inhibitor everolimus in relapsed aggressive lymphoma. Leukemia 2011; 25: 341–347.
Lam LT, Wright G, Davis RE, Lenz G, Farinha P, Dang L et al. Cooperative signaling through the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and nuclear factor-{kappa}B pathways in subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2008; 111: 3701–3713.
Ding BB, Yu JJ, Yu RY, Mendez LM, Shaknovich R, Zhang Y et al. Constitutively activated STAT3 promotes cell proliferation and survival in the activated B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2008; 111: 1515–1523.
Gupta M, Maurer MJ, Wellik LE, Law ME, Han JJ, Ozsan N et al. Expression of Myc, but not pSTAT3, is an adverse prognostic factor for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with epratuzumab/R-CHOP. Blood 2012; 120: 4400–4406.
Gupta M, Han JJ, Stenson M, Wellik L, Witzig TE . Regulation of STAT3 by histone deacetylase-3 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: implications for therapy. Leukemia 2012; 26: 1356–1364.
O'Shea JJ, Gadina M, Schreiber RD . Cytokine signaling in 2002: new surprises in the Jak/Stat pathway. Cell 2002; 109 (Suppl): S121–S131.
Yoshida K, Kharbanda S, Kufe D . Functional interaction between SHPTP1 and the Lyn tyrosine kinase in the apoptotic response to DNA damage. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 34663–34668.
Jiao H, Berrada K, Yang W, Tabrizi M, Platanias LC, Yi T . Direct association with and dephosphorylation of Jak2 kinase by the SH2-domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1. Mol Cell Biol 1996; 16: 6985–6992.
Han Y, Amin HM, Frantz C, Franko B, Lee J, Lin Q et al. Restoration of shp1 expression by 5-AZA-2'-deoxycytidine is associated with downregulation of JAK3/STAT3 signaling in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2006; 20: 1602–1609.
Banville D, Stocco R, Shen SH . Human protein tyrosine phosphatase 1C (PTPN6) gene structure: alternate promoter usage and exon skipping generate multiple transcripts. Genomics 1995; 27: 165–173.
Paling NR, Welham MJ . Tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 acts at different stages of development to regulate hematopoiesis. Blood 2005; 105: 4290–4297.
Wu C, Sun M, Liu L, Zhou GW . The function of the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 in cancer. Gene 2003; 306: 1–12.
Tsui FW, Martin A, Wang J, Tsui HW . Investigations into the regulation and function of the SH2 domain-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase, SHP-1. Immunologic Res 2006; 35: 127–136.
Oka T, Yoshino T, Hayashi K, Ohara N, Nakanishi T, Yamaai Y et al. Reduction of hematopoietic cell-specific tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 gene expression in natural killer cell lymphoma and various types of lymphomas/leukemias: combination analysis with cDNA expression array and tissue microarray. Am J Pathol 2001; 159: 1495–1505.
Oka T, Ouchida M, Koyama M, Ogama Y, Takada S, Nakatani Y et al. Gene silencing of the tyrosine phosphatase SHP1 gene by aberrant methylation in leukemias/lymphomas. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 6390–6394.
Chim CS, Fung TK, Cheung WC, Liang R, Kwong YL . SOCS1 and SHP1 hypermethylation in multiple myeloma: implications for epigenetic activation of the Jak/STAT pathway. Blood 2004; 103: 4630–4635.
Chim CS, Wong AS, Kwong YL . Epigenetic dysregulation of the Jak/STAT pathway by frequent aberrant methylation of SHP1 but not SOCS1 in acute leukaemias. Ann Hematol 2004; 83: 527–532.
Micallef IN, Maurer MJ, Wiseman GA, Nikcevich DA, Kurtin PJ, Cannon MW et al. Epratuzumab with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone chemotherapy in patients with previously untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2011; 118: 4053–4061.
Li LC, Dahiya R . MethPrimer: designing primers for methylation PCRs. Bioinformatics 2002; 18: 1427–1431.
Ronaghi M . Pyrosequencing sheds light on DNA sequencing. Genome Res 2001; 11: 3–11.
Lynch M, Chen L, Ravitz MJ, Mehtani S, Korenblat K, Pazin MJ et al. hnRNP K binds a core polypyrimidine element in the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) promoter, and its regulation of eIF4E contributes to neoplastic transformation. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25: 6436–6453.
Gupta M, Dillon SR, Ziesmer SC, Feldman AL, Witzig TE, Ansell SM et al. A proliferation-inducing ligand mediates follicular lymphoma B-cell proliferation and cyclin D1 expression through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-regulated mammalian target of rapamycin activation. Blood 2009; 113: 5206–5216.
Koyama M, Oka T, Ouchida M, Nakatani Y, Nishiuchi R, Yoshino T et al. Activated proliferation of B-cell lymphomas/leukemias with the SHP1 gene silencing by aberrant CpG methylation. Lab Invest 2003; 83: 1849–1858.
Dupont JM, Tost J, Jammes H, Gut IG . De novo quantitative bisulfite sequencing using the pyrosequencing technology. Anal Biochem 2004; 333: 119–127.
Colella S, Shen L, Baggerly KA, Issa JP, Krahe R . Sensitive and quantitative universal Pyrosequencing methylation analysis of CpG sites. Biotechniques 2003; 35: 146–150.
Candiloro IL, Mikeska T, Dobrovic A . Assessing combined methylation-sensitive high resolution melting and pyrosequencing for the analysis of heterogeneous DNA methylation. Epigenetics 2011; 6: 500–507.
Chou TC, Talalay P . Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul 1984; 22: 27–55.
Tan J, Yang X, Zhuang L, Jiang X, Chen W, Lee PL et al. Pharmacologic disruption of Polycomb-repressive complex 2-mediated gene repression selectively induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Genes Dev 2007; 21: 1050–1063.
Zhang Q, Raghunath PN, Vonderheid E, Odum N, Wasik MA . Lack of phosphotyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 expression in malignant T-cell lymphoma cells results from methylation of the SHP-1 promoter. Am J Pathol 2000; 157: 1137–1146.
Migone TS, Cacalano NA, Taylor N, Yi T, Waldmann TA, Johnston JA . Recruitment of SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 to the interleukin 2 receptor; loss of SHP-1 expression in human T-lymphotropic virus type I-transformed T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 3845–3850.
Khoury JD, Rassidakis GZ, Medeiros LJ, Amin HM, Lai R . Methylation of SHP1 gene and loss of SHP1 protein expression are frequent in systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Blood 2004; 104: 1580–1581.
Amara K, Trimeche M, Ziadi S, Laatiri A, Hachana M, Korbi S . Prognostic significance of aberrant promoter hypermethylation of CpG islands in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Ann Oncol 2008; 19: 1774–1786.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported through Iowa/Mayo Lymphoma Specialized Program of Research Excellence (P50 CA097274) to MG; R01CA127433 to TEW and the Predolin Foundation.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
TEW interpreted data, wrote the manuscript and provided clinical samples. GH performed the PTPN6 methylation (MSP-PCR and pyrosequencing for CpG1 and CpG2) and ChIP assay. SMO performed high-resolution methylation array. LEW performed PTPN6 IHC staining. MJS performed apoptosis. JJH performed PTPN6 western blotting and PTPN6 Q-PCR. AD scored and reviewed PTPN6 IHC slides. RBD edited the paper. MG designed and supervised the research, interpreted and analyzed the data, finalized the figures and wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Witzig, T., Hu, G., Offer, S. et al. Epigenetic mechanisms of protein tyrosine phosphatase 6 suppression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: implications for epigenetic therapy. Leukemia 28, 147–154 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.251
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.251
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
PGD2 displays distinct effects in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma depending on different concentrations
Cell Death Discovery (2023)
-
SHP1 loss augments DLBCL cellular response to ibrutinib: a candidate predictive biomarker
Oncogene (2023)
-
Novel targets for immunotherapy associated with exhausted CD8 + T cells in cancer
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2023)
-
Inhibition of SYK or BTK augments venetoclax sensitivity in SHP1-negative/BCL-2-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Leukemia (2019)
-
Prognostic and therapeutic significance of phosphorylated STAT3 and protein tyrosine phosphatase-6 in peripheral-T cell lymphoma
Blood Cancer Journal (2018)