Abstract
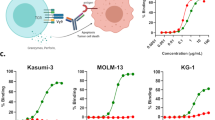
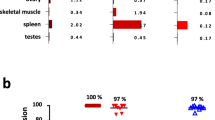
Owing to their clinical success, there is growing interest in novel bispecific antibodies (bsAbs) for retargeting of T cells to tumor cells including for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). One potential target for retargeting of T cells to AML blasts is the surface molecule CD33. Here we describe a novel modular targeting platform that consists of a universal effector module (EM) and individual target modules (TMs). Both modules can form an immune complex via a peptide epitope. The resulting targeting complex can functionally replace a conventional bsAb. By fusion of a costimulatory domain (for example, the extracellular CD137 ligand domain) to the TM, the targeting complex can even provide a costimulatory signal to the redirected T cells at their side of interaction with the tumor cell. Furthermore, we observed that an efficient killing of tumor cells expressing low levels of the tumor target CD33 becomes critical at low effector-to-target cell ratios but can be improved by costimulation via CD137 using our novel targeting system.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Müller D, Kontermann RE . Bispecific antibodies for cancer immunotherapy: current perspectives. BioDrugs 2010; 24: 89–98.
Stamova S, Koristka S, Keil J, Arndt C, Feldmann A, Michalk I et al. Cancer immunotherapy by retargeting of immune effector cells via recombinant bispecific antibody constructs. Antibodies 2012; 1: 172–198.
Hoffmann P, Hofmeister R, Brischwein K, Brandl C, Crommer S, Bargou R et al. Serial killing of tumor cells by cytotoxic T cells redirected with a CD19-/CD3-bispecific single-chain antibody construct. Int J Cancer 2005; 115: 98–104.
Offner S, Hofmeister R, Romaniuk A, Kufer P, Baeuerle PA . Induction of regular cytolytic T cell synapses by bispecific single-chain antibody constructs on MHC class I-negative tumor cells. Mol Immunol 2006; 43: 763–771.
Stamova S, Feldmann A, Cartellieri M, Arndt C, Koristka S, Apel F et al. Generation of single-chain bispecific green fluorescent protein fusion antibodies for imaging of antibody-induced T cell synapses. Anal Biochem 2012; 423: 261–268.
Bargou R, Leo E, Zugmaier G, Klinger M, Goebeler M, Knop S et al. Tumor regression in cancer patients by very low doses of a T cell-engaging antibody. Science 2008; 321: 974–977.
Nagorsen D, Baeuerle PA . Immunomodulatory therapy of cancer with T cell-engaging BiTE antibody blinatumomab. Exp Cell Res 2011; 317: 1255–1260.
Topp MS, Kufer P, Gökbuget N, Goebeler M, Klinger M, Neumann S et al. Targeted therapy with the T-cell-engaging antibody blinatumomab of chemotherapy-refractory minimal residual disease in B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients results in high response rate and prolonged leukemia-free survival. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 2493–2498.
Klinger M, Brandl C, Zugmaier G, Hijazi Y, Bargou RC, Topp MS et al. Immunopharmacologic response of patients with B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia to continuous infusion of T cell-engaging CD19/CD3-bispecific BiTE antibody blinatumomab. Blood 2012; 119: 6226–6233.
Feldmann A, Stamova S, Bippes CC, Bartsch H, Wehner R, Schmitz M et al. Retargeting of T cells to prostate stem cell antigen expressing tumor cells: comparison of different antibody formats. Prostate 2011; 71: 998–1011.
Robak T, Wierzbowska A . Current and emerging therapies for acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Ther 2009; 31: 2349–2370.
Zhong RK, Lane TA, Ball ED . Generation of T-cell lines to autologous acute myeloid leukemia cells by competitive limiting dilution culture of acute myeloid leukemia mononuclear cells. Exp Hematol 2008; 36: 486–494.
Draube A, Beyer M, Wolf J . Activation of autologous leukemia-specific T cells in acute myeloid leukemia: monocyte-derived dendritic cells cocultured with leukemic blasts compared with leukemia-derived dendritic cells. Eur J Haematol 2008; 81: 281–288.
Rezvani K, Yong AS, Tawab A, Jafarpour B, Eniafe R, Mielke S et al. Ex vivo characterization of polyclonal memory CD8+ T-cell responses to PRAME-specific peptides in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and acute and chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2009; 113: 2245–2255.
Bornhäuser M, Thiede C, Platzbecker U, Kiani A, Oelschlaegel U, Babatz J et al. Prophylactic transfer of BCR-ABL-, PR1-, and WT1-reactive donor T cells after T cell-depleted allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2011; 117: 7174–7184.
Stamova S, Cartellieri M, Feldmann A, Bippes CC, Bartsch H, Wehner R et al. Simultaneous engagement of the activatory receptors NKG2D and CD3 for retargeting of effector cells to CD33-positive malignant cells. Leukemia 2011; 25: 1053–1056.
Aigner M, Feulner J, Schaffer S, Kischel R, Kufer P, Schneider K et al. T lymphocytes can be effectively recruited for ex vivo and in vivo lysis of AML blasts by a novel CD33/CD3-bispecific BiTE antibody construct. Leukemia 2013; 27: 1107–1115.
Arndt C, von Bonin M, Cartellieri M, Feldmann A, Koristka S, Michalk I et al. Redirection of T cells with a first fully humanized bispecific CD33-CD3 antibody efficiently eliminates AML blasts without harming hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia 2013; 27: 964–967.
Dinndorf PA, Andrews RG, Benjamin D, Ridgway D, Wolff L, Bernstein ID . Expression of normal myeloid-associated antigens by acute leukemia cells. Blood 1986; 67: 1048–1053.
Legrand O, Perrot JY, Baudard M, Cordier A, Lautier R, Simonin G et al. The immunophenotype of 177 adults with acute myeloid leukemia: proposal of a prognostic score. Blood 2000; 96: 870–877.
Feldmann A, Arndt C, Töpfer K, Stamova S, Krone F, Cartellieri M et al. Novel humanized and highly efficient bispecific antibodies mediate killing of prostate stem cell antigen-expressing tumor cells by CD8+ and CD4+ T cells. J Immunol 2012; 189: 3249–3259.
Stamova S, Cartellieri M, Feldmann A, Arndt C, Koristka S, Bartsch H et al. Unexpected recombinations in single chain bispecific anti-CD3-anti-CD33 antibodies can be avoided by a novel linker module. Mol Immunol 2011; 49: 474–482.
Koristka S, Cartellieri M, Arndt C, Bippes CC, Feldmann A, Michalk I et al. Retargeting of regulatory T cells to surface-inducible autoantigen La/SS-B. J Autoimmun 2013; 42: 105–116.
Koristka S, Cartellieri M, Theil A, Feldmann A, Arndt C, Stamova S et al. Retargeting of human regulatory T cells by single-chain bispecific antibodies. J Immunol 2012; 188: 1551–1558.
Carmo-Fonseca M, Pfeifer K, Schröder HC, Vaz MF, Fonseca JE, Müller WE et al. Identification of La ribonucleoproteins as a component of interchromatin granules. Exp Cell Res 1989; 185: 73–85.
Dreier T, Baeuerle PA, Fichtner I, Grün M, Schlereth B, Lorenczewski G et al. T cell costimulus-independent and very efficacious inhibition of tumor growth in mice bearing subcutaneous or leukemic human B cell lymphoma xenografts by a CD19-/CD3- bispecific single-chain antibody construct. J Immunol 2003; 170: 4397–4402.
Schlereth B, Quadt C, Dreier T, Kufer P, Lorenczewski G, Prang N et al. T-cell activation and B-cell depletion in chimpanzees treated with a bispecific anti-CD19/anti-CD3 single-chain antibody construct. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2006; 55: 503–514.
Lutterbuese R, Raum T, Kischel R, Lutterbuese P, Schlereth B, Schaller E et al. Potent control of tumor growth by CEA/CD3-bispecific single-chain antibody constructs that are not competitively inhibited by soluble CEA. J Immunother 2009; 32: 341–352.
Amann M, D'Argouges S, Lorenczewski G, Brischwein K, Kischel R, Lutterbuese R et al. Antitumor activity of an EpCAM/CD3-bispecific BiTE antibody during long-term treatment of mice in the absence of T-cell anergy and sustained cytokine release. J Immunother 2009; 32: 452–464.
Fortmüller K, Alt K, Gierschner D, Wolf P, Baum V, Freudenberg N et al. Effective targeting of prostate cancer by lymphocytes redirected by a PSMA × CD3 bispecific single-chain diabody. Prostate 2011; 71: 588–596.
Berthon C, Driss V, Liu J, Kuranda K, Leleu X, Jouy N et al. In acute myeloid leukemia, B7-H1 (PD-L1) protection of blasts from cytotoxic T cells is induced by TLR ligands and interferon-gamma and can be reversed using MEK inhibitors. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2010; 59: 1839–1849.
Ma Q, Wang C, Jones D, Quintanilla KE, Li D, Wang Y et al. Adoptive transfer of PR1 cytotoxic T lymphocytes associated with reduced leukemia burden in a mouse acute myeloid leukemia xenograft model. Cytotherapy 2010; 12: 1056–1062.
Hornig N, Kermer V, Frey K, Diebolder P, Kontermann RE, Müller D . Combination of a bispecific antibody and costimulatory antibody-ligand fusion proteins for targeted cancer immunotherapy. J Immunother 2012; 35: 418–429.
Cunha AC, Weigle B, Kiessling A, Bachmann M, Rieber EP . Tissue-specificity of prostate specific antigens: comparative analysis of transcript levels in prostate and non-prostatic tissues. Cancer Lett 2006; 236: 229–238.
Kloss CC, Condomines M, Cartellieri M, Bachmann M, Sadelain M . Combinatorial antigen recognition with balanced signaling promotes selective tumor eradication by engineered T cells. Nat Biotechnol 2013; 31: 71–75.
Dreier T, Lorenczewski G, Brandl C, Hoffmann P, Syring U, Hanakam F et al. Extremely potent, rapid and costimulation-independent cytotoxic T-cell response against lymphoma cells catalyzed by a single-chain bispecific antibody. Int J Cancer 2002; 100: 690–697.
Haas C, Krinner E, Brischwein K, Hoffmann P, Lutterbüse R, Schlereth B et al. Mode of cytotoxic action of T cell-engaging BiTE antibody MT110. Immunobiology 2009; 214: 441–453.
Holliger P, Hudson PJ . Engineered antibody fragments and the rise of single domains. Nat Biotechnol 2005; 23: 1126–1136.
Yokota T, Milenic DE, Whitlow M, Schlom J . Rapid tumor penetration of a single-chain Fv and comparison with other immunoglobulin forms. Cancer Res 1992; 52: 3402–3408.
Acknowledgements
We thank Livia Schulze, Kristin Heidel, Barbara Uteß and Christine Gräfe for their excellent technical assistance; Professor Dr Dirk Lindemann for providing us with the lentiviral vector system; and Professor Dr Christian Thiede for providing the CD33+ cell lines MOLM-13, MV4-11 and OCI-AML3. This study was supported by a grant of the Medical faculty of the Technical University Dresden to Marc Cartellieri, a seed grant by the Center for Regenerative Therapies Dresden (CRTD), Technical University Dresden, and the José Carreras Stiftung to Michael Bachmann.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
MB, SS and GE have filed provisional patent application related to the antibodies directed to CD33 and La.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arndt, C., Feldmann, A., von Bonin, M. et al. Costimulation improves the killing capability of T cells redirected to tumor cells expressing low levels of CD33: description of a novel modular targeting system. Leukemia 28, 59–69 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.243
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.243
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The landscape of bispecific T cell engager in cancer treatment
Biomarker Research (2021)
-
Extended half-life target module for sustainable UniCAR T-cell treatment of STn-expressing cancers
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2020)
-
Challenges and strategies for next-generation bispecific antibody-based antitumor therapeutics
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2020)
-
An oligo-His-tag of a targeting module does not influence its biodistribution and the retargeting capabilities of UniCAR T cells
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Conventional CARs versus modular CARs
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2019)