Abstract
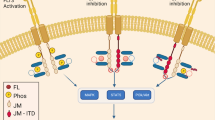
FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) normally functions in the survival/proliferation of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells, but its constitutive activation by internal tandem duplication (ITD) mutations correlates with a poor prognosis in AML. The development of FLT3 tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) is a promising strategy, but resistance that arises during the course of treatment caused by secondary mutations within the mutated gene itself poses a significant challenge. In an effort to predict FLT3 resistance mutations that might develop in patients, we used saturation mutagenesis of FLT3/ITD followed by selection of transfected cells in FLT3 TKI. We identified F621L, A627P, F691L and Y842C mutations in FLT3/ITD that confer varying levels of resistance to FLT3 TKI. Western blotting confirmed that some FLT3 TKI were ineffective at inhibiting FLT3 autophosphorylation and signaling through MAP kinase, STAT5 and AKT in some mutants. Balb/c mice transplanted with the FLT3/ITD Y842C mutation confirmed resistance to sorafenib in vivo but not to lestaurtinib. These results indicate a growing number of FLT3 mutations that are likely to be encountered in patients. Such knowledge, combined with known remaining sensitivity to other FLT3 TKI, will be important to establish as secondary drug treatments that can be substituted when these mutants are encountered.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Small D, Levenstein M, Kim E, Carrow C, Amin S, Rockwell P et al. STK-1, the human homolog of Flk-2/Flt-3, is selectively expressed in CD34+ human bone marrow cells and is involved in the proliferation of early progenitor/stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 459–463.
Rosnet O, Schiff C, Pebusque MJ, Marchetto S, Tonnelle C, Toiron Y et al. Human FLT3/FLK2 gene: cDNA cloning and expression in hematopoietic cells. Blood 1993; 82: 1110–1119.
Lavagna-Sevenier C, Marchetto S, Birnbaum D, Rosnet O . FLT3 signaling in hematopoietic cells involves CBL, SHC and an unknown P115 as prominent tyrosine-phosphorylated substrates. Leukemia 1998; 12: 301–310.
Rosnet O, Buhring HJ, deLapeyriere O, Beslu N, Lavagna C, Marchetto S et al. Expression and signal transduction of the FLT3 tyrosine kinase receptor. Acta Haematol 1996; 95: 218–223.
Lyman SD, James L, Vanden Bos T, de Vries P, Brasel K, Gliniak B et al. Molecular cloning of a ligand for the flt3/flk-2 tyrosine kinase receptor: a proliferative factor for primitive hematopoietic cells. Cell 1993; 75: 1157–1167.
Zhang S, Broxmeyer HE . Flt3 ligand induces tyrosine phosphorylation of gab1 and gab2 and their association with shp-2, grb2, and PI3 kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000; 277: 195–199.
Brown P, Levis M, Shurtleff S, Campana D, Downing J, Small D . FLT3 inhibition selectively kills childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells with high levels of FLT3 expression. Blood 2005; 105: 812–820.
Armstrong SA, Staunton JE, Silverman LB, Pieters R, den Boer ML, Minden MD et al. MLL translocations specify a distinct gene expression profile that distinguishes a unique leukemia. Nat Genet 2002; 30: 41–47.
Zheng R, Levis M, Piloto O, Brown P, Baldwin BR, Gorin NC et al. FLT3 ligand causes autocrine signaling in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood 2004; 103: 267–274.
Nakao M, Yokota S, Iwai T, Kaneko H, Horiike S, Kashima K et al. Internal tandem duplication of the flt3 gene found in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 1996; 10: 1911–1918.
Abu-Duhier FM, Goodeve AC, Wilson GA, Care RS, Peake IR, Reilly JT . Identification of novel FLT-3 Asp835 mutations in adult acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2001; 113: 983–988.
Yamamoto Y, Kiyoi H, Nakano Y, Suzuki R, Kodera Y, Miyawaki S et al. Activating mutation of D835 within the activation loop of FLT3 in human hematologic malignancies. Blood 2001; 97: 2434–2439.
Griffith J, Black J, Faerman C, Swenson L, Wynn M, Lu F et al. The structural basis for autoinhibition of FLT3 by the juxtamembrane domain. Mol Cell 2004; 13: 169–178.
Smith CC, Wang Q, Chin CS, Salerno S, Damon LE, Levis MJ et al. Validation of ITD mutations in FLT3 as a therapeutic target in human acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature 2012; 485: 260–263.
Alvarado Y, Kantarjian H, Ravandi F, Luthra R, Borthakur G, Manero GG et al. FLT3 inhibitor treatment in FLT3-mutated AML is associated with development of secondary FLT3-TKD mutations. Blood 2011; 118: 1493.
Zhang W, Konopleva M, Jacamo RO, Borthakur G, Chen W, Cortes JE et al. Acquired point mutations of TKD are responsible for sorafenib resistance in FLT3-ITD mutant AML. Blood 2011, 118.
Cools J, Mentens N, Furet P, Fabbro D, Clark JJ, Griffin JD et al. Prediction of resistance to small molecule FLT3 inhibitors: implications for molecularly targeted therapy of acute leukemia. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 6385–6389.
von Bubnoff N, Engh RA, Aberg E, Sanger J, Peschel C, Duyster J . FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3-internal tandem duplication tyrosine kinase inhibitors display a nonoverlapping profile of resistance mutations in vitro. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 3032–3041.
Bagrintseva K, Schwab R, Kohl TM, Schnittger S, Eichenlaub S, Ellwart JW et al. Mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of FLT3 define a new molecular mechanism of acquired drug resistance to PTK inhibitors in FLT3-ITD-transformed hematopoietic cells. Blood 2004; 103: 2266–2275.
Zhou J, Bi C, Janakakumara JV, Liu SC, Chng WJ, Tay KG et al. Enhanced activation of STAT pathways and overexpression of survivin confer resistance to FLT3 inhibitors and could be therapeutic targets in AML. Blood 2009; 113: 4052–4062.
Stolzel F, Steudel C, Oelschlagel U, Mohr B, Koch S, Ehninger G et al. Mechanisms of resistance against PKC412 in resistant FLT3-ITD positive human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Ann Hematol 89: 653–662.
Prescott H, Kantarjian H, Cortes J, Ravandi F . Emerging FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 inhibitors for the treatment of acute myelogenous leukemia. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 2011; 16: 407–423.
Tse KF, Allebach J, Levis M, Smith BD, Bohmer FD, Small D . Inhibition of the transforming activity of FLT3 internal tandem duplication mutants from AML patients by a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Leukemia 2002; 16: 2027–2036.
Azam M, Latek RR, Daley GQ . Mechanisms of autoinhibition and STI-571/imatinib resistance revealed by mutagenesis of BCR-ABL. Cell 2003; 112: 831–843.
Levis M, Allebach J, Tse KF, Zheng R, Baldwin BR, Smith BD et al. A FLT3-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor is cytotoxic to leukemia cells in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2002; 99: 3885–3891.
Tse KF, Mukherjee G, Small D . Constitutive activation of FLT3 stimulates multiple intracellular signal transducers and results in transformation. Leukemia 2000; 14: 1766–1776.
Zhu X, Kim JL, Newcomb JR, Rose PE, Stover DR, Toledo LM et al. Structural analysis of the lymphocyte-specific kinase Lck in complex with non-selective and Src family selective kinase inhibitors. Structure 1999; 7: 651–661.
Wood ER, Truesdale AT, McDonald OB, Yuan D, Hassell D, Dickerson SH et al. A unique structure for epidermal growth factor receptor bound to GW572016 (Lapatinib): relationships among protein conformation, inhibitor off-rate, and receptor activity in tumor cells. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 6652–6659.
Simard JR, Grutter C, Pawar V, Aust B, Wolf A, Rabiller M et al. High-throughput screening to identify inhibitors which stabilize inactive kinase conformations in p38alpha. J Am Chem Soc 2009; 131: 18478–18488.
Grebien F, Hantschel O, Wojcik J, Kaupe I, Kovacic B, Wyrzucki AM et al. Targeting the SH2-kinase interface in Bcr-Abl inhibits leukemogenesis. Cell 2011; 147: 306–319.
Breitenbuecher F, Markova B, Kasper S, Carius B, Stauder T, Bohmer FD et al. A novel molecular mechanism of primary resistance to FLT3-kinase inhibitors in AML. Blood 2009; 113: 4063–4073.
el-Shami K, Stone RM, Smith BD . FLT3 inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia. Expert Rev Hematol 2008; 1: 153–160.
Knapper S, Mills KI, Gilkes AF, Austin SJ, Walsh V, Burnett AK . The effects of lestaurtinib (CEP701) and PKC412 on primary AML blasts: the induction of cytotoxicity varies with dependence on FLT3 signaling in both FLT3-mutated and wild-type cases. Blood 2006; 108: 3494–3503.
Siendones E, Barbarroja N, Torres LA, Buendia P, Velasco F, Dorado G et al. Inhibition of Flt3-activating mutations does not prevent constitutive activation of ERK/Akt/STAT pathways in some AML cells: a possible cause for the limited effectiveness of monotherapy with small-molecule inhibitors. Hematol Oncol 2007; 25: 30–37.
Kurzrock R, Talpaz M . The molecular pathology of chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Br J Haematol 1991; 79 (Suppl 1): 34–37.
Druker BJ . Current treatment approaches for chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer J. 2001; 7 (Suppl 1): S14–S18.
Druker BJ, Talpaz M, Resta DJ, Peng B, Buchdunger E, Ford JM et al. Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2001; 344: 1031–1037.
O′Brien SG, Guilhot F, Larson RA, Grathman I, Baccarani M, Cervantes F et al. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 994–1004.
Apperley JF, Part I . mechanisms of resistance to imatinib in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Lancet Oncol 2007; 8: 1018–1029.
O′Hare T, Deininger MW, Eide CA, Clackson T, Druker BJ . Targeting the BCR-ABL signaling pathway in therapy-resistant Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 212–221.
Soverini S, Hochhaus A, Nicolini FE, Gruber F, Lange T, Saglio g et al. BCR-ABL kinase domain mutation analysis in chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: recommendations from an expert panel on behalf of European LeukemiaNet. Blood 2011; 118: 1208–1215.
Clark JJ, Cools J, Curley DP, Yu JC, Lokker NA, Giese NA et al. Variable sensitivity of FLT3 activation loop mutations to the small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor MLN518. Blood 2004; 104: 2867–2872.
Liu Y, Gray NS . Rational design of inhibitors that bind to inactive kinase conformations. Nat Chem Biol 2006; 2: 358–364.
Cowan-Jacob SW, Fendrich G, Floersheimer A, Furet P, Liebetanz J, Rummel G et al. Structural biology contributions to the discovery of drugs to treat chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 2007; 63: 80–93.
Weisberg E, Roesel J, Furet P, Bold G, Imbach P, Florsheimer J et al. Antileukemic effects of novel first- and second-generation FLT3 inhibitors: structure-affinity comparison. Genes Cancer 2010; 1: 1021–1032.
von Bubnoff N, Rummelt C, Menzel H, Sigl M, Peschel C, Duyster J . Identification of a secondary FLT3/A848P mutation in a patient with FLT3-ITD-positive blast phase CMML and response to sunitinib and sorafenib. Leukemia 2010; 24: 1523–1525.
Kindler T, Breitenbuecher F, Kasper S, Estey E, Giles F, Feldman E et al. Identification of a novel activating mutation (Y842C) within the activation loop of FLT3 in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Blood 2005; 105: 335–340.
Jiang J, Paez JG, Lee JC, Bo R, Stone RM, DeAngelo DJ et al. Identifying and characterizing a novel activating mutation of the FLT3 tyrosine kinase in AML. Blood 2004; 104: 1855–1858.
Mony U, Jawad M, Seedhouse C, Russell N, Pallis M . Resistance to FLT3 inhibition in an in vitro model of primary AML cells with a stem cell phenotype in a defined microenvironment. Leukemia 2008; 22: 1395–1401.
Sato T, Yang X, Knapper S, White P, Smith BD, Galkin S et al. FLT3 ligand impedes the efficacy of FLT3 inhibitors in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2011; 117: 3286–3293.
Yoshimoto G, Miyamoto T, Jabbarzadeh-Tabrizi S, Iino T, Rocnik JL, Kikushige Y et al. FLT3-ITD up-regulates MCL-1 to promote survival of stem cells in acute myeloid leukemia via FLT3-ITD-specific STAT5 activation. Blood 2009; 114: 5034–5043.
Heidel F, Solem FK, Breitenbuecher F, Lipka DB, Kasper S, Thiede MH et al. Clinical resistance to the kinase inhibitor PKC412 in acute myeloid leukemia by mutation of Asn-676 in the FLT3 tyrosine kinase domain. Blood 2006; 107: 293–300.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr Linzhao Cheng (Johns Hopkins University) for providing us with the L3GFP vector used to visualize FLT3/ITD engraftment and to members of the lab for numerous thoughtful discussions. This work was supported by grants from the NCI (CA90770 and CA90668), Leukemia and Lymphoma Society and Giant Food Pediatric Cancer Research Fund. DS is also supported by the Kyle Haydock Professorship.
Author contributions
ABW designed experiments, performed research, analyzed data and wrote the manuscript; LL and BN performed research; ML analyzed data; PB and DL analyzed data and wrote the manuscript; DS designed experiments, supervised the project, analyzed data and wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, A., Nguyen, B., Li, L. et al. Mutations of FLT3/ITD confer resistance to multiple tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Leukemia 27, 48–55 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.191
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.191
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Characterisation of FLT3 alterations in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
British Journal of Cancer (2024)
-
GNF-7, a novel FLT3 inhibitor, overcomes drug resistance for the treatment of FLT3‑ITD acute myeloid leukemia
Cancer Cell International (2023)
-
Blockade of de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis triggers autophagic degradation of oncoprotein FLT3-ITD in acute myeloid leukemia
Oncogene (2023)
-
An overview of arsenic trioxide-involved combined treatment algorithms for leukemia: basic concepts and clinical implications
Cell Death Discovery (2023)
-
Resistance to targeted therapies in acute myeloid leukemia
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis (2023)