Abstract
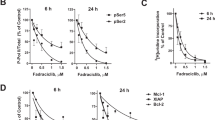
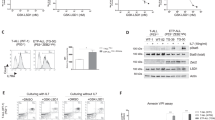
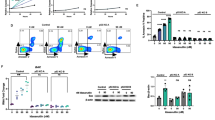
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most prevalent lymphoid malignancy in the elderly of the Western world. Although treatment options have improved over the past two decades, 10–15% of patients still have a poor prognosis and are often resistant to therapy. Aberrations in the p53 pathway, such as a deleted (del17p13) or mutated p53 gene, are highly enriched in this class of patients. In an extensive screen for p53-independent apoptosis inducers, actinomycin D was identified from 1496 substances and shown to induce apoptosis in primary CLL cells derived from high-risk patients including those with aberrant p53, revealing a novel p53-independent mechanism of action. Both pro-survival genes BCL2 and MCL1 are targeted by actinomycin D, in contrast to fludarabine the backbone of current treatment schedules. In the well-established TCL1 transgenic mouse model for high-risk CLL, actinomycin D treatment was more effective in reducing tumor load than fludarabine, with no evidence of resistance after three treatment cycles and an overall survival increase of over 300%. Tumor load reduction was coupled to BCL2 downregulation. Our results identify the clinically approved compound actinomycin D as a potentially valuable treatment option for CLL high-risk patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zenz T, Mertens D, Kuppers R, Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S . From pathogenesis to treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer 2010; 10: 37–50.
Zwiebel JA, Cheson BD . Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: staging and prognostic factors. Semin Oncol 1998; 25: 42–59.
Byrd JC, Gribben JG, Peterson BL, Grever MR, Lozanski G, Lucas DM et al. Select high-risk genetic features predict earlier progression following chemoimmunotherapy with fludarabine and rituximab in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: justification for risk-adapted therapy. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 437–443.
Dohner H, Fischer K, Bentz M, Hansen K, Benner A, Cabot G et al. p53 gene deletion predicts for poor survival and non-response to therapy with purine analogs in chronic B-cell leukemias. Blood 1995; 85: 1580–1589.
Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S, Benner A, Leupolt E, Krober A, Bullinger L et al. Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 1910–1916.
Eichhorst BF, Busch R, Hopfinger G, Pasold R, Hensel M, Steinbrecher C et al. Fludarabine plus cyclophosphamide versus fludarabine alone in first-line therapy of younger patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2006; 107: 885–891.
Grever MR, Lucas DM, Dewald GW, Neuberg DS, Reed JC, Kitada S et al. Comprehensive assessment of genetic and molecular features predicting outcome in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: results from the US Intergroup Phase III Trial E2997. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 799–804.
Lozanski G, Heerema NA, Flinn IW, Smith L, Harbison J, Webb J et al. Alemtuzumab is an effective therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia with p53 mutations and deletions. Blood 2004; 103: 3278–3281.
Rossi D, Cerri M, Deambrogi C, Sozzi E, Cresta S, Rasi S et al. The prognostic value of TP53 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is independent of Del17p13: implications for overall survival and chemorefractoriness. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 995–1004.
Zenz T, Krober A, Scherer K, Habe S, Buhler A, Benner A et al. Monoallelic TP53 inactivation is associated with poor prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: results from a detailed genetic characterization with long-term follow-up. Blood 2008; 112: 3322–3329.
Rossi D, Deaglio S, Dominguez-Sola D, Rasi S, Vaisitti T, Agostinelli C et al. Alteration of BIRC3 and multiple other NF-kappaB pathway genes in splenic marginal zone lymphoma. Blood 2011; 118: 4930–4934.
Rossi D, Rasi S, Fabbri G, Spina V, Fangazio M, Forconi F et al. Mutations of NOTCH1 are an independent predictor of survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2012; 119: 521–529.
Hallek M, Fischer K, Fingerle-Rowson G, Fink AM, Busch R, Mayer J et al. Addition of rituximab to fludarabine and cyclophosphamide in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2010; 376: 1164–1174.
Stilgenbauer S, Zenz T . Understanding and managing ultra high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2010; 2010: 481–488.
Zenz T, Mertens D, Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S . Importance of genetics in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Rev 2011; 25: 131–137.
Stilgenbauer S, Dohner H . Campath-1H-induced complete remission of chronic lymphocytic leukemia despite p53 gene mutation and resistance to chemotherapy. N Engl J Med 2002; 347: 452–453.
Lin TS, Ruppert AS, Johnson AJ, Fischer B, Heerema NA, Andritsos LA et al. Phase II study of flavopiridol in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia demonstrating high response rates in genetically high-risk disease. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 6012–6018.
Phelps MA, Lin TS, Johnson AJ, Hurh E, Rozewski DM, Farley KL et al. Clinical response and pharmacokinetics from a phase 1 study of an active dosing schedule of flavopiridol in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2009; 113: 2637–2645.
Perry RP, Kelley DE . Inhibition of RNA synthesis by actinomycin D: characteristic dose-response of different RNA species. J Cell Physiol 1970; 76: 127–139.
Sobell HM . Actinomycin and DNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1985; 82: 5328–5331.
Huang P, Sandoval A, Van Den NE, Keating MJ, Plunkett W . Inhibition of RNA transcription: a biochemical mechanism of action against chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells by fludarabine. Leukemia 2000; 14: 1405–1413.
Bichi R, Shinton SA, Martin ES, Koval A, Calin GA, Cesari R et al. Human chronic lymphocytic leukemia modeled in mouse by targeted TCL1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 6955–6960.
Hofbauer JP, Heyder C, Denk U, Kocher T, Holler C, Trapin D et al. Development of CLL in the TCL1 transgenic mouse model is associated with severe skewing of the T-cell compartment homologous to human CLL. Leukemia 2011; 25: 1452–1458.
Johnson AJ, Lucas DM, Muthusamy N, Smith LL, Edwards RB, De Lay MD et al. Characterization of the TCL-1 transgenic mouse as a preclinical drug development tool for human chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2006; 108: 1334–1338.
Bertilaccio MT, Scielzo C, Simonetti G, Ponzoni M, Apollonio B, Fazi C et al. A novel Rag2-/-gammac-/--xenograft model of human CLL. Blood 2010; 115: 1605–1609.
Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D, Caligaris-Cappio F, Dighiero G, Dohner H et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a report from the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia updating the National Cancer Institute-Working Group 1996 guidelines. Blood 2008; 111: 5446–5456.
Kuhn DM, Balkis M, Chandra J, Mukherjee PK, Ghannoum MA . Uses and limitations of the XTT assay in studies of Candida growth and metabolism. J Clin Microbiol 2003; 41: 506–508.
Merkel O, Heyder C, Asslaber D, Hamacher F, Tinhofer I, Holler C et al. Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis preferentially in B-CLL cells of patients with unfavourable prognostic factors including del17p13. J Mol Med 2008; 86: 541–552.
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR, Armstrong RC, Augeri DJ, Belli BA et al. An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 2005; 435: 677–681.
Zanesi N, Aqeilan R, Drusco A, Kaou M, Sevignani C, Costinean S et al. Effect of rapamycin on mouse chronic lymphocytic leukemia and the development of nonhematopoietic malignancies in Emu-TCL1 transgenic mice. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 915–920.
Kurtova AV, Balakrishnan K, Chen R, Ding W, Schnabl S, Quiroga MP et al. Diverse marrow stromal cells protect CLL cells from spontaneous and drug-induced apoptosis: development of a reliable and reproducible system to assess stromal cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance. Blood 2009; 114: 4441–4450.
Lemoine FM, Humphries RK, Abraham SD, Krystal G, Eaves CJ . Partial characterization of a novel stromal cell-derived pre-B-cell growth factor active on normal and immortalized pre-B cells. Exp Hematol 1988; 16: 718–726.
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 13944–13949.
Contri A, Brunati AM, Trentin L, Cabrelle A, Miorin M, Cesaro L et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells contain anomalous Lyn tyrosine kinase, a putative contribution to defective apoptosis. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 369–378.
Pallasch CP, Schulz A, Kutsch N, Schwamb J, Hagist S, Kashkar H et al. Overexpression of TOSO in CLL is triggered by B-cell receptor signaling and associated with progressive disease. Blood 2008; 112: 4213–4219.
Blagosklonny MV, Alvarez M, Fojo A, Neckers LM . bcl-2 protein downregulation is not required for differentiation of multidrug resistant HL60 leukemia cells. Leuk Res 1996; 20: 101–107.
Yan XJ, Albesiano E, Zanesi N, Yancopoulos S, Sawyer A, Romano E et al. B cell receptors in TCL1 transgenic mice resemble those of aggressive, treatment-resistant human chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 11713–11718.
Tam CS, O’Brien S, Wierda W, Kantarjian H, Wen S, Do KA et al. Long-term results of the fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab regimen as initial therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2008; 112: 975–980.
Keating MJ, Flinn I, Jain V, Binet JL, Hillmen P, Byrd J et al. Therapeutic role of alemtuzumab (Campath-1H) in patients who have failed fludarabine: results of a large international study. Blood 2002; 99: 3554–3561.
Pettitt AR, Matutes E, Oscier D . Alemtuzumab in combination with high-dose methylprednisolone is a logical, feasible and highly active therapeutic regimen in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia patients with p53 defects. Leukemia 2006; 20: 1441–1445.
Green DM . The treatment of stages I-IV favorable histology Wilms' tumor. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 1366–1372.
Coll-Mulet L, Iglesias-Serret D, Santidrian AF, Cosialls AM, de Frias M, Castano E et al. MDM2 antagonists activate p53 and synergize with genotoxic drugs in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 2006; 107: 4109–4114.
Kojima K, Konopleva M, McQueen T, O'Brien S, Plunkett W, Andreeff M . Mdm2 inhibitor Nutlin-3a induces p53-mediated apoptosis by transcription-dependent and transcription-independent mechanisms and may overcome Mdm2 and Atm-mediated resistance to fludarabine in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2006; 108: 993–1000.
Secchiero P, Barbarotto E, Tiribelli M, Zerbinati C, di Iasio MG, Gonelli A et al. Functional integrity of the p53-mediated apoptotic pathway induced by the nongenotoxic agent nutlin-3 in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL). Blood 2006; 107: 4122–4129.
Kojima K, Duvvuri S, Ruvolo V, Samaniego F, Younes A, Andreeff M . Decreased sensitivity of 17p-deleted chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells to a small molecule BCL-2 antagonist ABT-737. Cancer 2012; 118: 1023–1031.
Maurer U, Charvet C, Wagman AS, Dejardin E, Green DR . Glycogen synthase kinase-3 regulates mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and apoptosis by destabilization of MCL-1. Mol Cell 2006; 21: 749–760.
Wertz IE, Kusam S, Lam C, Okamoto T, Sandoval W, Anderson DJ et al. Sensitivity to antitubulin chemotherapeutics is regulated by MCL1 and FBW7. Nature 2011; 471: 110–114.
Inuzuka H, Shaik S, Onoyama I, Gao D, Tseng A, Maser RS et al. SCF(FBW7) regulates cellular apoptosis by targeting MCL1 for ubiquitylation and destruction. Nature 2011; 471: 104–109.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Klinische Malignom und Zytokinforschung Salzburg-Innsbruck GmbH (RG), the Jubiläumsfond der Österreichischen Nationalbank (Grant 12170 to RG), Spezialforschungsprogramm P021 (RG), Fonds zur Förderung der wissenschaftlichen Forschung P-18478-B12 (LK), L488-B13 (AE), P19481-B12 (AE), the Genome Austria Research project ‘Inflammobiota’ (LK) and the Novus Sanguis Consortium, LeJeune Foundation (LK). We are grateful to Richard Moriggl for critical discussion of the manuscript.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
OM and NW designed the research. NW, ES, TM, FH and TK performed the experimental work; M Schl and LK performed H&E stains of FFPE tissues; MS provided patient material; M Sche produced mRNA arrays; UD, JPH, AE performed murine experiments; OM and NW wrote the paper; OM, LK and RG did the final approval and correction of the manuscript. OM, LK and RG contributed to project development and obtained funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merkel, O., Wacht, N., Sifft, E. et al. Actinomycin D induces p53-independent cell death and prolongs survival in high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 26, 2508–2516 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.147
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.147
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Biosensor-based active ingredient recognition system for screening TNF-α inhibitors from lotus leaves
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2023)
-
New phenoxazinone-related alkaloids from strain Streptomyces sp. KIB-H1318
The Journal of Antibiotics (2018)
-
Inhibition of neurotensin receptor 1 induces intrinsic apoptosis via let-7a-3p/Bcl-w axis in glioblastoma
British Journal of Cancer (2017)
-
Effect of low doses of actinomycin D on neuroblastoma cell lines
Molecular Cancer (2016)