Abstract
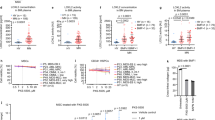
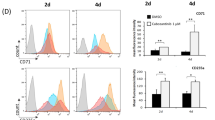
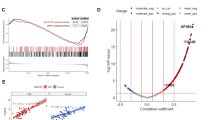
Inositide signaling pathways can have a role in the Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) progression to acute myeloid leukemia. Erythropoietin (EPO) is currently used in low-risk MDS, where it successfully corrects anemia in 50–70% of patients. However, some MDS patients are refractory to this treatment and little is known about the exact molecular mechanisms underlying the effect of EPO in these subjects. Here, we investigated the role of inositide pathways in low-risk MDS treated with EPO, mainly focusing on the Akt/PI-PLC (Phosphoinositide-Phospholipase C) gamma1 axis, which is activated by the EPO receptor, and PI-PLCbeta1/Cyclin D3 signaling, as Cyclin D3 is associated with hematopoietic proliferation and differentiation. Interestingly, EPO responder patients showed a specific activation of both the Akt/PI-PLCgamma1 pathway and beta-Globin gene expression, while nonresponders displayed an increase in PI-PLCbeta1 signaling. Moreover, in normal CD34+ cells induced to erythroid differentiation, PI-PLCbeta1 overexpression abrogated both EPO-induced Akt phosphorylation and beta-Globin expression. Overall, these findings suggest that PI-PLCbeta1 can act as a negative regulator of erythroid differentiation and confirm the involvement of Akt/PI-PLCgamma1 pathway in EPO signaling, therefore contributing to the comprehension of the effect of EPO in low-risk MDS and possibly paving the way to the identification of MDS patients at higher risk of refractoriness to EPO treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scott BL, Deeg HJ . Myelodysplastic syndromes. Annu Rev Med 2010; 61: 345–358.
Kelaidi C, Fenaux P . Darbepoetin alfa in anemia of myelodysplastic syndromes: present and beyond. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2010; 10: 605–614.
Martelli AM, Evangelisti C, Chappell W, Abrams SL, Basecke J, Stivala F et al. Targeting the translational apparatus to improve leukemia therapy: roles of the PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathway. Leukemia 2011; 25: 1064–1079.
Nyakern M, Tazzari PL, Finelli C, Bosi C, Follo MY, Grafone T et al. Frequent elevation of Akt kinase phosphorylation in blood marrow and peripheral blood mononuclear cells from high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome patients. Leukemia 2006; 20: 230–238.
Follo MY, Mongiorgi S, Bosi C, Cappellini A, Finelli C, Chiarini F et al. The Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin signal transduction pathway is activated in high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes and influences cell survival and proliferation. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 4287–4294.
Follo MY, Finelli C, Bosi C, Martinelli G, Mongiorgi S, Baccarani M et al. PI-PLCbeta-1 and activated Akt levels are linked to azacitidine responsiveness in high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 2008; 22: 198–200.
Ramazzotti G, Faenza I, Fiume R, Matteucci A, Piazzi M, Follo MY et al. The physiology and pathology of inositide signaling in the nucleus. J Cell Physiol 2011; 226: 14–20.
Faenza I, Matteucci A, Manzoli L, Billi AM, Aluigi M, Peruzzi D et al. A role for nuclear phospholipase Cbeta 1 in cell cycle control. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 30520–30524.
Faenza I, Ramazzotti G, Bavelloni A, Fiume R, Gaboardi GC, Follo MY et al. Inositide-dependent phospholipase C signaling mimics insulin in skeletal muscle differentiation by affecting specific regions of the cyclin D3 promoter. Endocrinology 2007; 148: 1108–1117.
Furukawa Y . Cell cycle control genes and hematopoietic cell differentiation. Leuk Lymphoma 2002; 43: 225–231.
Cooper AB, Sawai CM, Sicinska E, Powers SE, Sicinski P, Clark MR et al. A unique function for cyclin D3 in early B cell development. Nat Immunol 2006; 7: 489–497.
Follo MY, Faenza I, Fiume R, Ramazzotti G, McCubrey JA, Martelli AM et al. Revisiting nuclear phospholipase C signalling in MDS. Adv Biol Regul 2012; 52: 2–6.
Follo MY, Bosi C, Finelli C, Fiume R, Faenza I, Ramazzotti G et al. Real-time PCR as a tool for quantitative analysis of PI-PLCbeta1 gene expression in myelodysplastic syndrome. Int J Mol Med 2006; 18: 267–271.
Follo MY, Finelli C, Mongiorgi S, Clissa C, Bosi C, Testoni N et al. Reduction of phosphoinositide-phospholipase C beta1 methylation predicts the responsiveness to azacitidine in high-risk MDS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009; 106: 16811–16816.
Follo MY, Finelli C, Clissa C, Mongiorgi S, Bosi C, Martinelli G et al. Phosphoinositide-phospholipase C beta1 mono-allelic deletion is associated with myelodysplastic syndromes evolution into acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 782–790.
Elliott S . Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents. Cancer Treat Res 2011; 157: 55–74.
Cortelezzi A, Colombo G, Pellegrini C, Silvestris I, Moronetti Mazzeo L, Bosari S et al. Bone marrow glycophorin-positive erythroid cells of myelodysplastic patients responding to high-dose rHuEPO therapy have a different gene expression pattern from those of nonresponders. Am J Hematol 2008; 83: 531–539.
Bejar R, Levine R, Ebert BL . Unraveling the molecular pathophysiology of myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 504–515.
Marzo F, Lavorgna A, Coluzzi G, Santucci E, Tarantino F, Rio T et al. Erythropoietin in heart and vessels: focus on transcription and signalling pathways. J Thromb Thrombolysis 2008; 26: 183–187.
Wang Y, Wu J, Wang Z . Akt binds to and phosphorylates phospholipase C-gamma1 in response to epidermal growth factor. Mol Biol Cell 2006; 17: 2267–2277.
Marshall AJ, Niiro H, Yun TJ, Clark EA . Regulation of B-cell activation and differentiation by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and phospholipase Cgamma pathway. Immunol Rev 2000; 176: 30–46.
Kerbauy DB, Deeg HJ . Apoptosis and antiapoptotic mechanisms in the progression of myelodysplastic syndrome. Exp Hematol 2007; 35: 1739–1746.
Wilber A, Nienhuis AW, Persons DA . Transcriptional regulation of fetal to adult hemoglobin switching: new therapeutic opportunities. Blood 2011; 117: 3945–3953.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR et al. Proposals for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 1982; 51: 189–199.
Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood 2009; 114: 937–951.
Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1997; 89: 2079–2088.
Cheson BD, Greenberg PL, Bennett JM, Lowenberg B, Wijermans PW, Nimer SD et al. Clinical application and proposal for modification of the International Working Group (IWG) response criteria in myelodysplasia. Blood 2006; 108: 419–425.
di Giacomo V, Matteucci A, Stellacci E, Battistini A, Di Baldassarre A, Capitani S et al. Expression of signal transduction proteins during the differentiation of primary human erythroblasts. J Cell Physiol 2005; 202: 831–838.
Missiroli S, Etro D, Buontempo F, Ye K, Capitani S, Neri LM . Nuclear translocation of active AKT is required for erythroid differentiation in erythropoietin treated K562 erythroleukemia cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2009; 41: 570–577.
Faenza I, Matteucci A, Bavelloni A, Marmiroli S, Martelli AM, Gilmour RS et al. Nuclear PLCbeta(1) acts as a negative regulator of p45/NF-E2 expression levels in Friend erythroleukemia cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 2002; 1589: 305–310.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Italian MIUR-FIRB and the Italian Society of Experimental Hematology (SIES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Follo, M., Mongiorgi, S., Clissa, C. et al. Activation of nuclear inositide signalling pathways during erythropoietin therapy in low-risk MDS patients. Leukemia 26, 2474–2482 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.133
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.133