Abstract
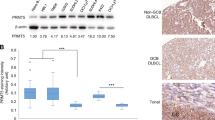
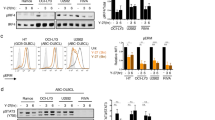
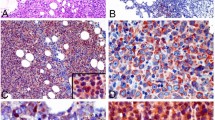
Hedgehog (HH) signaling is important in the pathogenesis of several malignancies. Recently, we described that HH signaling proteins are commonly expressed in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL); however, the functional role of HH pathway in DLBCL has not been explored. Here, we assessed the possibility that HH pathway activation contributes to the survival of DLBCL. We found that HH signaling inhibition induces predominantly cell-cycle arrest in DLBCL cells of germinal center (GC) B-cell type, and apoptosis in DLBCL cells of activated B-cell (ABC) type. Apoptosis after HH signaling inhibition in DLBCL cells of ABC type was associated with downregulation of BCL2; however HH inhibition was not associated with BCL2 downregulation in DLBCL of GC type. Functional inhibition of BCL2 significantly increased apoptosis induced by HH inhibition in DLBCL cells of both types. We also showed that DLBCL cells synthesize, secrete and respond to endogenous HH ligands, providing support for the existence of an autocrine HH signaling loop. Our findings provide novel evidence that dysregulation of HH pathway is involved in the biology of DLBCL and have significant therapeutic implications as they identify HH signaling as a potential therapeutic target in DLBCL, in particular for those lymphomas expressing the HH receptor smoothened.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armitage JO, Weisenburger DD . New approach to classifying non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: clinical features of the major histologic subtypes. Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Classification Project. J Clin Oncol 1998; 16: 2780–2795.
Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000; 403: 503–511.
Rosenwald A, Wright G, Chan WC, Connors JM, Campo E, Fisher RI et al. The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 1937–1947.
Savage KJ, Monti S, Kutok JL, Cattoretti G, Neuberg D, De Leval L et al. The molecular signature of mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma differs from that of other diffuse large B-cell lymphomas and shares features with classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2003; 102: 3871–3879.
Rosenwald A, Wright G, Leroy K, Yu X, Gaulard P, Gascoyne RD et al. Molecular diagnosis of primary mediastinal B cell lymphoma identifies a clinically favorable subgroup of diffuse large B cell lymphoma related to Hodgkin lymphoma. J Exp Med 2003; 198: 851–862.
Coiffier B . Treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Curr Hematol Rep 2005; 4: 7–14.
Kinzler KW, Bigner SH, Bigner DD, Trent JM, Law ML, O’Brien SJ et al. Identification of an amplified, highly expressed gene in a human glioma. Science 1987; 236: 70–73.
Hahn H, Wicking C, Zaphiropoulous PG, Gailani MR, Shanley S, Chidambaram A et al. Mutations of the human homolog of Drosophila patched in the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Cell 1996; 85: 841–851.
Johnson RL, Scott MP . New players and puzzles in the Hedgehog signaling pathway. Curr Opin Genet Dev 1998; 8: 450–456.
Porter JA, Young KE, Beachy PA . Cholesterol modification of hedgehog signaling proteins in animal development. Science 1996; 274: 255–259.
Murone M, Rosenthal A, de Sauvage FJ . Hedgehog signal transduction: from flies to vertebrates. Exp Cell Res 1999; 253: 25–33.
Eichberger T, Sander V, Schnidar H, Regl G, Kasper M, Schmid C et al. Overlapping and distinct transcriptional regulator properties of the GLI1 and GLI2 oncogenes. Genomics 2006; 87: 616–632.
Dai P, Akimaru H, Tanaka Y, Maekawa T, Nakafuku M, Ishii S . Sonic Hedgehog-induced activation of the Gli1 promoter is mediated by GLI3. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 8143–8152.
Lee J, Platt KA, Censullo P, Ruiz i Altaba A . Gli1 is a target of Sonic hedgehog that induces ventral neural tube development. Development 1997; 124: 2537–2552.
Wang B, Fallon JF, Beachy PA . Hedgehog-regulated processing of Gli3 produces an anterior/posterior repressor gradient in the developing vertebrate limb. Cell 2000; 100: 423–434.
Taipale J, Beachy PA . The Hedgehog and Wnt signalling pathways in cancer. Nature 2001; 411: 349–354.
Dierks C, Grbic J, Zirlik K, Beigi R, Englund NP, Guo GR et al. Essential role of stromally induced hedgehog signaling in B-cell malignancies. Nat Med 2007; 13: 944–951.
Hegde GV, Peterson KJ, Emanuel K, Mittal AK, Joshi AD, Dickinson JD et al. Hedgehog-induced survival of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells in a stromal cell microenvironment: a potential new therapeutic target. Mol Cancer Res 2008; 6: 1928–1936.
Singh RR, Cho-Vega JH, Davuluri Y, Ma S, Kasbidi F, Milito C et al. Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway is activated in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 2550–2558.
Kim JE, Singh RR, Cho-Vega JH, Drakos E, Davuluri Y, Khokhar FA et al. Sonic hedgehog-signaling proteins and ATP binding cassette G2 are aberrantly expressed in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Mod Pathol 2009; 22: 1312–1320.
Mehra S, Messner H, Minden M, Chaganti RS . Molecular cytogenetic characterization of non-Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002; 33: 225–234.
Elenitoba-Johnson KS, Jenson SD, Abbott RT, Palais RA, Bohling SD, Lin Z et al. Involvement of multiple signaling pathways in follicular lymphoma transformation: p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase as a target for therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 7259–7264.
Compagno M, Lim WK, Grunn A, Nandula SV, Brahmachary M, Shen Q et al. Mutations of multiple genes cause deregulation of NF-kappaB in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 2009; 459: 717–721.
Ericson J, Morton S, Kawakami A, Roelink H, Jessell TM . Two critical periods of Sonic Hedgehog signaling required for the specification of motor neuron identity. Cell 1996; 87: 661–673.
Kobune M, Takimoto R, Murase K, Iyama S, Sato T, Kikuchi S et al. Drug resistance is dramatically restored by hedgehog inhibitors in CD34+ leukemic cells. Cancer Sci 2009; 100: 948–955.
Dahmane N, Sanchez P, Gitton Y, Palma V, Sun T, Beyna M et al. The Sonic Hedgehog–Gli pathway regulates dorsal brain growth and tumorigenesis. Development 2001; 128: 5201–5212.
Kimura H, Stephen D, Joyner A, Curran T . Gli1 is important for medulloblastoma formation in Ptc1+/− mice. Oncogene 2005; 24: 4026–4036.
Pestell RG, Albanese C, Reutens AT, Segall JE, Lee RJ, Arnold A . The cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in hormonal regulation of proliferation and differentiation. Endocr Rev 1999; 20: 501–534.
Lazebnik YA, Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S, Poirier GG, Earnshaw WC . Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase by a proteinase with properties like ICE. Nature 1994; 371: 346–347.
Bar EE, Chaudhry A, Farah MH, Eberhart CG . Hedgehog signaling promotes medulloblastoma survival via Bc/II. Am J Pathol 2007; 170: 347–355.
Bigelow RL, Chari NS, Unden AB, Spurgers KB, Lee S, Roop DR et al. Transcriptional regulation of bcl-2 mediated by the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway through gli-1. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 1197–1205.
Real PJ, Cao Y, Wang R, Nikolovska-Coleska Z, Sanz-Ortiz J, Wang S et al. Breast cancer cells can evade apoptosis-mediated selective killing by a novel small molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 7947–7953.
Vestergaard J, Lind-Thomsen A, Pedersen MW, Jarmer HO, Bak M, Hasholt L et al. GLI1 is involved in cell cycle regulation and proliferation of NT2 embryonal carcinoma stem cells. DNA Cell Biol 2008; 27: 251–256.
Oliver TG, Grasfeder LL, Carroll AL, Kaiser C, Gillingham CL, Lin SM et al. Transcriptional profiling of the Sonic hedgehog response: a critical role for N-myc in proliferation of neuronal precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 7331–7336.
Morton JP, Mongeau ME, Klimstra DS, Morris JP, Lee YC, Kawaguchi Y et al. Sonic hedgehog acts at multiple stages during pancreatic tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 5103–5108.
Graninger WB, Seto M, Boutain B, Goldman P, Korsmeyer SJ . Expression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-2-Ig fusion transcripts in normal and neoplastic cells. J Clin Invest 1987; 80: 1512–1515.
Saito M, Novak U, Piovan E, Basso K, Sumazin P, Schneider C et al. BCL6 suppression of BCL2 via Miz1 and its disruption in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 11294–11299.
Sanchez P, Hernandez AM, Stecca B, Kahler AJ, DeGueme AM, Barrett A et al. Inhibition of prostate cancer proliferation by interference with SONIC HEDGEHOG–GLI1 signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 12561–12566.
Stecca B, Mas C, Clement V, Zbinden M, Correa R, Piguet V et al. Melanomas require HEDGEHOG–GLI signaling regulated by interactions between GLI1 and the RAS–MEK/AKT pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 5895–5900.
Yauch RL, Gould SE, Scales SJ, Tang T, Tian H, Ahn CP et al. A paracrine requirement for hedgehog signalling in cancer. Nature 2008; 455: 406–410.
Nolan-Stevaux O, Lau J, Truitt ML, Chu GC, Hebrok M, Fernandez-Zapico ME et al. GLI1 is regulated through Smoothened-independent mechanisms in neoplastic pancreatic ducts and mediates PDAC cell survival and transformation. Genes Dev 2009; 23: 24–36.
Sacedon R, Diez B, Nunez V, Hernandez-Lopez C, Gutierrez-Frias C, Cejalvo T et al. Sonic hedgehog is produced by follicular dendritic cells and protects germinal center B cells from apoptosis. J Immunol 2005; 174: 1456–1461.
Riobo NA, Lu K, Ai X, Haines GM, Emerson Jr CP . Phosphoinositide 3-kinase and Akt are essential for Sonic Hedgehog signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 4505–4510.
Kasperczyk H, Baumann B, Debatin KM, Fulda S . Characterization of sonic hedgehog as a novel NF-kappaB target gene that promotes NF-kappaB-mediated apoptosis resistance and tumor growth in vivo. FASEB J 2009; 23: 21–33.
Nakashima H, Nakamura M, Yamaguchi H, Yamanaka N, Akiyoshi T, Koga K et al. Nuclear factor-kappaB contributes to hedgehog signaling pathway activation through sonic hedgehog induction in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 7041–7049.
Kasper M, Regl G, Frischauf AM, Aberger F . GLI transcription factors: mediators of oncogenic Hedgehog signalling. Eur J Cancer 2006; 42: 437–445.
Rubin LL, de Sauvage FJ . Targeting the Hedgehog pathway in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2006; 5: 1026–1033.
Vega F, Cho-Vega JH, Lennon PA, Luthra MG, Bailey J, Breeden M et al. Splenic marginal zone lymphomas are characterized by loss of interstitial regions of chromosome 7q, 7q31.32 and 7q36.2 that include the protection of telomere 1 (POT1) and sonic hedgehog (SHH) genes. Br J Haematol 2008; 142: 216–226.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Michael G Rosenblum Department of Experimental Therapeutics and Dr Felipe Samaniego, Department of Lymphoma and Myeloma, MD Anderson Cancer Center for providing cell lines. This research was supported by funds from the University Cancer Foundation (Institutional Research Grant) at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center (to FV), from the CLL Global Research Foundation (to FV) and from the Wendy Will Case Cancer Foundation (to RRS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R., Kim, J., Davuluri, Y. et al. Hedgehog signaling pathway is activated in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and contributes to tumor cell survival and proliferation. Leukemia 24, 1025–1036 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.35
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.35
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Protease nexin-1 prevents growth of human B cell lymphoma via inhibition of sonic hedgehog signaling
Blood Cancer Journal (2018)
-
The tumour microenvironment in B cell lymphomas
Nature Reviews Cancer (2014)
-
Identification of an NF-κB p50/p65-responsive site in the human MIR155HG promoter
BMC Molecular Biology (2013)
-
Functional inhibition of BCL2 is needed to increase the susceptibility to apoptosis to SMO inhibitors in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of germinal center subtype
Annals of Hematology (2013)
-
Loss of TCR-beta F1 and/or EZRIN expression is associated with unfavorable prognosis in nodal peripheral T-cell lymphomas
Blood Cancer Journal (2013)