Abstract
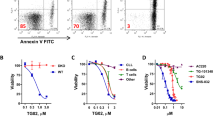
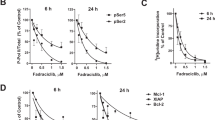
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is characterized by slow accumulation of malignant cells, which are supported in the microenvironment by cell–cell interactions and soluble cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF). We evaluated the effect of the small molecule TNF inhibitor LMP-420 on primary CLL cells. The mean concentration of LMP-420 required to induce 50% cytotoxicity (ED50) at 72 h was 245 n. LMP-420-induced time- and dose-dependent apoptosis, as shown by annexin V staining, caspase activation and DNA fragmentation. These changes were associated with decreased expression of anti-apoptotic proteins Mcl-1, Bcl-xL and Bcl-2. CLL cells from patients with poor prognostic indicators showed LMP-420 sensitivity equal to that for cells from patients with favorable characteristics. In addition, LMP-420 potentiated the cytotoxic effect of fludarabine and inhibited in vitro proliferation of stimulated CLL cells. Gene expression profiling indicated that the mechanism of action of LMP-420 may involve suppression of nuclear factor-κB and immune response pathways in CLL cells. LMP-420 had minimal effects on normal peripheral blood mononuclear cell, B- and T-cell function, and hematopoietic colony formation. Our data suggest that LMP-420 may be a useful treatment for CLL with negligible hematologic toxicities.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wierda W, O’Brien S, Wen S, Faderl S, Garcia-Manero G, Thomas D et al. Chemoimmunotherapy with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab for relapsed and refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 4070–4078.
Tam CS, O’Brien S, Wierda W, Kantarjian H, Wen S, Do K-A et al. Long-term results of the fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab regimen as initial therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2008; 112: 975–980.
Wadhwa PD, Morrison VA . Infectious complications of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Semin Oncol 2006; 33: 240–249.
Foa R, Massaia M, Cardona S, Tos AG, Bianchi A, Attisano C et al. Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells: a possible regulatory role of TNF in the progression of the disease. Blood 1990; 76: 393–400.
Digel W, Stefanic M, Schoniger W, Buck C, Raghavachar A, Frickhofen N et al. Tumor necrosis factor induces proliferation of neoplastic B cells from chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1989; 73: 1242–1246.
Ferrajoli A, Keating MJ, Manshouri T, Giles FJ, Dey A, Estrov Z et al. The clinical significance of tumor necrosis factor-alpha plasma level in patients having chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2002; 100: 1215–1219.
Hale L, Cianciolo G . Treatment of experimental colitis in mice with LMP-420, an inhibitor of TNF transcription. J Inflamm 2008; 5: 4.
Haraguchi S, Day N, Kamchaisatian W, Beigier-Pompadre M, Stenger S, Tangsinmankong N et al. LMP-420, a small-molecule inhibitor of TNF-alpha, reduces replication of HIV-1 and mycobacterium tuberculosis in human cells. AIDS Res Therapy 2006; 3: 8.
Woyach JA, Lin TS, Lucas MS, Heerema N, Moran ME, Cheney C et al. A phase I/II study of rituximab and etanercept in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and small lymphocytic lymphoma. Leukemia 2009; 23: 912–918.
Tsimberidou AM, Thomas D, O’Brien S, Andreeff M, Kurzrock R, Keating M et al. Recombinant human soluble tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor (p75) fusion protein Enbrel in patients with refractory hematologic malignancies. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2002; 50: 237–242.
Weinberg JB, Volkheimer AD, Chen Y, Beasley BE, Jiang N, Lanasa MC et al. Clinical and molecular predictors of disease severity and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Am J Hematol 2007; 82: 1063–1070.
Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S, Benner A, Leupolt E, Krober A, Bullinger L et al. Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 1910–1916.
Adams DJ, Levesque MC, Weinberg JB, Smith KL, Flowers JL, Moore J et al. Nitric oxide enhancement of fludarabine cytotoxicity for B-CLL lymphocytes. Leukemia 2001; 15: 1852–1859.
Friesen C, Herr I, Krammer PH, Debatin KM . Involvement of the CD95 (APO-1/FAS) receptor/ligand system in drug-induced apoptosis in leukemia cells. Nat Med 1996; 2: 574–577.
Thomas D, Folker S, Manuela K, Tobias D, Grayson BL, Hermann W et al. Immunostimulatory CpG-oligonucleotides induce functional high affinity IL-2 receptors on B-CLL cells: costimulation with IL-2 results in a highly immunogenic phenotype. Exp Hematol 2000; 28: 558–568.
Johnson WE, Li C, Rabinovic A . Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics 2007; 8: 118–127.
Chang JT, Nevins JR . GATHER: a systems approach to interpreting genomic signatures. Bioinformatics 2006; 22: 2926–2933.
Bild AH, Yao G, Chang JT, Wang Q, Potti A, Chasse D et al. Oncogenic pathway signatures in human cancers as a guide to targeted therapies. Nature 2006; 439: 353–357.
Wyllie AH, Kerr JF, Currie AR . Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol 1980; 68: 251–306.
Granziero L, Ghia P, Circosta P, Gottardi D, Strola G, Geuna M et al. Survivin is expressed on CD40 stimulation and interfaces proliferation and apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2001; 97: 2777–2783.
Reittie JE, Yong KL, Panayiotidis P, Hoffbrand AV . Interleukin-6 inhibits apoptosis and tumour necrosis factor induced proliferation of B-chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Leuk Lymphoma 1996; 22: 83–90,, follow 186, color plate VI.
Tangye SG, Raison RL . Human cytokines suppress apoptosis of leukaemic CD5+ B cells and preserve expression of bcl-2. Immunol Cell Biol 1997; 75: 127–135.
Buschle M, Campana D, Carding SR, Richard C, Hoffbrand AV, Brenner MK . Interferon gamma inhibits apoptotic cell death in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Exp Med 1993; 177: 213–218.
Grdisa M . Influence of CD40 ligation on survival and apoptosis of B-CLL cells in vitro. Leuk Res 2003; 27: 951–956.
Luqman M, Klabunde S, Lin K, Georgakis GV, Cherukuri A, Holash J et al. The antileukemia activity of a human anti-CD40 antagonist antibody, HCD122, on human chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 2008; 112: 711–720.
Schattner EJ, Mascarenhas J, Reyfman I, Koshy M, Woo C, Friedman SM et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells can express CD40 ligand and demonstrate T-cell type costimulatory capacity. Blood 1998; 91: 2689–2697.
Chiorazzi N . Cell proliferation and death: forgotten features of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2007; 20: 399–413.
Longo PG, Laurenti L, Gobessi S, Petlickovski A, Pelosi M, Chiusolo P et al. The Akt signaling pathway determines the different proliferative capacity of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B-cells from patients with progressive and stable disease. Leukemia 2006; 21: 110–120.
Li X, Bu X, Lu B, Avraham H, Flavell RA, Lim B . The hematopoiesis-specific GTP-binding protein RhoH is GTPase deficient and modulates activities of other Rho GTPases by an inhibitory function. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 1158–1171.
Mathew R, Karp CM, Beaudoin B, Vuong N, Chen G, Chen HY et al. Autophagy suppresses tumorigenesis through elimination of p62. Cell 2009; 137: 1062–1075.
Furman RR, Asgary Z, Mascarenhas JO, Liou H-C, Schattner EJ . Modulation of NF-{kappa}B activity and apoptosis in chronic. J Immunol 2000; 164: 2200–2206.
Fitzgerald KA, Rowe DC, Barnes BJ, Caffrey DR, Visintin A, Latz E et al. LPS-TLR4 signaling to IRF-3/7 and NF-kappaB involves the toll adapters TRAM and TRIF. J Exp Med 2003; 198: 1043–1055.
Jeremias I, Kupatt C, Baumann B, Herr I, Wirth T, Debatin KM . Inhibition of nuclear factor kappaB activation attenuates apoptosis resistance in lymphoid cells. Blood 1998; 91: 4624–4631.
Pepper C, Hewamana S, Brennan P, Fegan C . NF-kappaB as a prognostic marker and therapeutic target in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Future Oncol 2009; 5: 1027–1037.
Pickering BM, de Mel S, Lee M, Howell M, Habens F, Dallman CL et al. Pharmacological inhibitors of NF-kappaB accelerate apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells. Oncogene 2007; 26: 1166–1177.
Van Den Neste E, Bontemps F, Delacauw A, Cardoen S, Louviaux I, Scheiff JM et al. Potentiation of antitumor effects of cyclophosphamide derivatives in B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells by 2-chloro-2′-deoxyadenosine. Leukemia 1999; 13: 918–925.
Schwanen C, Hecker T, Hubinger G, Wolfle M, Rittgen W, Bergmann L et al. In vitro evaluation of bendamustine induced apoptosis in B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2002; 16: 2096–2105.
Silber R, Degar B, Costin D, Newcomb EW, Mani M, Rosenberg CR et al. Chemosensitivity of lymphocytes from patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia to chlorambucil, fludarabine, and camptothecin analogs. Blood 1994; 84: 3440–3446.
Morabito F, Stelitano C, Callea I, Filangeri M, Oliva B, Sculli G et al. In vitro sensitivity of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B-cells to fludarabine, 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine and chlorambucil: correlation with clinico-hematological and immunophenotypic features. Haematologica 1996; 81: 224–231.
Johnston JB, Paul JT, Neufeld NJ, Haney N, Kropp DM, Hu X et al. Role of myeloid cell factor-1 (Mcl-1) in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 2004; 45: 2017–2027.
Kitada S, Andersen J, Akar S, Zapata JM, Takayama S, Krajewski S et al. Expression of apoptosis-regulating proteins in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: correlations with in vitro and in vivo chemoresponses. Blood 1998; 91: 3379–3389.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health, the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, the Veterans Affairs Research Service and institutional awards from Duke University. We thank the patients and healthy volunteers for donating blood for this research. We also thank Derek Cyr for biostatistical consultation and Nelson Chao for critically reading and reviewing the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mowery, Y., Weinberg, J., Kennedy, M. et al. LMP-420: a novel purine nucleoside analog with potent cytotoxic effects for CLL cells and minimal toxicity for normal hematopoietic cells. Leukemia 24, 1580–1587 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.150
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.150