Abstract
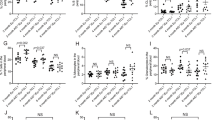
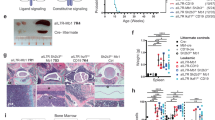
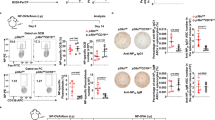
RhoH is a hematopoietic-specific, GTPase-deficient member of the Rho GTPase family that functions as a regulator of thymocyte development and T-cell receptor signaling by facilitating localization of zeta-chain-associated protein kinase 70 (ZAP70) to the immunological synapse. Here we investigated the function of RhoH in the B-cell lineage. B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling was intact in Rhoh−/− mice. Because RhoH interacts with ZAP70, which is a prognostic factor in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), we analyzed the mRNA levels of RhoH in primary human CLL cells and showed a 2.3-fold higher RhoH expression compared with normal B cells. RhoH expression in CLL positively correlated with the protein levels of ZAP70. Deletion of Rhoh in a murine model of CLL (Eμ-TCL1Tg mice) significantly delayed the accumulation of CD5+IgM+ leukemic cells in peripheral blood and the leukemic burden in the peritoneal cavity, bone marrow and spleen of Rhoh−/− mice compared with their Rhoh+/+ counterparts. Phosphorylation of AKT and ERK in response to BCR stimulation was notably decreased in Eμ-TCL1Tg;Rhoh−/− splenocytes. These data suggest that RhoH has a function in the progression of CLL in a murine model and show RhoH expression is altered in human primary CLL samples.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiorazzi N, Rai KR, Ferrarini M . Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Eng J Med 2005; 352: 804–815.
Crespo M, Bosch F, Villamor N, Bellosillo B, Colomer D, Rozman M et al. ZAP-70 expression as a surrogate for immunoglobulin-variable-region mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1764–1775.
Rassenti LZ, Huynh L, Toy TL, Chen L, Keating MJ, Gribben JG et al. ZAP-70 compared with immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene mutation status as a predictor of disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 893–901.
Chen L, Widhopf G, Huynh L, Rassenti L, Rai KR, Weiss A et al. Expression of ZAP-70 is associated with increased B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2002; 100: 4609–4614.
Chen L, Apgar J, Huynh L, Dicker F, Giago-McGahan T, Rassenti L et al. ZAP-70 directly enhances IgM signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2005; 105: 2036–2041.
Chen L, Huynh L, Apgar J, Tang L, Rassenti L, Weiss A et al. ZAP-70 enhances IgM signaling independent of its kinase activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2008; 111: 2685–2692.
Williams DA, Zheng Y, Cancelas JA . Rho GTPases and regulation of hematopoietic stem cell localization. Methods Enzymol 2008; 439: 365–393.
Li X, Bu X, Lu B, Avraham H, Flavell RA, Lim B . The hematopoiesis-specific GTP-binding protein RhoH is GTPase deficient and modulates activities of other Rho GTPases by an inhibitory function. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 1158–1171.
Gu Y, Chae H, Siefring J, Jast iJ, Hildeman D, Williams DA . RhoH, a GTPase recruits and activates Zap70 required for T cell receptor signaling and thymocyte development. Nat Immunol 2006; 7: 1182–1190.
Dorn T, Kuhn U, Bungartz G, Stiller S, Bauer M, Ellwart J et al. RhoH is important for positive thymocyte selection and T-cell receptor signaling. Blood 2007; 109: 2346–2355.
Dallery E, Galiegue-Zouitina S, Collyn-d'Hooghe M, Quief S, Denis C, Hildebrand MP et al. TTF, a gene encoding a novel small G protein, fuses to the lymphoma-associated LAZ3 gene by t(3;4) chromosomal translocation. Oncogene 1995; 10: 2171–2178.
Preudhomme C, Roumier C, Hildebrand MP, Dallery-Prudhomme E, Lantoine D, Lai JL et al. Nonrandom 4p13 rearrangements of the RhoH/TTF gene, encoding a GTP-binding protein, in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and multiple myeloma. Oncogene 2000; 19: 2023–2032.
Pasqualucci L, Neumeister P, Goossens T, Nanjangud G, Chaganti RS, Kuppers R et al. Hypermutation of multiple proto-oncogenes in B-cell diffuse large-cell lymphomas. Nature 2001; 412: 341–346.
Hiraga J, Katsumi A, Iwasaki T, Abe A, Kiyoi H, Matsushita T et al. Prognostic analysis of aberrant somatic hypermutation of RhoH gene in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2007; 21: 1846–1847.
Gaidano G, Pasqualucci L, Capello D, Berra E, Deambrogi C, Rossi D et al. Aberrant somatic hypermutation in multiple subtypes of AIDS-associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2003; 102: 1833–1841.
Montesinos-Rongen M, Van Roost D, Schaller C, Wiestler OD, Deckert M . Primary diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of the central nervous system are targeted by aberrant somatic hypermutation. Blood 2004; 103: 1869–1875.
Bichi R, Shinton SA, Martin ES, Koval A, Calin GA, Cesari R et al. Human chronic lymphocytic leukemia modeled in mouse by targeted TCL1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 6955–6960.
Johnson AJ, Lucas DM, Muthusamy N, Smith LL, Edwards RB, De Lay MD et al. Characterization of the TCL-1 transgenic mouse as a preclinical drug development tool for human chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2006; 108: 1334–1338.
Verbeke G, Molenberghs G . Linear Mixed Models for Longitudinal Data. Springer-Verlag: New York, 2000.
SAS Institute, Inc. SAS/STAT User's Guide, vol. 1, 2, 3. SAS Institute, Inc.: Cary, NC, 2002.
Yan XJ, Albesiano E, Zanesi N, Yancopoulos S, Sawyer A, Romano E et al. B cell receptors in TCL1 transgenic mice resemble those of aggressive, treatment-resistant human chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 11713–11718.
Gu Y, Jasti AC, Jansen M, Siefring JE . RhoH, a hematopoietic-specific Rho GTPase, regulates proliferation, survival, migration, and engraftment of hematopoietic progenitor cells. Blood 2005; 105: 1467–1475.
Scielzo C, Camporeale A, Geuna M, Alessio M, Poggi A, Zocchi MR et al. ZAP-70 is expressed by normal and malignant human B-cell subsets of different maturational stage. Leukemia 2006; 20: 689–695.
Law CL, Sidorenko SP, Chandran KA, Draves KE, Chan AC, Weiss A et al. Molecular cloning of human Syk. A B cell protein-tyrosine kinase associated with the surface immunoglobulin M-B cell receptor complex. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 12310–12319.
Chan AC, van Oers NS, Tran A, Turka L, Law CL, Ryan JC et al. Differential expression of ZAP-70 and Syk protein tyrosine kinases, and the role of this family of protein tyrosine kinases in TCR signaling. J Immunol 1994; 152: 4758–4766.
Latour S, Chow LM, Veillette A . Differential intrinsic enzymatic activity of Syk and Zap-70 protein-tyrosine kinases. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 22782–22790.
Zoller KE, MacNeil IA, Brugge JS . Protein tyrosine kinases Syk and ZAP-70 display distinct requirements for Src family kinases in immune response receptor signal transduction. J Immunol 1997; 158: 1650–1659.
Narducci MG, Pescarmona E, Lazzeri C, Signoretti S, Lavinia AM, Remotti D et al. Regulation of TCL1 expression in B- and T-cell lymphomas and reactive lymphoid tissues. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 2095–2100.
Herling M, Patel KA, Khalili J, Schlette E, Kobayashi R, Medeiros LJ et al. TCL1 shows a regulated expression pattern in chronic lymphocytic leukemia that correlates with molecular subtypes and proliferative state. Leukemia 2006; 20: 280–285.
Pekarsky Y, Koval A, Hallas C, Bichi R, Tresini M, Malstrom S et al. Tcl1 enhances Akt kinase activity and mediates its nuclear translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 3028–3033.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (Grant CA113969 to DAW), the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (RA 1705/1-1 to IR), the St Baldrick's Foundation (LUWM) and the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (JCB). Patient samples and IGHV sequence data were obtained through the CLL Research Consortium (CRC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
YG, JAC, TM and DAW designed research and provided scientific advice; IR, AS-A, DZD, LUWM and VS performed research; IR, AS-A, DZD, LUWM and PJ analyzed data; CMC, DML and JCB contributed vital new reagents; IR, AS-A and DAW wrote the paper.
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website (http://www.nature.com/leu)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanchez-Aguilera, A., Rattmann, I., Drew, D. et al. Involvement of RhoH GTPase in the development of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 24, 97–104 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.217
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.217
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Molecular basis and current insights of atypical Rho small GTPase in cancer
Molecular Biology Reports (2024)
-
Exome sequencing of the TCL1 mouse model for CLL reveals genetic heterogeneity and dynamics during disease development
Leukemia (2019)
-
Maintenance and pharmacologic targeting of ROR1 protein levels via UHRF1 in t(1;19) pre-B-ALL
Oncogene (2018)
-
Development of CLL in the TCL1 transgenic mouse model is associated with severe skewing of the T-cell compartment homologous to human CLL
Leukemia (2011)