Abstract
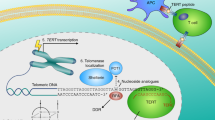
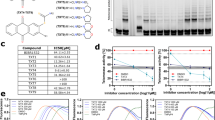
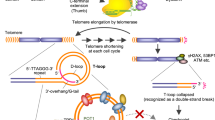
Human telomerase, the reverse transcriptase which extends the life span of a cell by adding telomeric repeats to chromosome ends, is expressed in most cancer cells but not in the majority of normal somatic cells. Inhibition of telomerase therefore holds great promise as anticancer therapy. We have synthesized a novel telomerase inhibitor GRN163L, a lipid—attached phosphoramidate oligonucleotide complementary to template region of the RNA subunit of telomerase. Here, we report that GRN163L is efficiently taken up by human myeloma cells without any need of transfection and is resistant to nucleolytic degradation. The exposure of myeloma cells to GRN163L led to an effective inhibition of telomerase activity, reduction of telomere length and apoptotic cell death after a lag period of 2–3 weeks. Mismatch control oligonucleotides had no effect on growth of myeloma cells. The in vivo efficacy of GRN163L was confirmed in two murine models of human multiple myeloma. In three independent experiments, significant reduction in tumor cell growth and better survival than control mice was observed. Furthermore, GRN163L-induced myeloma cell death could be significantly enhanced by Hsp90 inhibitor 17AAG. These data provide the preclinical rationale for clinical evaluation of GRN163L in myeloma and in combination with 17AAG.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Day JP, Marder BA, Morgan WF . Telomeres and their possible role in chromosome stabilization. Environ Mol Mutagen 1993; 22: 245–249.
Allshire RC, Gosden JR, Cross SH, Cranston G, Rout D, Sugawara N et al. Telomeric repeat from T. thermophila cross hybridizes with human telomeres. Nature 1988; 332: 656–659.
Moyzis RK, Buckingham JM, Cram LS, Dani M, Deaven LL, Jones MD et al. A highly conserved repetitive DNA sequence, (TTAGGG)n, present at the telomeres of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988; 85: 6622–6626.
Cong YS, Wright WE, Shay JW . Human telomerase and its regulation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2002; 66: 407–425, table of contents.
Hayflick L . The cellular basis for biological aging. In: Finch CE, Hayflick L (eds). Handbook of the Biology of Aging. Van Nostrand Reinhold Co.: NY, 1977, pp 159–186.
Gong JG, Costanzo A, Yang HQ, Melino G, Kaelin Jr WG, Levrero M et al. The tyrosine kinase c-Abl regulates p73 in apoptotic response to cisplatin-induced DNA damage. Nature 1999; 399: 806–809.
Stiewe T, Putzer BM . p73 in apoptosis. Apoptosis 2001; 6: 447–452.
Blackburn EH, Greider CW, Henderson E, Lee MS, Shampay J, Shippen-Lentz D . Recognition and elongation of telomeres by telomerase. Genome 1989; 31: 553–560.
Counter CM, Avilion AA, LeFeuvre CE, Stewart NG, Greider CW, Harley CB et al. Telomere shortening associated with chromosome instability is arrested in immortal cells which express telomerase activity. EMBO J 1992; 11: 1921–1929.
Kim NW, Piatyszek MA, Prowse KR, Harley CB, West MD, Ho PL et al. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science 1994; 266: 2011–2015.
Lord RV, Salonga D, Danenberg KD, Peters JH, DeMeester TR, Park JM et al. Telomerase reverse transcriptase expression is increased early in the Barrett's metaplasia, dysplasia, adenocarcinoma sequence. J Gastrointest Surg 2000; 4: 135–142.
Broccoli D, Young JW, de Lange T . Telomerase activity in normal and malignant hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 9082–9086.
Shay JW, Bacchetti S . A survey of telomerase activity in human cancer. Eur J Cancer 1997; 33: 787–791.
Shay JW . Telomerase in human development and cancer. J Cell Physiol 1997; 173: 266–270.
Shay JW, Wright WE . The reactivation of telomerase activity in cancer progression. Trends Genet 1996; 12: 129–131.
Bodnar AG, Ouellette M, Frolkis M, Holt SE, Chiu CP, Morin GB et al. Extension of life-span by introduction of telomerase into normal human cells. Science 1998; 279: 349–352.
Bechter OE, Eisterer W, Pall G, Hilbe W, Kuhr T, Thaler J . Telomere length and telomerase activity predict survival in patients with B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 4918–4922.
Shammas MA, Shmookler Reis RJ, Akiyama M, Koley H, Chauhan D, Hideshima T et al. Telomerase inhibition and cell growth arrest by G-quadruplex interactive agent in multiple myeloma. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics 2003; 2: 825–833.
Fu W, Begley JG, Killen MW, Mattson MP . Anti-apoptotic role of telomerase in pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 7264–7271.
Nakajima A, Tauchi T, Sashida G, Sumi M, Abe K, Yamamoto K et al. Telomerase inhibition enhances apoptosis in human acute leukemia cells: possibility of antitelomerase therapy. Leukemia 2003; 17: 560–567.
Sumi M, Tauchi T, Sashida G, Nakajima A, Gotoh A, Shin-Ya K et al. A G-quadruplex-interactive agent, telomestatin (SOT-095), induces telomere shortening with apoptosis and enhances chemosensitivity in acute myeloid leukemia. Int J Oncol 2004; 24: 1481–1487.
Tauchi T, Shin-Ya K, Sashida G, Sumi M, Nakajima A, Shimamoto T et al. Activity of a novel G-quadruplex-interactive telomerase inhibitor, telomestatin (SOT-095), against human leukemia cells: involvement of ATM-dependent DNA damage response pathways. Oncogene 2003; 22: 5338–5347.
Seimiya H, Oh-hara T, Suzuki T, Naasani I, Shimazaki T, Tsuchiya K et al. Telomere shortening and growth inhibition of human cancer cells by novel synthetic telomerase inhibitors MST-312, MST-295, and MST-1991. Mol Cancer Ther 2002; 1: 657–665.
Shammas MA, Koley H, Beer DG, Li C, Goyal RK, Munshi NC . Growth arrest, apoptosis, and telomere shortening of Barrett's-associated adenocarcinoma cells by a telomerase inhibitor. Gastroenterology 2004; 126: 1337–1346.
Shammas MA, Reis RJ, Li C, Koley H, Hurley LH, Anderson KC et al. Telomerase inhibition and cell growth arrest after telomestatin treatment in multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 770–776.
Akiyama M, Hideshima T, Shammas MA, Hayashi T, Hamasaki M, Tai YT et al. Effects of oligonucleotide N3′ → P5′ thio-phosphoramidate (GRN163) targeting telomerase RNA in human multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 6187–6194.
Shammas MA, Liu X, Gavory G, Raney KD, Balasubramanian S, Shmookler Reis RJ . Targeting the single-strand G-rich overhang of telomeres with PNA inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis of human immortal cells. Exp Cell Res 2004; 295: 204–214.
Shammas MA, Simmons CG, Corey DR, Reis RJ . Telomerase inhibition by peptide nucleic acids reverses ‘immortality’ of transformed human cells. Oncogene 1999; 18: 6191–6200.
Shammas MA, Koley H, Batchu RB, Bertheau RC, Protopopov A, Munshi NC et al. Telomerase inhibition by siRNA causes senescence and apoptosis in Barrett's adenocarcinoma cells: mechanism and therapeutic potential. Mol Cancer 2005; 4: 24.
Yatabe N, Kyo S, Kondo S, Kanaya T, Wang Z, Maida Y et al. 2-5A antisense therapy directed against human telomerase RNA inhibits telomerase activity and induces apoptosis without telomere impairment in cervical cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther 2002; 9: 624–630.
Shammas MA, Simmons CG, Corey DR, Shmookler Reis RJ . Telomerase inhibition by peptide nucleic acids reverses ‘immortality’ of transformed human cells. Oncogene 1999; 18: 6191–6200.
Shammas MA, Shmookler Reis RJ, Li C, Koley H, Hurley LH, Anderson KC et al. Telomerase inhibition and cell growth arrest after telomestatin treatment in multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 770–776.
Workman P . Overview: translating Hsp90 biology into Hsp90 drugs. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2003; 3: 297–300.
Noguchi M, Yu D, Hirayama R, Ninomiya Y, Sekine E, Kubota N et al. Inhibition of homologous recombination repair in irradiated tumor cells pretreated with Hsp90 inhibitor 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 351: 658–663.
Powers MV, Workman P . Targeting of multiple signalling pathways by heat shock protein 90 molecular chaperone inhibitors. Endocr Relat Cancer 2006; 13 (Suppl 1): S125–S135.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by NIH-P50-100007 Developmental Research Award to MAS, and Merit Review Award from the Department of Veterans Affairs and NIH—RO1-CA124929 (NCM); NIH-P050-100007and NIH-PO1-78378 (NCM and KCA). NCM is a Leukemia Society Scholar in Translational Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shammas, M., Koley, H., Bertheau, R. et al. Telomerase inhibitor GRN163L inhibits myeloma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Leukemia 22, 1410–1418 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.81
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.81
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Regulation of telomerase towards tumor therapy
Cell & Bioscience (2023)
-
Telomere length and hTERT genetic variants as potential prognostic markers in multiple myeloma
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Exosomal telomerase transcripts reprogram the microRNA transcriptome profile of fibroblasts and partially contribute to CAF formation
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Interleukin 8 is a biomarker of telomerase inhibition in cancer cells
BMC Cancer (2018)
-
Role of apurinic/apyrimidinic nucleases in the regulation of homologous recombination in myeloma: mechanisms and translational significance
Blood Cancer Journal (2018)