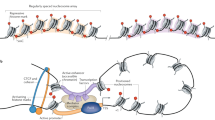
Abstract
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-chip and ChIP-seq technologies are rapidly expanding our capacity to interrogate the location of transcription factor-binding sites in the human genome and to map the pattern of chromatin modifications associated with the regulation of gene expression. The application of these techniques to the study of hematologic malignancies will complement gene expression profiling studies to elucidate the structure and function of oncogenic transcriptional networks involved in the pathogenesis of leukemias and lymphomas.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Teitell M, Pandolfi P . Molecular genetics of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Annu Rev Pathol 2008; 4.
Ferrando A, Look A . Clinical implications of recurring chromosomal and associated molecular abnormalities in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Semin Hematol 2000; 37: 381–395.
Golub T, Slonim D, Tamayo P, Huard C, Gaasenbeek M, Mesirov J et al. Molecular classification of cancer: class discovery and class prediction by gene expression monitoring. Science 1999; 286: 531–537.
Ferrando A, Neuberg D, Staunton J, Loh M, Huard C, Raimondi S et al. Gene expression signatures define novel oncogenic pathways in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell 2002; 1: 75–87.
Yeoh E, Ross M, Shurtleff S, Williams W, Patel D, Mahfouz R et al. Classification, subtype discovery, and prediction of outcome in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia by gene expression profiling. Cancer Cell 2002; 1: 133–143.
Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh T, Schones D, Wang Z et al. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell 2007; 129: 823–837.
Jain N, Rossi A, Garcia-Manero G . Epigenetic therapy of leukemia: An update. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2009; 41: 72–80.
Krivtsov A, Armstrong S . MLL translocations, histone modifications and leukaemia stem-cell development. Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: 823–833.
Griffiths E, Gore S . DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibitors in the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes. Semin Hematol 2008; 45: 23–30.
Atallah E, Garcia-Manero G . Use of hypomethylating agents in myelodysplastic syndromes. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2007; 5: 544–552.
Wang T, Tavera-Mendoza L, Laperriere D, Libby E, MacLeod N, Nagai Y et al. Large-scale in silico and microarray-based identification of direct 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 target genes. Mol Endocrinol 2005; 19: 2685–2695.
U M, Shen L, Oshida T, Miyauchi J, Yamada M, Miyashita T . Identification of novel direct transcriptional targets of glucocorticoid receptor. Leukemia 2004; 18: 1850–1856.
Park D, Vuong P, de Vos S, Douer D, Koeffler H . Comparative analysis of genes regulated by PML/RAR alpha and PLZF/RAR alpha in response to retinoic acid using oligonucleotide arrays. Blood 2003; 102: 3727–3736.
Wang D, Sevcikova S, Wen H, Roberts S, Lipsick J . v-Myb represses the transcription of Ets-2. Oncogene 2007; 26: 1238–1244.
Zeisig B, Milne T, García-Cuéllar M, Schreiner S, Martin M, Fuchs U et al. Hoxa9 and Meis1 are key targets for MLL-ENL-mediated cellular immortalization. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 617–628.
Grandori C, Gomez-Roman N, Felton-Edkins Z, Ngouenet C, Galloway D, Eisenman R et al. c-Myc binds to human ribosomal DNA and stimulates transcription of rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I. Nat Cell Biol 2005; 7: 311–318.
Tamura T, Thotakura P, Tanaka T, Ko M, Ozato K . Identification of target genes and a unique cis element regulated by IRF-8 in developing macrophages. Blood 2005; 106: 1938–1947.
Palomero T, Odom D, O'Neil J, Ferrando A, Margolin A, Neuberg D et al. Transcriptional regulatory networks downstream of TAL1/SCL in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2006; 108: 986–992.
Smith R, Owen L, Trem D, Wong J, Whangbo J, Golub T et al. Expression profiling of EWS/FLI identifies NKX2.2 as a critical target gene in Ewing's sarcoma. Cancer Cell 2006; 9: 405–416.
Hudson M, Snyder M . High-throughput methods of regulatory element discovery. Biotechniques 2006; 41: 673, 675, 677 passim.
Ren B, Cam H, Takahashi Y, Volkert T, Terragni J, Young R et al. E2F integrates cell cycle progression with DNA repair, replication, and G(2)/M checkpoints. Genes Dev 2002; 16: 245–256.
Weinmann A, Yan P, Oberley M, Huang T, Farnham P . Isolating human transcription factor targets by coupling chromatin immunoprecipitation and CpG island microarray analysis. Genes Dev 2002; 16: 235–244.
Weinmann A, Farnham P . Identification of unknown target genes of human transcription factors using chromatin immunoprecipitation. Methods 2002; 26: 37–47.
Martone R, Euskirchen G, Bertone P, Hartman S, Royce T, Luscombe N et al. Distribution of NF-kappaB-binding sites across human chromosome 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 12247–12252.
O'Neill LP, VerMilyea MD, Turner BM . Epigenetic characterization of the early embryo with a chromatin immunoprecipitation protocol applicable to small cell populations. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 835–841.
Kim TH, Barrera LO, Zheng M, Qu C, Singer MA, Richmond TA et al. A high-resolution map of active promoters in the human genome. Nature 2005; 436: 876–880.
Li W, Meyer CA, Liu XS . A hidden Markov model for analyzing ChIP-chip experiments on genome tiling arrays and its application to p53 binding sequences. Bioinformatics 2005; 21 (Suppl 1): i274–i282.
Gibbons FD, Proft M, Struhl K, Roth FP . Chipper: discovering transcription-factor targets from chromatin immunoprecipitation microarrays using variance stabilization. Genome Biol 2005; 6: R96.
Qi Y, Rolfe A, MacIsaac KD, Gerber GK, Pokholok D, Zeitlinger J et al. High-resolution computational models of genome binding events. Nat Biotechnol 2006; 24: 963–970.
Zheng M, Barrera L, Ren B, Wu Y . ChIP-chip: data, model, and analysis. Biometrics 2007; 63: 787–796.
Yochum G, Cleland R, Goodman R . A genome-wide screen for {beta}-catenin binding sites identifies a downstream enhancer element that controls c-Myc gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 2008; 28: 7368–7379.
Zeller K, Zhao X, Lee C, Chiu K, Yao F, Yustein J et al. Global mapping of c-Myc binding sites and target gene networks in human B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 17834–17839.
Liu Y, Li F, Handler J, Huang C, Xiang Y, Neretti N et al. Global regulation of nucleotide biosynthetic genes by c-Myc. PLoS ONE 2008; 3: e2722.
Chi KR . The year of sequencing. Nat Methods 2008; 5: 11–14.
Mardis E . Next-generation DNA sequencing methods. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 2008; 9: 387–402.
Boyle A, Davis S, Shulha H, Meltzer P, Margulies E, Weng Z et al. High-resolution mapping and characterization of open chromatin across the genome. Cell 2008; 132: 311–322.
Robertson G, Hirst M, Bainbridge M, Bilenky M, Zhao Y, Zeng T et al. Genome-wide profiles of STAT1 DNA association using chromatin immunoprecipitation and massively parallel sequencing. Nat Methods 2007; 4: 651–657.
Johnson D, Mortazavi A, Myers R, Wold B . Genome-wide mapping of in vivo protein–DNA interactions. Science 2007; 316: 1497–1502.
Jothi R, Cuddapah S, Barski A, Cui K, Zhao K . Genome-wide identification of in vivo protein-DNA binding sites from ChIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36: 5221–5231.
Valouev A, Johnson D, Sundquist A, Medina C, Anton E, Batzoglou S et al. Genome-wide analysis of transcription factor binding sites based on ChIP-Seq data. Nat Methods 2008; 5: 829–834.
Schmidt D, Stark R, Wilson MD, Brown GD, Odom DT . Genome-scale validation of deep-sequencing libraries. PLoS ONE 2008; 3: e3713.
Gangwal K, Sankar S, Hollenhorst P, Kinsey M, Haroldsen S, Shah A et al. Microsatellites as EWS/FLI response elements in Ewing's sarcoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 10149–10154.
Truscott M, Harada R, Vadnais C, Robert F, Nepveu A . p110 CUX1 cooperates with E2F transcription factors in the transcriptional activation of cell cycle-regulated genes. Mol Cell Biol 2008; 28: 3127–3138.
Leung J, Ehmann G, Giangrande P, Nevins J . A role for Myc in facilitating transcription activation by E2F1. Oncogene 2008; 27: 4172–4179.
Rabinovich A, Jin V, Rabinovich R, Xu X, Farnham P . E2F in vivo binding specificity: comparison of consensus versus nonconsensus binding sites. Genome Res 2008; 18: 1763–1777.
Elnitski L, Jin V, Farnham P, Jones S . Locating mammalian transcription factor binding sites: a survey of computational and experimental techniques. Genome Res 2006; 16: 1455–1464.
Hayakawa J, Mittal S, Wang Y, Korkmaz KS, Adamson E, English C et al. Identification of promoters bound by c-Jun/ATF2 during rapid large-scale gene activation following genotoxic stress. Mol Cell 2004; 16: 521–535.
Impey S, McCorkle S, Cha-Molstad H, Dwyer J, Yochum G, Boss J et al. Defining the CREB regulon: a genome-wide analysis of transcription factor regulatory regions. Cell 2004; 119: 1041–1054.
Zhang X, Odom D, Koo S, Conkright M, Canettieri G, Best J et al. Genome-wide analysis of cAMP-response element binding protein occupancy, phosphorylation, and target gene activation in human tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 4459–4464.
Phuc Le P, Friedman JR, Schug J, Brestelli JE, Parker JB, Bochkis IM et al. Glucocorticoid receptor-dependent gene regulatory networks. PLoS Genet 2005; 1: e16.
Townsend M, Weinmann A, Matsuda J, Salomon R, Farnham P, Biron C et al. T-bet regulates the terminal maturation and homeostasis of NK and Valpha14i NKT cells. Immunity 2004; 20: 477–494.
Beima K, Miazgowicz M, Lewis M, Yan P, Huang T, Weinmann A . T-bet binding to newly identified target gene promoters is cell type-independent but results in variable context-dependent functional effects. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 11992–12000.
Marson A, Kretschmer K, Frampton G, Jacobsen E, Polansky J, MacIsaac K et al. Foxp3 occupancy and regulation of key target genes during T-cell stimulation. Nature 2007; 445: 931–935.
Hug B, Ahmed N, Robbins J, Lazar M . A chromatin immunoprecipitation screen reveals protein kinase Cbeta as a direct RUNX1 target gene. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 825–830.
Kim J, Chu J, Shen X, Wang J, Orkin S . An extended transcriptional network for pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. Cell 2008; 132: 1049–1061.
O'Neil J, Look A . Mechanisms of transcription factor deregulation in lymphoid cell transformation. Oncogene 2007; 26: 6838–6849.
Aifantis I, Raetz E, Buonamici S . Molecular pathogenesis of T-cell leukaemia and lymphoma. Nat Rev Immunol 2008; 8: 380–390.
Elefanty A, Begley C, Hartley L, Papaevangeliou B, Robb L . SCL expression in the mouse embryo detected with a targeted lacZ reporter gene demonstrates its localization to hematopoietic, vascular, and neural tissues. Blood 1999; 94: 3754–3763.
Bash R, Hall S, Timmons C, Crist W, Amylon M, Smith R et al. Does activation of the TAL1 gene occur in a majority of patients with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia? A pediatric oncology group study. Blood 1995; 86: 666–676.
Kelliher M, Seldin D, Leder P . Tal-1 induces T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia accelerated by casein kinase IIalpha. EMBO J 1996; 15: 5160–5166.
Condorelli G, Facchiano F, Valtieri M, Proietti E, Vitelli L, Lulli V et al. T-cell-directed TAL-1 expression induces T-cell malignancies in transgenic mice. Cancer Res 1996; 56: 5113–5119.
O'Neil J, Shank J, Cusson N, Murre C, Kelliher M . TAL1/SCL induces leukemia by inhibiting the transcriptional activity of E47/HEB. Cancer Cell 2004; 5: 587–596.
Palomero T, Lim W, Odom D, Sulis M, Real P, Margolin A et al. NOTCH1 directly regulates c-MYC and activates a feed-forward-loop transcriptional network promoting leukemic cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 18261–18266.
Palomero T, Sulis M, Cortina M, Real P, Barnes K, Ciofani M et al. Mutational loss of PTEN induces resistance to NOTCH1 inhibition in T-cell leukemia. Nat Med 2007; 13: 1203–1210.
Ciofani M, Zúñiga-Pflücker J . Notch promotes survival of pre-T cells at the beta-selection checkpoint by regulating cellular metabolism. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 881–888.
Jarriault S, Brou C, Logeat F, Schroeter E, Kopan R, Israel A . Signalling downstream of activated mammalian Notch. Nature 1995; 377: 355–358.
Palomero T, Dominguez M, Ferrando A . The role of the PTEN/AKT Pathway in NOTCH1-induced leukemia. Cell Cycle 2008; 7: 965–970.
Palomero T, Ferrando A . Oncogenic NOTCH1 control of MYC and PI3K: challenges and opportunities for anti-NOTCH1 therapy in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias and lymphomas. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 5314–5317.
Li Z, Van Calcar S, Qu C, Cavenee W, Zhang M, Ren B . A global transcriptional regulatory role for c-Myc in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 8164–8169.
Parekh S, Prive G, Melnick A . Therapeutic targeting of the BCL6 oncogene for diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Leuk Lymphoma 2008; 49: 874–882.
Polo J, Juszczynski P, Monti S, Cerchietti L, Ye K, Greally J et al. Transcriptional signature with differential expression of BCL6 target genes accurately identifies BCL6-dependent diffuse large B cell lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 3207–3212.
Ranuncolo S, Polo J, Dierov J, Singer M, Kuo T, Greally J et al. Bcl-6 mediates the germinal center B cell phenotype and lymphomagenesis through transcriptional repression of the DNA-damage sensor ATR. Nat Immunol 2007; 8: 705–714.
Phan R, Dalla-Favera R . The BCL6 proto-oncogene suppresses p53 expression in germinal-centre B cells. Nature 2004; 432: 635–639.
Phan R, Saito M, Basso K, Niu H, Dalla-Favera R . BCL6 interacts with the transcription factor Miz-1 to suppress the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 and cell cycle arrest in germinal center B cells. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 1054–1060.
Shaffer AL, Emre NC, Lamy L, Ngo VN, Wright G, Xiao W et al. IRF4 addiction in multiple myeloma. Nature 2008; 454: 226–231.
Figueroa M, Reimers M, Thompson R, Ye K, Li Y, Selzer R et al. An integrative genomic and epigenomic approach for the study of transcriptional regulation. PLoS ONE 2008; 3: e1882.
Kuang S, Tong W, Yang H, Lin W, Lee M, Fang Z et al. Genome-wide identification of aberrantly methylated promoter associated CpG islands in acute lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2008; 22: 1529–1538.
Roman-Gomez J, Jimenez-Velasco A, Castillejo JA, Agirre X, Barrios M, Navarro G et al. Promoter hypermethylation of cancer-related genes: a strong independent prognostic factor in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2004; 104: 2492–2498.
Roman-Gomez J, Cordeu L, Agirre X, Jimenez-Velasco A, San Jose-Eneriz E, Garate L et al. Epigenetic regulation of Wnt-signaling pathway in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2007; 109: 3462–3469.
Guenther M, Jenner R, Chevalier B, Nakamura T, Croce C, Canaani E et al. Global and Hox-specific roles for the MLL1 methyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 8603–8608.
Acevedo L, Iniguez A, Holster H, Zhang X, Green R, Farnham P . Genome-scale ChIP-chip analysis using 10 000 human cells. Biotechniques 2007; 43: 791–797.
Pop M, Salzberg S . Bioinformatics challenges of new sequencing technology. Trends Genet 2008; 24: 142–149.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (R01CA120196 and R01CA129382 to AF); the WOLF Foundation (AF), the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (Grants 1287-08, 7189-08 and 6237-08 to AF), the Cancer Research Institute (AF), the Swim Across America Foundation (AF). Adolfo Ferrando is a Leukemia and Lymphoma Society Scholar. Teresa Palomero is a recipient of a Young Investigator Award from the Alex's Lemonade Stand Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palomero, T., Ferrando, A. Genomic tools for dissecting oncogenic transcriptional networks in human leukemia. Leukemia 23, 1236–1242 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.394
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.394
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Lymphoma: current status of clinical and preclinical imaging with radiolabeled antibodies
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (2017)