Abstract
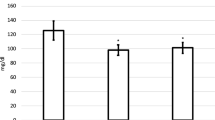
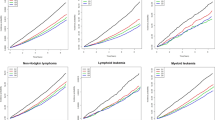
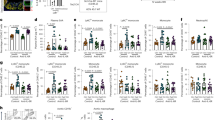
Survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells requires sustained activation of the antiapoptotic PI-3-K/Akt pathway, and many therapies for CLL cause leukemia cell death by triggering apoptosis. Blood lipoprotein particles are either pro- or antiapoptotic. High-density lipoprotein particles are antiapoptotic through sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3-mediated activation of the PI-3-K/Akt pathway. Apolipoprotein E4 (apoE4)–very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) increase apoptosis, but the apoE2-VLDL and apoE3-VLDL isoforms do not. As increased B-cell apoptosis favors longer survival of CLL patients, we hypothesized that APOE4 genotype would beneficially influence the clinical course of CLL. We report here that women (but not men) with an APOE4 genotype had markedly longer survival than non-APOE4 patients. VLDL is metabolized to low-density lipoprotein through lipoprotein lipase. Higher levels of lipoprotein lipase mRNA in these CLL patients correlated with shorter survival. The beneficial effect of APOE4 in CLL survival is likely mediated through APOE4 allele-specific regulation of leukemia cell apoptosis. The APOE allele and genotype distribution in these CLL patients is the same as in unaffected control populations, suggesting that although APOE genotype influences CLL outcome and response to therapy, it does not alter susceptibility to developing this disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiorazzi N, Rai KR, Ferrarini M . Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 804–815.
Keating MJ . Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. In: Henderson ES, Lister TA, Greaves MF (eds). Leukemia, 7th edn. Saunders: Philadelphia, 2002, pp 131–151.
Cuni S, Perez-Aciego P, Perez-Chacon G, Vargas JA, Sanchez A, Martin-Saavedra FM et al. A sustained activation of PI3K/NF-kappaB pathway is critical for the survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Leukemia 2004; 18: 1391–1400.
DeKroon R, Robinette JB, Hjelmeland AB, Wiggins E, Blackwell M, Mihovilovic M et al. APOE4-VLDL inhibits the HDL-activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt Pathway via the phosphoinositol phosphatase SHIP2. Circ Res 2006; 99: 829–836.
DeKroon RM, Mihovilovic M, Goodger ZV, Robinette JB, Sullivan PM, Saunders AM et al. ApoE genotype-specific inhibition of apoptosis. J Lipid Res 2003; 44: 1566–1573.
Weinberg JB, Volkheimer AD, Chen Y, Beasley BE, Jiang N, Lanasa MC et al. Clinical and molecular predictors of disease severity and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Am J Hematol 2007; 82: 1063–1070.
Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Grever M, Kay N, Keating MJ, O′Brien S et al. National Cancer Institute-sponsored Working Group guidelines for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: revised guidelines for diagnosis and treatment. Blood 1996; 87: 4990–4997.
Volkheimer AD, Weinberg JB, Beasley BE, Whitesides JF, Gockerman JP, Moore JO et al. Progressive immunoglobulin gene mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: evidence for antigen-driven intraclonal diversification. Blood 2007; 109: 1559–1567.
Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel D, George-Hyslop PH, Pericak-Vance MA, Joo SH et al. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 1993; 43: 1467–1472.
Mihovilovic M, Hulette C, Gilbert JR . Strategy to analyze thymic transcription of alpha-3 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor submit. Methods Neurosc 1993; 12: 169–190.
Davignon J, Cohn JS, Mabile L, Bernier L . Apolipoprotein E and atherosclerosis: insight from animal and human studies. Clin Chim Acta 1999; 286: 115–143.
Schaefer EJ, Lamon-Fava S, Johnson S, Ordovas JM, Schaefer MM, Castelli WP et al. Effects of gender and menopausal status on the association of apolipoprotein E phenotype with plasma lipoprotein levels. Results from the Framingham Offspring Study. Arterioscler Thromb 1994; 14: 1105–1113.
Oppezzo P, Vasconcelos Y, Settegrana C, Jeannel D, Vuillier F, Legarff-Tavernier M et al. The LPL/ADAM29 expression ratio is a novel prognosis indicator in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2005; 106: 650–657.
Nuckel H, Huttmann A, Klein-Hitpass L, Schroers R, Fuhrer A, Sellmann L et al. Lipoprotein lipase expression is a novel prognostic factor in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 2006; 47: 1053–1061.
Heintel D, Kienle D, Shehata M, Krober A, Kroemer E, Schwarzinger I et al. High expression of lipoprotein lipase in poor risk B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2005; 19: 1216–1223.
Damle RN, Wasil T, Fais F, Ghiotto F, Valetto A, Allen SL et al. Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 1840–1847.
Hamblin TJ, Davis Z, Gardiner A, Oscier DG, Stevenson FK . Unmutated Ig V-H genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 1848–1854.
Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S, Benner A, Leupolt E, Krober A, Bullinger L et al. Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 1910–1916.
Schwarz JK, Yarbro JW . Scientific basis of cancer chemotherapy. In: Perry MC (ed). The Chemotherapy Source Book. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, 2001, pp 1–6.
Ji ZS, Pitas RE, Mahley RW . Differential cellular accumulation/retention of apolipoprotein E mediated by cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Apolipoproteins E3 and E2 greater than e4. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 13452–13460.
Mulder M, Lombardi P, Jansen H, van Berkel TJ, Frants RR, Havekes LM . Low density lipoprotein receptor internalizes low density and very low density lipoproteins that are bound to heparan sulfate proteoglycans via lipoprotein lipase. J Biol Chem 1993; 268: 9369–9375.
Molica S . Sex differences in incidence and outcome of chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients. Leuk Lymphoma 2006; 47: 1477–1480.
Huang P, Feng L, Oldham EA, Keating MJ, Plunkett W . Superoxide dismutase as a target for the selective killing of cancer cells. Nature 2000; 407: 390–395.
Narasimhan P, Amaral L . Lymphopenic response of patients presenting with chronic lymphocytic leukemia associated with carcinoma of the prostate to diethylstilbestrol: correlation of response to the in vitro synthesis of RNA by patient lymphocytes and its relationship to transcortin. Am J Hematol 1980; 8: 369–375.
Gao N, Rahmani M, Dent P, Grant S . 2-Methoxyestradiol-induced apoptosis in human leukemia cells proceeds through a reactive oxygen species and Akt-dependent process. Oncogene 2005; 24: 3797–3809.
Haynes MP, Sinha D, Russell KS, Collinge M, Fulton D, Morales-Ruiz M et al. Membrane estrogen receptor engagement activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase via the PI3-kinase-Akt pathway in human endothelial cells. Circ Res 2000; 87: 677–682.
Wang JM, Irwin RW, Brinton RD . Activation of estrogen receptor alpha increases and estrogen receptor beta decreases apolipoprotein E expression in hippocampus in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 16983–16988.
Raber J, Bongers G, LeFevour A, Buttini M, Mucke L . Androgens protect against apolipoprotein E4-induced cognitive deficits. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 5204–5209.
Dallongeville J, Lussier-Cacan S, Davignon J . Modulation of plasma triglyceride levels by apoE phenotype: a meta-analysis. J Lipid Res 1992; 33: 447–454.
Ferrieres J, Sing CF, Roy M, Davignon J, Lussier-Cacan S . Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Sex-specific effects. Arterioscler Thromb 1994; 14: 1553–1560.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients for their participation, and the Hematology–Oncology nurses and physician assistants for their special contributions. The work was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health, the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society and the VA Research Service (JBW); Glenn/AFAR (RD); and GlaxoSmithKline and the Deane Laboratory (WJS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weinberg, J., Volkheimer, A., Mihovilovic, M. et al. Apolipoprotein E genotype as a determinant of survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 22, 2184–2192 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.241
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.241
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Somatic mutations in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) identified by exome sequencing
Leukemia (2011)
-
Reduced expression of the tumor suppressor PHLPP1 enhances the antiapoptotic B-cell receptor signal in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B-cells
Leukemia (2010)
-
Serum metabolome analysis by 1H-NMR reveals differences between chronic lymphocytic leukaemia molecular subgroups
Leukemia (2010)