Abstract
Objective:
Evaluate the effect of Hepatitis B vaccine (HepB) on C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in healthy term infants.
Study design:
A prospective controlled study in an academic medical center serving an inner city community. Subjects were singleton, term and late pre-term infants delivered vaginally with normal physical examination and without risk factors for or signs of sepsis. CRP levels were measured in cord blood and at the time of newborn genetic screening. The early HepB group received HepB within a few hours after birth. The late HepB group had HepB delayed until after the repeat CRP.
Result:
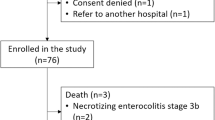
One hundred and eighty-two infants were enrolled (94 early HepB, 88 late HepB) with similar demographic features in each group. Neither the mean cord CRP (early HepB, 0.24±0.23 vs late HepB, 0.30±0.68 mg l−1, P=0.37) nor the median of the repeat CRP (early HepB, 2.6 (interquartile range, 1.18 to 7.03) vs late HepB, 1.7 (interquartile range, 0.73 to 5.8) mg l−1, P=0.14) showed significant differences between the two groups.
Conclusion:
HepB does not affect CRP levels in healthy term infants.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Philip AG, Mills PC . Use of C-reactive protein in minimizing antibiotic exposure: experience with infants initially admitted to a well-baby nursery. Pediatrics 2000; 106 (1): E4.
Ehl S, Gering B, Bartmann P, Högel J, Pohlandt F . C-reactive protein is a useful marker for guiding duration of antibiotic therapy in suspected neonatal bacterial infection. Pediatrics 1997; 99 (2): 216–221.
Franz AR, Bauer K, Schalk A, Garland SM, Bowman ED, Rex K et al. Measurement of interleukin 8 in combination with C-reactive protein reduced unnecessary antibiotic therapy in newborn infants: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics 2004; 114 (1): 1–8.
Benitz WE, Han MY, Madan A, Ramachandra P . Serial serum C-reactive protein levels in the diagnosis of neonatal infection. Pediatrics 1998; 102 (4): E41.
Chiesa C, Signore F, Assumma M, Buffone E, Tramontozzi P, Osborn JF et al. Serial measurements of C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 in the immediate postnatal period: reference intervals and analysis of maternal and perinatal confounders. Clin Chem 2001; 47 (6): 1016–1022.
Forest JC, Larivière F, Dolcé P, Masson M, Nadeau L . C-reactive protein as biochemical indicator of bacterial infection in neonates. Clin Biochem 1986; 19 (3): 192–194.
Mathai E, Christopher U, Mathai M, Jana AK, Rose D, Bergstrom S . Is C-reactive protein level useful in differentiating infected from uninfected neonates among those at risk of infection? Indian Pediatr 2004; 41 (9): 895–900.
Chiesa C, Natale F, Pascone R, Osborn JF, Pacifico L, Bonci E et al. C reactive protein and procalcitonin: reference intervals for preterm and term newborns during the early neonatal period. Clin Chim Acta 2011; 412 (11–12): 1053–1059.
Christian LM, Iams JD, Porter K, Glaser R . Inflammatory responses to trivalent influenza virus vaccine among pregnant women. Vaccine 2011; 29 (48): 8982–8987.
Paine NJ, Ring C, Bosch JA, Drayson MT, Veldhuijzen van Zanten . JJCS. The time course of the inflammatory response to the Salmonella typhi vaccination. Brain Behav Immun 2013; 30: 73–79.
Pourcyrous M, Korones SB, Arheart KL, Bada HS . Primary immunization of premature infants with gestational age <35 weeks: cardiorespiratory complications and C-reactive protein responses associated with administration of single and multiple separate vaccines simultaneously. J Pediatr 2007; 151 (2): 167–172.
Celik IH, Demirel G, Canpolat FE, Erdeve O, Dilmen U . Inflammatory responses to hepatitis B virus vaccine in healthy term infants. Eur J Pediatr 2013; 172 (6): 839–842.
Mast EE, Margolis HS, Fiore AE, Brink EW, Goldstein ST, Wang SA et al. A comprehensive immunization strategy to eliminate transmission of hepatitis B virus infection in the United States: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) part 1: immunization of infants, children, and adolescents. MMWR Recomm Rep 2005; 54 (RR-16): 1–31.
Committee on Infectious Diseases (American Academy of Pediatrics). Recommended childhood and adolescent immunization schedule—United States, 2014. Pediatrics 2014; 133 (2): 357–363.
Rossetti A, Perrone S, Bindi I, Longini M, Felici C, Proietti F et al. C-Reactive Protein in Term Newborns during the First 48 Hours of Life; [Abstract] PAS 2014. Abstract #4106.174.
Gerdes JS . Diagnosis and management of bacterial infections in the neonate. Pediatr Clin North Am 2004; 51 (4): 939–959, viii–ix.
Weitkamp J-H, Aschner JL . Diagnostic use of C-reactive protein (CRP) in assessment of neonatal sepsis. Neoreviews 2005; 6 (11): e508–e515.
Acknowledgements
We would like to dedicate this manuscript to the memory of Louis I Weisberg, MD who conceived of this study. We thank Matilde Irigoyen, MD for her editorial assistance in preparing this manuscript. The study was funded by the Louis I Weisberg, MD Memorial Neonatology Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dapaah-Siakwan, F., Gunasekaran, A. & Schutzman, D. C-reactive protein levels following hepatitis B vaccine in healthy newborns. J Perinatol 36, 231–234 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2015.160
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2015.160