Abstract
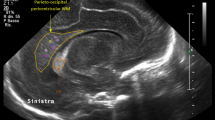
We report on a preterm neonate of 30 weeks gestational age who presented with marked muscular hypotonia and severe respiratory failure at birth and was diagnosed with congenital myotonic dystrophy. Neuroimaging at 36 gestational weeks demonstrated diffuse T2-hyperintense signal of the supratentorial white matter and a simplified gyration and sulcation pattern. Follow-up imaging showed progressive myelination, brain maturation and decrease in T2-signal of the white matter. We discuss possible pathomechanisms for white matter signal abnormalities in this neonate.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harper PS . Myotonic dystrophy In: Karpati G, Hilton-Jones D, Griggs RC (eds) Disorders of Voluntary Muscle. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge pp 541–559 2001.
Udd B, Krahe R . The myotonic dystrophies: molecular, clinical, and therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol 2012; 11 (10): 891–905.
Wesstrom G, Bensch J, Schollin J . Congenital myotonic dystrophy. Incidence, clinical aspects and early prognosis. Acta Paediatr Scand 1986; 75 (5): 849–854.
Hageman AT, Gabreels FJ, Liem KD, Renkawek K, Boon JM . Congenital myotonic dystrophy; a report on thirteen cases and a review of the literature. J Neurol Sci 1993; 115 (1): 95–101.
Campbell C, Sherlock R, Jacob P, Blayney M . Congenital myotonic dystrophy: assisted ventilation duration and outcome. Pediatrics 2004; 113 (4): 811–816.
Kaliman P, Llagostera E . Myotonic dystrophy protein kinase (DMPK) and its role in the pathogenesis of myotonic dystrophy 1. Cell Signal 2008; 20 (11): 1935–1941.
Prasad AN, Prasad C . The floppy infant: contribution of genetic and metabolic disorders. Brain Dev 2003; 25 (7): 457–476.
Haranaka M, Endo A, Kohira R, Fujita Y, Takada M, Ohkubo O et al. [Brain lesion in congenital myotonic dystrophy]. No To Hattatsu 2000; 32 (3): 268–273.
Charrow J . A newborn girl with hypotonia and respiratory failure. Pediatr Ann 2007; 36 (12): 777, 781-782.
Hashimoto T, Tayama M, Miyazaki M, Murakawa K, Kawai H, Nishitani H et al. Neuroimaging study of myotonic dystrophy. I. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. Brain Dev 1995; 17 (1): 24–27.
Wozniak JR, Mueller BA, Ward EE, Lim KO, Day JW . White matter abnormalities and neurocognitive correlates in children and adolescents with myotonic dystrophy type 1: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Neuromuscul Disord 2011; 21 (2): 89–96.
Minnerop M, Weber B, Schoene-Bake JC, Roeske S, Mirbach S, Anspach C et al. The brain in myotonic dystrophy 1 and 2: evidence for a predominant white matter disease. Brain 2011; 134 (Pt 12): 3530–3546.
Tanabe Y, Iai M, Tamai K, Fujimoto N, Sugita K . Neuroradiological findings in children with congenital myotonic dystrophy. Acta Paediatr 1992; 81 (8): 613–617.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Professor Ronald D Cohn, Division of Clinical and Metabolic Genetics, the Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto, Canada, and Professor Jaap Valk, Department of Radiology, VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, for interesting and helpful discussions about this patient.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bosemani, T., Jasien, J., Johnston, M. et al. Neonatal neuroimaging findings in congenital myotonic dystrophy. J Perinatol 34, 159–160 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2013.142
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2013.142