Abstract
Objective:
The objective of this study is to investigate the relationship between glycemic status and severe retinopathy of prematurity (ROP).
Study Design:
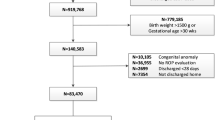
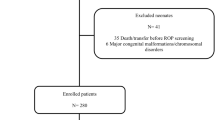
This is a retrospective cohort study of 114 infants <1000 g admitted to a level IV neonatal intensive care unit within 48 h of life. A cumulative, time-weighted glucose level (TWGL) derived from plotting glucose values over time was included in logistic regression analysis to identify predictors for severe ROP.
Result:
Infants had 26.6±2 weeks gestational age and had a birth weight of 782±136 g. TWGL during first 10 and 30 days of life were greater in the severe ROP group (P<0.01). Unlike single events of glucose levels ⩾150 mg dl−1, 10 days TWGL ⩾100 mg dl−1 (odds ratio (OR) 5.2, P<0.02) and 30 days TWGL ⩾118 mg dl−1 (OR 5.7, P<0.02) were predictors for severe ROP (univariate). Multivariate regression confirmed 30 days TWGL ⩾118 mg dl−1 (OR 9.4 to 10) and gram-positive sepsis (OR 4.1 to 5) as predictors for severe ROP (P<0.05).
Conclusion:
High overall glycemic status is associated with the development of severe ROP.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanco CL, Baillargeon JG, Morrison RL, Gong AK . Hyperglycemia in extremely low birth weight infants in a predominantly Hispanic population and related morbidities. J Perinatol 2006; 26 (12): 737–741.
Milcic TL . Neonatal glucose homeostasis. Neonatal Netw 2008; 27 (3): 203–207.
Montassir H, Maegaki Y, Ogura K, Kurozawa Y, Nagata I, Kanzaki S et al. Associated factors in neonatal hypoglycemic brain injury. Brain Dev 2009; 31 (9): 649–656.
Hay Jr WW, Raju TN, Higgins RD, Kalhan SC, Devaskar SU . Knowledge gaps and research needs for understanding and treating neonatal hypoglycemia: workshop report from Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. J Pediatr 2009; 155 (5): 612–617.
Straussman S, Levitsky LL . Neonatal hypoglycemia. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2010; 17 (1): 20–24.
Bedrossian R . Retinopathy of prematurity (retrolental fibroplasia) and its relationship to oxygen. AMA Arch Ophthalmol 1953; 50 (2): 266–267.
Patz A, Hoeck LE, De La Cruz E . Studies on the effect of high oxygen administration in retrolental fibroplasia. I. Nursery observations. Am J Ophthalmol 1952; 35 (9): 1248–1253.
O’Connor AR, Birch EE, Spencer R . Factors affecting development of motor skills in extremely low birth weight children. Strabismus 2009; 17 (1): 20–23.
Ertl T, Gyarmati J, Gaal V, Szabo I . Relationship between hyperglycemia and retinopathy of prematurity in very low birth weight infants. Biol Neonate 2006; 89 (1): 56–59.
Garg R, Agthe AG, Donohue PK, Lehmann CU . Hyperglycemia and retinopathy of prematurity in very low birth weight infants. J Perinatol 2003; 23 (3): 186–194.
Rautonen J, Makela A, Boyd H, Apajasalo M, Pohjavuori M . CRIB and SNAP: assessing the risk of death for preterm neonates. Lancet 1994; 343 (8908): 1272–1273.
Harkavy KL, Scanlon JW, Chowdhry PK, Grylack LJ . Dexamethasone therapy for chronic lung disease in ventilator- and oxygen-dependent infants: a controlled trial. J Pediatr 1989; 115 (6): 979–983.
Yeh TF, Lin YJ, Hsieh WS, Lin HC, Lin CH, Chen JY et al. Early postnatal dexamethasone therapy for the prevention of chronic lung disease in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome: a multicenter clinical trial. Pediatrics 1997; 100 (4): E3.
Waitzman MB . Introductory comments for session V ‘neovasculogenesis’ presented at the fifth symposium, the International Society on Metabolic Eye Disease October 24–26, 1982. Metab Pediatr Syst Ophthalmol 1983; 7 (2): 71–74.
Yoo MH, Yoon YH, Chung H, Cho KS, Koh JY . Insulin increases retinal hemorrhage in mild oxygen-induced retinopathy in the rat: inhibition by riluzole. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2007; 48 (12): 5671–5676.
Shennan AT, Dunn MS, Ohlsson A, Lennox K, Hoskins EM . Abnormal pulmonary outcomes in premature infants: prediction from oxygen requirement in the neonatal period. Pediatrics 1988; 82 (4): 527–532.
Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H . Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1500 gm. J Pediatr 1978; 92 (4): 529–534.
Subhani M, Combs A, Weber P, Gerontis C, DeCristofaro JD . Screening guidelines for retinopathy of prematurity: the need for revision in extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2001; 107 (4): 656–659.
Screening examination of premature infants for retinopathy of prematurity. Pediatrics 2006; 117 (2): 572–576.
Bozzetti P, Ferrari MM, Marconi AM, Ferrazzi E, Pardi G, Makowski EL et al. The relationship of maternal and fetal glucose concentrations in the human from midgestation until term. Metabolism 1988; 37 (4): 358–363.
Iglesias Platas I, Thio Lluch M, Pociello Alminana N, Morillo Palomo A, Iriondo Sanz M, Krauel Vidal X . Continuous glucose monitoring in infants of very low birth weight. Neonatology 2009; 95 (3): 217–223.
Lucey JF, Dangman B . A reexamination of the role of oxygen in retrolental fibroplasia. Pediatrics 1984; 73 (1): 82–96.
Kermorvant-Duchemin E, Sapieha P, Sirinyan M, Beauchamp M, Checchin D, Hardy P et al. Understanding ischemic retinopathies: emerging concepts from oxygen-induced retinopathy. Doc Ophthalmol 2010; 120 (1): 51–60.
You JJ, Yang CH, Chen MS, Yang CM . Cysteine-rich 61, a member of the CCN family, as a factor involved in the pathogenesis of proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2009; 50 (7): 3447–3455.
Aiello LP, Northrup JM, Keyt BA, Takagi H, Iwamoto MA . Hypoxic regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in retinal cells. Arch Ophthalmol 1995; 113 (12): 1538–1544.
Gaynon MW . Rethinking STOP-ROP: is it worthwhile trying to modulate excessive VEGF levels in prethreshold ROP eyes by systemic intervention? A review of the role of oxygen, light adaptation state, and anemia in prethreshold ROP. Retina 2006; 26 (7 Suppl): S18–S23.
Laron Z, Avitzur Y, Klinger B . Carbohydrate metabolism in primary growth hormone resistance (Laron syndrome) before and during insulin-like growth factor-I treatment. Metabolism 1995; 44 (10 Suppl 4): 113–118.
Beardsall K, Ogilvy-Stuart AL, Frystyk J, Chen JW, Thompson M, Ahluwalia J et al. Early elective insulin therapy can reduce hyperglycemia and increase insulin-like growth factor-I levels in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr 2007; 151 (6): 611–617, 617 e611.
Qazi Y, Maddula S, Ambati BK . Mediators of ocular angiogenesis. J Genet 2009; 88 (4): 495–515.
Di Fiore JM, Bloom JN, Orge F, Schutt A, Schluchter M, Cheruvu VK et al. A higher incidence of intermittent hypoxemic episodes is associated with severe retinopathy of prematurity. J Pediatr 2010; 157 (1): 69–73.
Atherton A, Hill DW, Keen H, Young S, Edwards EJ . The effect of acute hyperglycaemia on the retinal circulation of the normal cat. Diabetologia 1980; 18 (3): 233–237.
Nyengaard JR, Ido Y, Kilo C, Williamson JR . Interactions between hyperglycemia and hypoxia: implications for diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 2004; 53 (11): 2931–2938.
Beardsall K, Ogilvy-Stuart AL, Ahluwalia J, Thompson M, Dunger DB . The continuous glucose monitoring sensor in neonatal intensive care. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2005; 90 (4): F307–F310.
Stein I, Neeman M, Shweiki D, Itin A, Keshet E . Stabilization of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA by hypoxia and hypoglycemia and coregulation with other ischemia-induced genes. Mol Cell Biol 1995; 15 (10): 5363–5368.
DiBiasie A . Evidence-based review of retinopathy of prematurity prevention in VLBW and ELBW infants. Neonatal Netw 2006; 25 (6): 393–403.
Shah VA, Yeo CL, Ling YL, Ho LY . Incidence, risk factors of retinopathy of prematurity among very low birth weight infants in Singapore. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2005; 34 (2): 169–178.
Nair PM, Ganesh A, Mitra S, Ganguly SS . Retinopathy of prematurity in VLBW and extreme LBW babies. Indian J Pediatr 2003; 70 (4): 303–306.
Smolkin T, Steinberg M, Sujov P, Mezer E, Tamir A, Makhoul IR . Late postnatal systemic steroids predispose to retinopathy of prematurity in very-low-birth-weight infants: a comparative study. Acta Paediatr 2008; 97 (3): 322–326.
Chye JK, Lim CT, Leong HL, Wong PK . Retinopathy of prematurity in very low birth weight infants. Ann Acad Med Singapore 1999; 28 (2): 193–198.
Hartel C, Haase B, Browning-Carmo K, Gebauer C, Kattner E, Kribs A et al. Does the enteral feeding advancement affect short-term outcomes in very low birth weight infants? J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2009; 48 (4): 464–470.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Jennifer Shepard, Denise FitzSimon, Robert Bennett, and Jessica Moore for their support and Kelli Price and Julia Hinojos for their administrative assistance. This study was supported in part by The Thomas Wilson Sanitarium for Children of Baltimore City.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Journal of Perinatology website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chavez-Valdez, R., McGowan, J., Cannon, E. et al. Contribution of early glycemic status in the development of severe retinopathy of prematurity in a cohort of ELBW infants. J Perinatol 31, 749–756 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2011.19
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2011.19
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hyperglycemia and prematurity: a narrative review
Pediatric Research (2023)
-
FGF21 via mitochondrial lipid oxidation promotes physiological vascularization in a mouse model of Phase I ROP
Angiogenesis (2023)
-
Correlation between hyperglycemia and glycated albumin with retinopathy of prematurity
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Association between neonatal hyperglycemia and retinopathy of prematurity: a meta-analysis
European Journal of Pediatrics (2021)
-
Association between hyperglycemia and retinopathy of prematurity: a systemic review and meta-analysis
Scientific Reports (2015)