Abstract
Objective:
To assess the efficacy and safety of bosentan as an adjuvant therapy of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN).
Study Design:
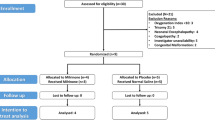
Forty-seven neonates with PPHN were randomly assigned to receive either bosentan (n=24) or placebo (n=23). Efficacy was evaluated with a favorable outcome defined as fulfilling all the following criteria (for example, oxygenation index <15, normal pulmonary artery pressure (<20 mm Hg) and no premature discontinuation of the drug because of drug-related toxicity or lack of efficacy). Evaluation of safety was done by monitoring drug-related adverse events.
Result:
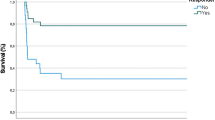
Bosentan treatment was superior to placebo with a favorable response in 87.5% of patients treated with bosentan as compared with 20% of those who received placebo (P<0.0001). None of patients in the bosentan group had drug-related clinical or laboratory adverse events.
Conclusion:
Bosentan may be a useful adjuvant therapy of PPHN.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morin III FC, Stenmark KR . Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: state of the art. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1995; 151: 2010–2032.
Steinhorn RH, Millard SL, Moran III FC . Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: role of nitric oxide and endothelin in pathophysiology and treatment. Clin Perinatol 1995; 22: 405–428.
Konduri GG . New approaches for persistent pulmonary hypertension of newborn. Clin Perinatol 2004; 31: 591–611.
Endo A, Ayusawa M, Minato M, Takada M, Takahashi S, Harada K . Endogenous nitric oxide and endothelin-1 in persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Eur J Pediatr 2001; 160: 217–222.
Ivy DD, Le Cras TD, Horan MP, Abmen SH . Increased lung preproET-1 and decreased ETB-receptor gene expression in fetal pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol 1998; 274 (Part 1): L535–L541.
Rosenberg AA, Kennaugh J, Koppenhafer SL, Loomis M, Chatfield BA, Abman SH . Elevated immunoreactive endothelin-1 levels in newborn infants with persistent pulmonary hypertension. J Pediatr 1993; 123: 109–114.
Christou H, Adatia I, Van Marter L, Kane JW, Thompson JE, Stark AR et al. Effect of inhaled nitric oxide on endothelin-1 and cyclic guanosine 5-monophosphate concentration in newborn infants with persistent pulmonary hypertension. J Pediatr 1997; 130: 603–611.
Walsh MC, Stork EK . Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Clin Perinatol 2001; 28: 609–627.
Nakwan N, Choksuchat D, Saksawad R, Thammachote P, Nakwan N . Successful treatment of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn with bosentan. Acta Paediatr 2009; 98: 1683–1685.
Galie N, Hinderliter A, Torbicki A, Fourme T, Simonneau G, Pulido T et al. Effects of the oral endothelin-receptor antagonist bosentan on echocardiographic and Doppler measures in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003; 41: 1380–1386.
Rubin LJ, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Galie N, Black CM, Keogh A et al. Bosentan therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 896–903.
Barst R, Ivy D, Dingemanse J, Widlitz A, Schmitt K, Doran A et al. Pharmacokinetics, safety, and efficacity of bosentan in pediatric patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2003; 73: 372–382.
Goissen C, Ghyselen L, Tourneux P, Krim G, Storme L, Bou P et al. Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn with transposition of the great arteries: successful treatment with bosentan. Eur J Pediatr 2008; 167: 437–440.
Radicioni M, Bruni A, Camerini P . Combination therapy for life-threatening pulmonary hypertension in a premature infant: first report on bosentan use. Eur J Pediatr 2011 e-pub ahead of print 8 March 2011; doi:10.1007/s00431-011-1422-9.
Ostrea EM, Villanueva-Uy ET, Natarajan G, Uy HG . Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: pathogenesis, etiology, and management. Paediatr Drugs 2006; 8: 179–188.
Deakins KM . Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Respir Care 2009; 54: 1252–1262.
Ichiba H, Matsunami S, Itoh F, Ueda T, Ohsasa Y, Yamano T . Three-year follow up of term and near-term infants treated with inhaled nitric oxide. Pediatr Int 2003; 45: 290–293.
Latini G, Del Vecchio A, De Felice C, Verrotti A, Bossone E . Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: therapeutical approach. Mini Rev Med Chem 2008; 8: 1507–1513.
Nassi N, Daniotti M, Agostiniani S, Lombardi E, Favilli S, Donzelli GP . Sildenafil as “first line therapy” in pulmonary persistent hypertension of the newborn? J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2010; 23 (S3): 104–105.
Kusuda S, Shishida N, Miyagi N, Hirabayashi M, Kim TJ . Cerebral blood flow during treatment for pulmonary hypertension. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 1999; 80: F30–F33.
Leavitt AM, Watchko JF, Bennett FC, Folsom RC . Neurodevelopmental outcome following persistent pulmonary hypertension of the neonate. J Perinatol 1987; 7: 288–291.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the major contribution of pediatric cardiologists and colleagues at the neonatal intensive care unit, Abha General Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamed, W., Ismail, M. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, prospective study of bosentan for the treatment of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. J Perinatol 32, 608–613 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2011.157
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2011.157
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
B-natriuretic peptide serum levels in neonates with persistent pulmonary hypertension
Egyptian Pediatric Association Gazette (2021)
-
The use of supplemental hydrocortisone in the management of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn
Journal of Perinatology (2021)
-
Management of Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia in Newborn — Paradigm Shift and Ethical Issues
The Indian Journal of Pediatrics (2017)
-
Considerations in the management of hypoxemic respiratory failure and persistent pulmonary hypertension in term and late preterm neonates
Journal of Perinatology (2016)