Abstract
Objective:
Measuring serum tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and Regulated upon Activation Normal T cell Expressed and Secreated (RANTES) in neonatal sepsis and determining whether early and late onset sepsis were associated with differences in their concentrations.
Study Design:
In 15 neonates showing clinical signs of early- or late-onset infection, serum TNF-α and RANTES were determined at first suspicion of sepsis and before starting antibiotics. Fifteen healthy neonates were included as controls.
Results:
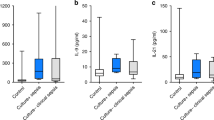
Serum TNF-α white blood cells and C-reactive protein (CRP) were significantly higher, whereas RANTES was significantly lower in the septic group compared with the non-septic group. There was no significant difference in RANTES or TNF-α levels between infants having early or late-onset sepsis. Similar to term neonates, premature neonates, responded to infection with increased TNF-α and decreased RANTES, with no statistical differences between both groups.
Conclusion:
In this study TNF-α is the best diagnostic test of neonatal sepsis, followed by CRP, when evaluated at first suspicion of sepsis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaushik SL, Parmar VR, Grover N, Grover PS, Kaushik R . Neonatal sepsis in hospital-born babies. J Commun Dis 1998; 30: 147–152.
Baltimore RS . Neonatal nosocomial infections. Semin Perinatol 1998; 22: 25–32.
Ng PC . Diagnostic markers of infection in neonates. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2004; 89: F229–F235.
Pöschl JM, Weiss T, Fallahi F, Linderkamp O . Reactive hyperemia of skin microcirculation in septic neonates. Acta Paediatr 1994; 83: 808–811.
Bone RC . Immunologic dissonance: a continuing evolution in our understanding of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome and the multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Ann Intern Med 1996; 125: 690–691.
Cavaillon JM, Adib-Conquy M, Fitting C, Adrie C, Payen D . Cytokine cascade in sepsis. Scand J Infect Dis 2003; 35: 535–544.
Adams DH, Lloyd AR . Chemokines: leukocyte recruitment and activation cytokines. Lancet 1997; 349: 490–495.
Baggliolini M, Dewald B, Moser B . Human chemokines: an update. Ann Rev Immunol 1997; 15: 675–705.
Rollins BJ . Chemokines. Blood 1997; 90: 909–928.
Schall TJ, Greaves DR . RANTES. In: Oppenheim JJ, Feldmann (eds). Cytokine References: A Compendium of Cytokines and Other Mediators of Host Defence. Academic Press: New York, 2000, pp 1161–1166.
Bacon KB, Premack BA, Gardner P, Schall TJ . Activation of dual T cell signaling pathways by the chemokine RANTES. Science 1995; 269: 1727–1730.
Ng PC, Li K, Leung TF, Wong RP, Li G, Chui KM et al. Early prediction of sepsis-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation with interleukin-10, interleukin-6, and RANTES in preterm infants. Clin Chem 2006; 52 (6): 1181–1189.
De Bont ES, Martens A, Van Raan J . Diagnostic value of plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in newborn sepsis. Acta Pediatr 1994; 83: 696–699.
Doellner H, Arntzen KJ, Haereid PE . Interleukin-6 concentrations in neonates evaluated for sepsis. J Pediatr 1998; 132: 295–299.
Silveira RC, Procianoy RS . Evaluation of interleukin-6, tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta for early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Acta Paediatr 1999; 88: 647–650.
Weinberg GA, Powel KR . Laboratory aids for diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. In: Remington JS, Klein JO (eds). Infectious Diseases of The Fetus and Newborn Infant. WB Saunders: Philadelphia, 2001, pp 1327–1344.
Grether JK, Nelson KB . Maternal infection and cerebral palsy in infants of normal birth weight. JAMA 1997; 278: 207–210.
Leviton A, Paneth N, Reuss ML . Maternal infection, fetal inflammatory response, and brain damage in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res 1999; 46: 566–575.
Dammann O, Leviton A . Maternal intrauterine infection, cytokines, and brain damage in preterm newborn. Pediatr Res 1997; 42: 1–8.
Romero R, Gomez R, Ghezzi F . A fetal systemic inflammatory response is followed by spontaneous onset of preterm parturition. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998; 179: 186–189.
Martin H, Olander B, Norman M . Reactive hyperemia and interleukin 6, interleukin 8, and tumor necrosis factor-α in the diagnosis of early-onset neonatal sepsis. Pediatrics 2001; 108 (4): 61.
Krolak-Olejnik B, Olejnik I, Kaomierczak W . C-C chemokines in the umbilical cord blood of preterm and term neonates. J Ped Neonatal 2005; 2 (1): NT36.
Wasek-Buko M, Behrendt J, Stojewska M, Krolak-Olejnik B, Karpe J, Godula-Stuglik U . Serum chemokine RANTES as an immunological indicator of early-onset neonatal sepsis In: 17th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID). 31 March–04 April 2007; ICC, Munich, Germany. (Abstract 1733_1042).
Krolak-Olejnik B, Beck B, Olejnik I . Umbilical serum concentrations of chemokines (RANTES and MGSA/GRO-) in preterm and term neonates. Pediatr Int 2006; 48: 586–590.
Dammann O, Phillips TM, Allred EN . Mediators of fetal inflammation in extremely low gestational age newborns. Cytokine 2001; 13: 234–239.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shouman, B., Badr, R. Regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted and tumor necrosis factor-α in septic neonates. J Perinatol 30, 192–196 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2009.167
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2009.167
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cytokine profiles of preterm neonates with fungal and bacterial sepsis
Pediatric Research (2012)