Abstract
Objective:
To examine the effect of mode of birth on plasma purine and malondialdehyde levels in normal term infants.
Study Design:
Umbilical arterial cord blood was obtained immediately after birth from a convenience sample of 119 normal term newborns born by vaginal delivery, with or without oxytocin augmentation or by elective cesarean delivery. Plasma was analyzed for purine and/or malondialdehyde levels. Numeric data were analyzed utilizing independent samples t-test and ordinal data were analyzed using Mann–Whitney test. Correlation coefficients were obtained using Spearman's ρ.
Result:
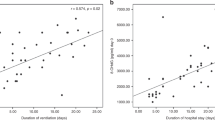
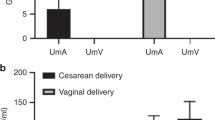
Uric acid levels were significantly elevated (P<0.001) in neonates undergoing vaginal birth, compared to neonates born by elective cesarean delivery. When the effect of oxytocin and length of labor was analyzed, neonates born to mothers on oxytocin had lower hypoxanthine, significantly lower xanthine (P=0.05) and higher uric acid levels. In addition, malondialdehyde levels were significantly higher (P<0.006) in neonates born to mothers who received oxytocin compared to neonates born to mothers without oxytocin augmentation. We also found significant correlations between malondialdehyde (MDA) and hypoxanthine (r=−0.465, P<0.039) and between MDA and xanthine (r=−0.753, P=0.003) in neonates born via oxytocin-augmented birth. Mode of birth had no statistically significant effect on clinical outcomes, although infants born by elective cesarean had higher incidence of acute respiratory distress and transient tachypnea of the newborn compared to those born vaginally.
Conclusion:
Neonates born by elective cesarean had the lowest purine levels in cord blood compared to neonates born vaginally. Oxytocin augmentation is associated with some degree of uterine hyperstimulation which may enhance the ATP degradation pathway resulting in the rapid conversion of hypoxanthine to xanthine and xanthine to uric acid. Significantly higher MDA levels in neonates whose mothers received oxytocin as well as significant correlation between MDA and the purines hypoxanthine and xanthine, suggest free-radical production, most likely due to xanthine oxidase activation. However, despite differences in plasma purine and malondialdehyde levels, no significant differences were seen in neonatal outcome. Further studies are required to fully characterize the effect of mode of birth on purine metabolism and free-radical production.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wakatsuki A, Okatani Y, Izumiya C, Ikenoue N . Effect of ischemia-reperfusion on xanthine oxidase activity in fetal rat brain capillaries. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999; 181 (3): 731–735.
Dorrepaal CA, Berger HM, Benders MJ, Van Zoeren-Grobben D, Van de Bor M, Van Bel F . Nonprotein-bound iron in post asphyxial reperfusion injury of the newborn. Pediatrics 1996; 98: 883–889.
Beckman JS, Beckman TW, Chen J, Marshall PA, Freeman BA . Apparent hydroxyl radical production by peroxynitrite: implications for endothelial injury from nitric oxide and superoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990; 87: 1620–1624.
Schmidt H, Grune T, Muller R, Siems WG, Wauer RR . Increased levels of lipid peroxidation products malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal after perinatal hypoxia. Pediatr Res 1996; 40: 15–20.
Junge HD, Kunzel W, Klock FK . Acute reduction of uterine blood flow and fetal heart rate changes in pregnant sheep near term. J Perinat Med 1977; 5: 39–55.
Siristatidis C, Salamalekis E, Kassanos D, Loghis C, Creatsas G . Evaluation of fetal intrapartum hypoxia by middle cerebral and umbilical artery doppler velocimetry with simultaneous cardiotocography and pulse oximetry. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2004; 270: 265–270.
Monkus ES, Nyhan WL, Fogel BJ, Yankow S . Concentrations of uric acid in the serum of neonatal infants and their mothers. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1970; 108: 91–97.
Manzke H, Spreter von Kreudenstein P, Dorner K, Kruse K . Quantitative measurements of the urinary excretion of creatinine, uric acid, hypoxanthine and xanthine, uracil, cyclic AMP, and cyclic GMP in healthy newborn infants. Eur J Pediatr 1980; 133: 157–161.
Wallenburg HCS, van Kreel BK . Fetal and maternal concentrations of uric acid and oxypurines during labor and post partum. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1980; 136: 513–517.
Irestedt L, Dahlin I, Hertzberg T, Sollevi A, Lagercrantz H . Adenosine concentration in umbilical cord blood of newborn infants after vaginal delivery and cesarean section. Pediatr Res 1989; 26: 106–108.
Cighetti G, Debiasi S, Paroni R, Allevi P . Free and total malondialdehyde assessment in biological matrices by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry: what is needed for an accurate detection. Anal Biochem 1999; 266: 222–229.
Cighetti G, Allevi P, Anastasia L, Bortone L, Paroni R . Use of methyl malondialdehyde as an internal standard for malondialdehyde detection: validation by isotope-dilution gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Clin Chem 2002; 48: 2266–2269.
Paroni R, Fermo I, Cighetti G . Validation of methyl malondialdehyde as internal standard for malondialdehyde detection by capillary electrophoresis. Anal Biochem 2002; 307: 92–98.
Pacheco LD, Rosen MP, Gei AF, Saade GR, Hankins GD . Management of uterine hyperstimulation with concomitant use of oxytocin and terbutaline. Am J Perinatol 2006; 23: 377–380.
Li H, Gudmundsson S, Olofsson P . Acute centralization of blood flow in compromised human fetuses evoked by uterine contractions. Early Hum Dev 2006; 82 (11): 747–752.
Khaw KS, Wang CC, Ngan Kee WD, Pang CP, Rogers MS . Effects of high inspired oxygen fraction during elective caesarean section under spinal anaesthesia on maternal and fetal oxygenation and lipid peroxidation. Br J Anaesth 2002; 88 (1): 18–23.
Hack M, Fanaroff AA, Klaus MH, Mendelawitz BD, Merkatz IR . Neonatal respiratory distress following elective delivery: a preventable disease? Am J Obstet Gynecol 1976; 126: 43–47.
Jain L, Eaton DC . Physiology of fetal lung fluid clearance and the effect of labor. Semin Perinatol 2006; 30 (1): 34–43.
Teng RJ, Ye YZ, Parks DA, Beckman JS . Urate produced during hypoxia protects heart proteins from peroxynitrite-mediated protein nitration. Free Radic Biol Med 2002; 33 (9): 1243–1249.
Hooper D, Scott G, Zborek A, Mikheeva T, Kean R, Koprowski R et al. Uric acid, a peroxynitrite scavenger, inhibits CNS inflammation, blood-CNS barrier permeability changes, and tissue damage in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. FASEB J 2000; 14: 691–698.
Perlman JM, Risser R . Relationship of uric acid concentrations and severe intraventricular hemorrhage/leukomalacia in the premature infant. J Pediatr Res 1998; 132: 436–439.
Streitman K, Tóth A, Horváth I, Tálosi G . Renal injury in perinatal hypoxia: ultrasonography and changes in renal function. Eur J Pediatr 2001; 160 (8): 473–477.
Acknowledgements
This study is partially funded by NIH Grants R21NR010407 (DA) and NIH IMSD 2R25GM060501 (TC). We thank Laura Gouveia, Katherine Angeles and LLUMC obstetric nurses and physicians for helping us with data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calderon, T., Wu, W., Rawson, R. et al. Effect of mode of birth on purine and malondialdehyde in umbilical arterial plasma in normal term newborns. J Perinatol 28, 475–481 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2008.29
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2008.29
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Labor induction with oxytocin in pregnant rats is not associated with oxidative stress in the fetal brain
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Correlation of perilipin 2 and lipid metabolism in elective cesarean section and vaginal delivery: a prospective study with oxidative and apoptotic pathways
Molecular Biology Reports (2021)