Abstract
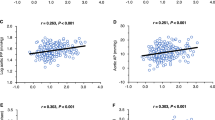
Local renin–angiotensin system (RAS) activity in the kidneys is a pathogenetic factor in patients with primary hypertension. This study aimed to determine the relationship between local kidney RAS activity and blood pressure variability, as the literature currently lacks any such study. The study included 73 consecutive primary hypertensive patients. All patients underwent 24-h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring to determine the average real variability (ARV) index, as an indicator of blood pressure variability. Local RAS activity was determined using the urine angiotensinogen/creatinine (UAGT/UCre) ratio. The high UAGT/UCre ratio group had significantly higher mean 24-h systolic ARV than the low UAGT/UCre ratio group (13.2±3.4 vs 11.0±2.6, P=0.003). Similarly, the high UAGT/UCre ratio group had significantly higher mean 24-h diastolic ARV than the low UAGT/UCre ratio group (10.8±3.2 vs 8.7±2.2, P=0.001). Multivariate regression analysis showed that Log(UAGT/UCre) was an independent predictor of both 24-h diastolic ARV and 24-h systolic ARV. Local RAS activity in the kidneys might have a role in blood pressure variability. On the basis of these findings, we think that additional prospective studies are needed to more fully discern the effect of local RAS activity on blood pressure variability.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kobori H, Nangaku M, Navar LG, Nishiyama A . The intrarenal renin-angiotensin system: from physiology to the pathobiology of hypertension and kidney disease. Pharmacol Rev 2007; 59: 251–287.
Baltatu O, Silva JA Jr ., Ganten D, Bader M . The brain renin-angiotensin system modulates angiotensin II-induced hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy. Hypertension 2000; 35: 409–412.
Lantelme P, Rohrwasser A, Gociman B, Hillas E, Cheng T, Petty G et al. Effects of dietary sodium and genetic background on angiotensinogen and Renin in mouse. Hypertension 2002; 39: 1007–1014.
Navar LG . The intrarenal renin-angiotensin system in hypertension. Kidney Int 2004; 65: 1522–1532.
Parati G, Faini A, Valentini M . Blood pressure variability: its measurement and significance in hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep 2006; 8: 199–204.
Mancia G, Parati G, Pomidossi G, Casadei R, Di Rienzo M, Zanchetti A . Arterial baroreflexes and blood pressure and heart rate variabilities in humans. Hypertension 1986; 8: 147–153.
Parati G, Saul JP, Di Rienzo M, Mancia G . Spectral analysis of blood pressure and heart rate variability in evaluating cardiovascular regulation. A critical appraisal. Hypertension 1995; 25: 1276–1286.
Conway J, Boon N, Davies C, Jones JV, Sleight P . Neural and humoral mechanisms involved in blood pressure variability. J Hypertens 1984; 2: 203–208.
Kotsis V, Stabouli S, Karafillis I, Papakatsika S, Rizos Z, Miyakis S et al. Arterial stiffness and 24 h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in young healthy volunteers: the early vascular ageing Aristotle University Thessaloniki Study (EVA-ARIS Study). Atherosclerosis 2011; 219 (1): 194–199.
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS . Estimation of the concentration of low- density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 1972; 18: 499–502.
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 2009; 150: 604–612.
Mena L, Pintos S, Queipo NV, Aizpurua JA, Maestre G, Sulbaran T . A reliable index for the prognostic significance of blood pressure variability. J Hypertens 2005; 23: 505–511.
Stergiou GS, Jaenecke B, Giovas PP, Chang A, Chung-Yueh Y, Tan TM . A tool for reliable self-home blood pressure monitoring designed according to the European Society of Hypertension recommendations: the Microlife WatchBP Home monitor. Blood Press Monit 2007; 12: 127–131.
Stergiou GS, Giovas PP, Gkinos CP, Patouras JD . Validation of the Microlife WatchBP Home device for self home blood pressure measurement according to the International Protocol. Blood Press Monit 2007; 12: 185–188.
Hackenthal E, Paul M, Ganten D, Taugner R . Morphology, physiology, and molecular biology of renin secretion. Physiol Rev 1990; 70: 1067–1116.
Navar LG, Imig JD, Zou L, Wang CT . Intrarenal production of angiotensin II. Semin Nephrol 1997; 17: 412–422.
Kobori H, Ozawa Y, Suzaki Y, Prieto-Carrasquero MC, Nishiyama A, Shoji T et al. Young Scholars Award Lecture: Intratubular angiotensinogen in hypertension and kidney diseases. Am J Hypertens 2006; 19: 541–550.
Ingelfinger JR, Zuo WM, Fon EA, Ellison KE, Dzau VJ . In situ hybridization evidence for angiotensinogen messenger RNA in the rat proximal tubule. An hypothesis for the intrarenal renin angiotensin system. J Clin Invest 1990; 85: 417–423.
Kobori H, Harrison-Bernard LM, Navar LG . Enhancement of angiotensinogen expression in angiotensin II-dependent hypertension. Hypertension 2001; 37: 1329–1335.
Kobori H, Harrison-Bernard LM, Navar LG . Urinary excretion of angiotensinogen reflects intrarenal angiotensinogen production. Kidney international 2002; 61: 579–585.
Konishi Y, Nishiyama A, Morikawa T, Kitabayashi C, Shibata M, Hamada M et al. Relationship between urinary angiotensinogen and salt sensitivity of blood pressure in patients with IgA nephropathy. Hypertension 2011; 58: 205–211.
Yamamoto T, Nakagawa T, Suzuki H, Ohashi N, Fukasawa H, Fujigaki Y et al. Urinary angiotensinogen as a marker of intrarenal angiotensin II activity associated with deterioration of renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2007; 18: 1558–1565.
Kobori H, Urushihara M, Xu JH, Berenson GS, Navar LG . Urinary angiotensinogen is correlated with blood pressure in men (Bogalusa Heart Study). J Hypertens 2010; 28: 1422–1428.
Michel FS, Norton GR, Maseko MJ, Majane OH, Sareli P, Woodiwiss AJ . Urinary angiotensinogen excretion is associated with blood pressure independent of the circulating Renin-Angiotensin system in a group of african ancestry. Hypertension 2014; 64: 149–156.
Kamiyama M, Zsombok A, Kobori H . Urinary angiotensinogen as a novel early biomarker of intrarenal renin-angiotensin system activation in experimental type 1 diabetes. J Pharmacol Sci 2012; 119: 314–323.
Erdogmus S, Sengul S, Kocak S, Kurultak I, Celebi ZK, Kutlay S et al. Urinary angiotensinogen level is correlated with proteinuria in renal transplant recipients. Transplant Proc 2013; 45: 935–939.
Kobori H, Alper AB Jr ., Shenava R, Katsurada A, Saito T, Ohashi N et al. Urinary angiotensinogen as a novel biomarker of the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system status in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 2009; 53: 344–350.
Bohlender J, Bader M, Menard J, Nussberger J . Blood pressure and renin-angiotensin system resetting in transgenic rats with elevated plasma Val5-angiotensinogen. J Hypertens 2012; 30: 1597–1605.
Ying J, Stuart D, Hillas E, Gociman BR, Ramkumar N, Lalouel JM et al. Overexpression of mouse angiotensinogen in renal proximal tubule causes salt-sensitive hypertension in mice. Am J Hypertens 2012; 25: 684–689.
Ramkumar N, Stuart D, Ying J, Kohan DE . A possible interaction between systemic and renal angiotensinogen in the control of blood pressure. Am J Hypertens 2013; 26: 473–480.
Pringle E, Phillips C, Thijs L, Davidson C, Staessen JA, de Leeuw PW et al. Systolic blood pressure variability as a risk factor for stroke and cardiovascular mortality in the elderly hypertensive population. J Hypertens 2003; 21: 2251–2257.
Verdecchia P, Angeli F, Gattobigio R, Rapicetta C, Reboldi G . Impact of blood pressure variability on cardiac and cerebrovascular complications in hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2007; 20: 154–161.
Veerabhadrappa P, Diaz KM, Feairheller DL, Sturgeon KM, Williamson S, Crabbe DL et al. Enhanced blood pressure variability in a high cardiovascular risk group of African Americans: FIT4Life Study. J Am Soc Hypertens 2010; 4: 187–195.
Mancia G, Bombelli M, Corrao G, Facchetti R, Madotto F, Giannattasio C et al. Metabolic syndrome in the Pressioni Arteriose Monitorate E Loro Associazioni (PAMELA) study: daily life blood pressure, cardiac damage, and prognosis. Hypertension 2007; 49: 40–47.
Siche JP, Herpin D, Asmar RG, Poncelet P, Chamontin B, Comparat V et al. Non-invasive ambulatory blood pressure variability and cardiac baroreflex sensitivity. J Hypertens 1995; 13: 1654–1659.
Diaz KM, Feairheller DL, Sturgeon KM, Veerabhadrappa P, Williamson ST, Crabbe DL et al. Increased nitric oxide and attenuated diastolic blood pressure variability in african americans with mildly impaired renal function. Int J Hypertens 2011; 2010: 137206.
Parati G, Ochoa JE, Lombardi C, Salvi P, Bilo G . Assessment and interpretation of blood pressure variability in a clinical setting. Blood Press 2013; 22: 345–354.
Shan ZZ, Dai SM, Fang F, Su DF . Angiotensin II contents in plasma, and cardiac and renal tissues of sinoaortic denervated rats. Sheng Li Xue Bao 2003; 55: 75–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozkayar, N., Dede, F., Akyel, F. et al. Relationship between blood pressure variability and renal activity of the renin–angiotensin system. J Hum Hypertens 30, 297–302 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2015.71
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2015.71
This article is cited by
-
Short-term blood pressure variability as a potential therapeutic target for kidney disease
Clinical Hypertension (2023)
-
Effect of angiotensin II receptor blocker and salt supplementation on short-term blood pressure variability in type 2 diabetes
Journal of Human Hypertension (2020)
-
Positive association between KCNJ5 rs2604204 (A/C) polymorphism and plasma aldosterone levels, but also plasma renin and angiotensin I and II levels, in newly diagnosed hypertensive Chinese: a case–control study
Journal of Human Hypertension (2017)