Abstract
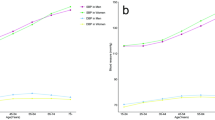
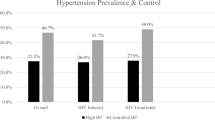
We determined the prevalence of hypertension and the level of awareness, treatment and control of hypertension among Palestinian adults in a population-based cross-sectional survey. Two-stage stratified sampling method was used to select 2077 participants from the general population aged 25 years and over. Trained observers obtained two blood pressure (BP) measurements from each individual by the use of a standardized mercury sphygmomanometer after a 5-min sitting rest. Information on sociogeographical factors and antihypertensive medications was obtained using a standard questionnaire. Hypertension was defined as a mean systolic BP (SBP) ⩾140 mm Hg, diastolic BP (DBP) ⩾90 mm Hg, and/or use of antihypertensive medications. The overall prevalence of hypertension was 27.6%, with a higher percentage among men (29.2 vs 26.4%; P=0.04). Hypertension increased with age in both men and women. Among hypertensive patients, 51.0% were aware of their elevated BP, 40.2% had treatment and only 9.5% achieved targeted BP control (<140/90 mm Hg). Patients under antihypertensive treatment showed SBP and DBP that were only 3.1 mm Hg and 2.5 mm Hg lower than individuals without antihypertensive treatment, respectively. The data show that hypertension prevalence among Palestinian adults is high, whereas the proportions of awareness treatment and control of hypertension were low. Concerted public health effort is urgently required to improve the detection, treatment and control of hypertension in Palestine.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khosh-Chashm K . The impact of urbanization on health in the countries of the Eastern Mediterranean region. Eastern Mediterranean Health J 1998; 4: S137–S148.
Hammoud EI . Changing demographic and vital statistics patterns in the region during the past 50 years. Eastern Mediterranean Health J 1998; 4: S58–S65.
Alwan A . Cardiovascular disease in the Eastern Mediterranean region. World Health Stat Q 1993; 46: 97–100.
Nissenen A, Bothig S, Granroth H, Lopez A . Hypertension in developing countries. World Health Stat Q 1988; 41: 141–154.
Abdul-Rahim H, Abu-Rmeileh N, Husseini A, Holmboe-Ottesen G, Jervell J, Bjertness E . Obesity and selected co-morbidities in an urban Palestinian population. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2001; 25 (11): 1736–1740.
Health Survey—2000: main findings. Ramallah (PS): Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics 2000.
Abdul-Rahim HF, Husseini A, Bjertness E, Giacaman R, Gordon NH, Jervell J . The metabolic syndrome in the West Bank population: an urban-rural comparison. Diabetes Care 2001; 24 (2): 275–279.
Berlowitz DR, Ash AS, Hickey EC, Friedman RH, Kader B, Moskowitz MA . Outcomes of hypertension care: simple measures are not that simple. Med Care 1997; 35: 742–746.
Whelton PK, Gu D, Wu X, Wenqi G, Muntner P . Factors associated with hypertension awareness, treatment, and control in a representative sample of the Chinese population. Hypertens 2004; 43: 578–585.
Husseini A, Abdul-Rahim H, Awartani F, Jervell J, Bjertness E . Prevalence of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance in a rural Palestinian population. Eastern Mediterranean Health J 2000; 6 (5–6): 1039–1045.
Abdul-Rahim HF, Husseini A, Giacaman R, Jervell J, Bjertness E . Diabetes mellitus in an urban Palestinian population: prevalence and associated factors. Eastern Mediterranean Health J 2001; 7 (1–2): 67–78.
Demographic Distribution in Palestine. Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics. Health Statistics 2007. http://www.pcbs.gov.ps/Portals/_pcbs/PressRelease/census2007_e.pdf.
Perloff D, Grim C, Flack J, Frohlich ED, Hill M, McDonald M et al. Human blood pressure determination by sphygmomanometry. Circulation 1993; 88 (1): 2460–2470.
The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure 2004.
Joint National Committee. The sixth report of the Joint National Committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure. Arch Intern Med 1997; 157 (21): 2413–2446.
World Health Organization-International Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension. Guidelines Subcommittee. J Hypertens 1999; 17 (2): 151–183.
Al-Nozha M, Abdullah M, Arafah R, Khalil MZ, Khan NB, Al-Mazrou YY et al. Hypertension in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J 2007; 28 (1): 77–84.
Kamadjeu RM, Edwards R, Atanga JS, Unwin N, Kiawi EC, Mbanya JC . Prevalence, awareness and management of hypertension in Cameroon: findings of the 2003 Cameroon Burden of Diabetes Baseline Survey. J Hum Hypertens 2006; 20 (1): 91–92.
Ibrahim M, Rizk H, Appel L, el Aroussy W, Helmy S, Sharaf Y et al. Hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control in Egypt. Results from the Egyptian National Hypertension Project (NHP). Hypertension 1995; 26 (6): 886–890.
Erem C, Hacihasanoglu A, Kocak M, Deger O, Topbas M . Prevalence of prehypertension and hypertension and associated risk factors among Turkish adults: Trabzon Hypertension Study. J Public Health 2009; 31 (1): 47–58.
Son PT, Quang N, Viet NL, Khai PG, Wall S, Weinehall L et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in Vietnam—results from a national survey. J Hum Hypertens 2012; 26: 268–280.
Ordunez-Garcia PO, Espinosa-Brito AD, Cooper RS, Kaufman JS, Nieto FJ . Hypertension in Cuba: evidence of a narrow black-white difference. J Hum Hypertens 1998; 12 (2): 111–116.
Gupta PC, Gupta R, Pednekar MS . Hypertension prevalence and blood pressure trends in 88 653 subjects in Mumbai, India. J Hum Hypertens 2004; 18 (12): 907–910.
Degli Esposti E, Di Martino M, Sturani A, Russo P, Dradi C, Falcinelli S et al. Risk factors for uncontrolled hypertension in Italy. J Hum Hypertens 2004; 18 (3): 207–213.
Van Minh H, Byass P, Chuc K, Wall S . Gender differences in prevalence and socioeconomic determinants of hypertension: findings fromthe WHO STEPs survey in a rural community of Vietnam. J Hum Hypertens 2006; 20 (2): 109–115.
Kearney P, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton K, He J . Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 2005; 365 (9455): 217–223.
Kershaw K, Diez Roux A, Carnethon M, Darwin C, Goff DC Jr, Post W et al. Geographic variation in hypertension prevalence among blacks and whites: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Am J Hypertens 2010; 23 (1): 46–53.
Reynolds K, Dongfengb G, Muntner P, Wu X, Chen J, Huang G et al. Geographic variations in the prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in China. J Hypertens 2003; 21 (7): 1273–1281.
Rampal L, Rampal S, Azhar M, Rahman A . Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in Malaysia: a national study of 16,440 subjects. Public Health 2008; 122 (1): 11–18.
Alsuwaida A, Alghonaim M . Gender disparities in the awareness and control of hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens 2011; 33 (5): 354–357.
Meng X, Dong G, Wang D, Liu M, Lin Q, Tian S et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, control, and risk factors associated with hypertension in urban adults from 33 communities of China: the CHPSNE study. J Hypertens 2011; 29 (7): 1303–1310.
Psaltopoulou T, Orfanos P, Naska A, Lenas D, Trichopoulos D, Trichopoulou A . Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in a general population sample of 26,913 adults in the Greek EPIC study. Int J Epidemiol 2004; 33 (6): 1345–1352.
Egan Zhao Y, Axon R . US trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension, 1988–2008. J Am Med Assoc 2010; 303 (20): 2043–2050.
Ostchega Y, Hughes P, Wright J, McDowell M, Louis T . Are demographic characteristics, health care access and utilization, and comorbid conditions associated with hypertension among US adults? Am J Hypertens 2008; 21 (2): 159–165.
Burt VL, Whelton P, Roccella EJ, Brown C, Cutler JA, Higgins M et al. Prevalence of hypertension in the US adult population: results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988 –1991. Hypertension 1995; 25: 305–313.
Henauw SD, Bacquer DD, Fonteyne W, Stam M, Kornitzer M, Backer GD . Trends in the prevalence, detection, treatment and control of arterial hypertension in the Belgian adult population. J Hypertens 1998; 16: 277–284.
Havlik RJ . Predictors of hypertension. Population studies. Am J Hypertens 1991; 4: 5865–5895.
Falaschetti E, Chaudhury M, Mindell J, Poulter N . Continued improvement in hypertension management in England: results from the health survey for England 2006. Hypertension 2009; 53 (3): 480–486.
Cheung B, Ong K, Man Y, Lam K, Lau C . Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension: United States National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001-2002. J Clin Hypertens 2006; 8 (2): 93–98.
Acknowledgements
Technical and financial support for this study was made available by the Palestinian American Research Council. We also wish to thank Dr Asa’d Ramlawi, Head of the primary care department at the Palestinian Ministry of Health for his support. This project is Funded by the Palestinian American Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khdour, M., Hallak, H., Shaeen, M. et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in the Palestinian population. J Hum Hypertens 27, 623–628 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2013.26
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2013.26
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Prevalence and risk factors of prehypertension and hypertension in Algeria
BMC Public Health (2022)
-
Prevalence of hypertension and pre-hypertension in the Middle East region: a systematic review & meta-analysis
Journal of Human Hypertension (2022)
-
The hypertension cascade of care in the midst of conflict: the case of the Gaza Strip
Journal of Human Hypertension (2022)
-
Hypertension in the Middle East: current state, human factors, and barriers to control
Journal of Human Hypertension (2022)
-
Factors associated with self-efficacy in patients with hypertension: a cross-sectional study from Palestine
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition (2021)