Abstract
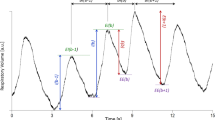
The baroreflex control of circulation is always operating and modulates blood pressure and heart rate oscillations. Thus, the study of cardiovascular variability in humans is performed in a closed-loop model and the physiology of post-sinoaortic denervation is completely unknown in humans. We dissected for the first time the different components of systolic arterial pressure (SAP) and RR-interval spectra in a patient with ‘baroreflex failure’ (due to mixed cranial nerve neuroma) who represents a human model to investigate the cardiovascular regulation in an open-loop condition. Interactions among cardiovascular variability signals and respiratory influences were described using the multivariate parametric ARXAR model with the following findings: (1) rhythms unrelated to respiration were detected only at frequencies lower than classical low frequency (LF; Slow-LF, around 0.02 Hz) both in SAP an RR spectra, (2) small high-frequency (HF) modulation is present and related with respiration at rest and in tilt (but for SAP only) and (3) the Slow-LF fluctuations detected both in SAP and RR oscillate independently as the multivariate model shows no relationships between SAP and RR, and these oscillations are not phase related. Thus, we showed that in a patient with impaired baroreflex arc integrity the Slow-LF rhythms for RR have a central origin that dictates fluctuations on RR at the same rhythm but unrelated to the oscillation of SAP (which may be related with both peripheral activity and central rhythms). The synchronization in LF band is a hallmark of integrity of baroreflex arc whose impairment unmasks lower frequency rhythms in SAP and RR whose fluctuations oscillate independently.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robertson D, Hollister AS, Biaggioni I, Netterville JL, Mosqueda-Garcia R, Robertson RM . The diagnosis and treatment of baroreflex failure. N Engl J Med 1993; 329: 1449–1455.
Ketch T, Biaggioni I, Robertson RM, Robertson D . Four faces of baroreflex failure. Hypertensive crisis, volatile hypertension, orthostatic tachycardia, and malignant vagotonia. Circulation 2002; 105: 2518–2523.
Manger WM . Baroreflex failure—a diagnostic challenge. N Engl J Med 1994; 329: 1494–1495.
Jordan J, Shannon JR, Black BK, Costa F, Ertl AC, Furlan R et al. Malignant vagotonia due to selective baroreflex failure. Hypertension 1997; 30: 1072–1077.
Dworkin BR, Tang X, Snyder AJ, Dworkin S . Carotid and aortic baroreflexes of the rat: II. Open-loop frequency response and the blood pressure spectrum. Am J Physiol Regul Integ Comp Physiol 2000; 279: R1922–R1933.
Fazan R, de Oliveira M, da Silva VJD, Joaquim LF, Montano N, Porta A et al. Frequency-dependent baroreflex modulation of blood pressure and heart rate variability in conscious mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2005; 289: H1968–H1975.
Guasti L, Simoni C, Scamoni C, Sarzi Braga S, Crespi C, Cimpanelli M et al. Mixed cranial nerve neuroma revealing itself as baroreflex failure. Auton Neurosci 2006; 130: 57–60.
Eckberg DL, Sleight P . Human Baroreflex in Health and Disease. Clarendon Press: Oxford, 1992.
La Rovere MT, Bigger JT, Marcus FI, Mortara A, Schwartz PJ, For the ATRAMI (Autonomic Tone Reflexes After Myocardial Infarction) Investigators. Baroreflex sensitivity and heart rate variability in prediction of total cardiac mortality after myocardial infarction. Lancet 1998; 351: 478–484.
Guasti L, Simoni C, Mainardi L, Crespi C, Cimpanelli M, Klersy C et al. Global link between heart rate and blood pressure oscillations at rest and during mental arousal in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Auton Neurosci 2005; 120: 80–87.
Benditt DG, Ferguson DW, Grubb BP, Kapoor WN, Kugler J, Lerman BB et al. Tilt table testing for assessing syncope. ACC expert consensus document, 1996. J Am Coll Cardiol 1996; 28: 263–275.
Baselli G, Cerutti S . Identification techniques applied to processing of signals from cardiovascular system. Med Inf (Lond) 1985; 10: 223–235.
Baselli G, Porta A, Rimoldi O, Pagani M, Cerutti S . Spectral decomposition in multichannel recordings based on multivariate parametric identification. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 1997; 44: 1092–1101.
Baselli G, Porta A, Cerutti S, Caiani EG, Lucini D, Pagani M . RR-arterial pressure variability relationships. Auton Neurosci 2001; 90: 57–65.
Ljung L . System Identification: Theory for the User. Englewood Cliffs, Prentice-Hall: NY, 1999.
Timmers HJLM, Wieling W, Karemaker JM, Lenders JWM . Denervation of carotid baro- and chemoreceptors in humans. J Physiol 2003; 553.1: 3–11.
Timmers HJLM, Karemaker JM, Wieling W, Marres HAM, Folgering HTM, Lenders JWM . Baroreflex and chemoreflex function after bilateral carotid body tumour resection. J Hypertens 2003; 21: 591–599.
Timmers HJLM, Karemaker JM, Wieling W, Marres HAM, Lenders JWM . Baroreflex control of muscle sympathetic nerve activity after carotid body tumor resection. Hypertension 2003; 42: 143–149.
Sharabi Y, Dendi R, Holmes C, Goldstein DS . Baroreflex failure as a late sequela of neck irradiation. Hypertension 2003; 42: 110–116.
Towne JB, Bernhard VM . The relationship of postoperative hypertension to complications following carotid endarterectomy. Surgery 1980; 88: 575–580.
Diez Porres L, Garcia Iglesias F, Perez Martin G, Garcia Puig J, Gil Aguado A . Multiple paraganglioma: careful with surgery. Rev Clin Esp 2003; 203: 434–438.
Heusser K, Tank J, Luft FC, Jordan J . Baroreflex failure. Hypertension 2005; 45: 834–839.
Schuster H, Wienker TF, Toka HR, Bahring S, Jeschke E, Toka O et al. Autosomal dominant hypertension and brachydactyly in a Turkish kindred resembles essential hypertension. Hypertension 1996; 28: 1085–1092.
Jordan J, Toka HR, Heusser K, Toka O, Shannon JR, Tank J et al. Severely impaired baroreflex-buffering in patient with monogenic hypertension and neurovascular contact. Circulation 2000; 102: 2611–2618.
Milunsky J, DeStefano AL, Huang XL, Baldwin CT, Michels VV, Jako G et al. Familiar paragangliomas: linkage to chromosome 11q23 and clinical implications. Am J Med Genet 1997; 72: 66–70.
Phillips AM, Jardine DL, Parkin PJ, Hughes T, Ikram H . Brain stem stroke causing baroreflex failure and paroxymal hypertension. Stroke 2000; 31: 1997–2001.
Biaggioni I, Whetsell WO, Jobe J, Nadeau JH . Baroreflex failure in a patient with central nervous system lesions involving the nucleus-tractus-solitarii. Hypertension 1994; 23: 491–495.
Lanfranchi PA, Somers VK . Arterial baroreflex function and cardiovascular variability: interactions and implications. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2002; 283: R815–R826.
Cerutti C, Barres C, Paultre C . Baroreflex modulation of blood pressure and heart rate variabilities in rats: assessment by spectral analysis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 1994; 266: H1993–H2000.
Jacob HJ, Ramanathan A, Pan SG, Brody MJ, Myers GA . Spectral analysis of arterial pressure lability in rats with sinoaortic deafferentation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 1995; 268: R1481–R1488.
Dworkin BR, Dworkin S, Tang X . Carotid and aortic baroreflexes of the rat: I. Open-loop steady-state properties and blood pressure variability. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2000; 279: R1910–R1921.
Radaelli A, Castiglioni P, Centola M, Cesana F, Balestri G, Ferrari AU et al. Adrenergic origin of very low-frequency blood pressure oscillations in the unanesthetized rat. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2006; 290: H357–H364.
Baselli G, Porta A, Pagani M . Coupling arterial windkessel with peripheral vasomotion: modeling the effects on low frequency oscillations. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2006; 53: 53–64.
Massimini M, Porta A, Mariotti M, Malliani A, Montano N . Heart rate variability is encoded in the spontaneous discharge of thalamic somatosensory neurones in cat. J Physiol 2000; 526: 387–396.
Montano N, Lombardi F, Gnecchi Ruscone T, Contini M, Finocchiaro ML, Baselli G et al. Spectral analysis of sympathetic discharge, RR interval, and systolic arterial pressure in decerebrate cats. J Auton Nerv Syst 1992; 40: 21–32.
Montano N, Porta A, Malliani A . Evidence for central organization of cardiovascular rhythms. Ann NY Acad Sci 2001; 940: 299–306.
James MA, Robinson TG, Panerai RB, Potter JF . Arterial baroreceptor-cardiac reflex sensitivity in the elderly. Hypertension 1996; 28: 953–960.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guasti, L., Mainardi, L., Baselli, G. et al. Components of arterial systolic pressure and RR-interval oscillation spectra in a case of baroreflex failure, a human open-loop model of vascular control. J Hum Hypertens 24, 417–426 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2009.79
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2009.79
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cardiac autonomic modulation in non-frail, pre-frail and frail elderly women: a pilot study
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research (2015)