Abstract
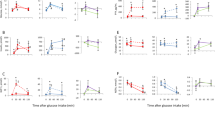
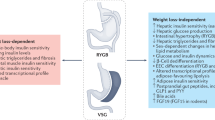
The gut hormone incretins have an important physiological role in meal-related insulin release and post-prandial glucose control. In addition to weight loss, the incretin hormones have a role in glucose control after bariatric surgery. The release of incretins, and specifically of glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1, in response to the ingestion of nutrients, is greatly enhanced after gastric bypass (RYGBP). The rapid transit of food from the gastric pouch to the distal ileum is responsible for the greater GLP-1 release after RYGBP. The incretin effect on insulin secretion, or the greater insulin response to oral glucose compared to an isoglycemic intravenous glucose challenge, is severely impaired in patients with type 2 diabetes, but is recovered rapidly after RYGBP. The improvement in insulin secretion rate and β-cell sensitivity to oral glucose after RYGBP is mediated by endogenous GLP-1, and is abolished by exendin 9–39, a specific GLP-1 receptor antagonist. While calorie restriction and weight loss have major effects on the rapid and sustained improvement of fasted glucose metabolism, the enhanced incretin effect is a key player in post-prandial glucose control after RYGBP.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
We are sorry, but there is no personal subscription option available for your country.
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holst JJ . The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol Rev 2007; 87: 1409–1439.
Courcoulas AP, Christian NJ, Belle SH, Berk PD, Flum DR, Garcia L et al. Weight change and health outcomes at 3 years after bariatric surgery among individuals with severe obesity. JAMA 2013; 310: 2416–2425.
Schauer PR, Mingrone G, Ikramuddin S, Wolfe B . Clinical outcomes of metabolic surgery: efficacy of glycemic control, weight loss, and remission of diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016; 39: 902–911.
Dixon JB, O'Brien PE, Playfair J, Chapman L, Schachter LM, Skinner S et al. Adjustable gastric banding and conventional therapy for type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2008; 299: 316–323.
Schauer PR, Burguera B, Ikramuddin S, Cottam D, Gourash W, Hamad G et al. Effect of laparoscopic Roux-en Y gastric bypass on type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Surg 2003; 238: 467–484; discussion 84–85.
Arterburn DE, Bogart A, Sherwood NE, Sidney S, Coleman KJ, Haneuse S et al. A multisite study of long-term remission and relapse of type 2 diabetes mellitus following gastric bypass. Obes Surg 2013; 23: 93–102.
Laferrère B, Teixeira J, McGinty J, Tran H, Egger JR, Colarusso A et al. Effect of weight loss by gastric bypass surgery versus hypocaloric diet on glucose and incretin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008; 93: 2479–2485.
Holst JJ, Gribble F, Horowitz M, Rayner CK . Roles of the gut in glucose homeostasis. Diabetes Care 2016; 39: 884–892.
Perley MJ, Kipnis DM . Plasma insulin responses to oral and intravenous glucose: studies in normal and diabetic sujbjects. J Clin Invest 1967; 46: 1954–1962.
Creutzfeldt W, Nauck M . Gut hormones and diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Rev 1992; 8: 149–177.
Heller H . The state in the blood and the excretion by the kidney of the antidiuretic principle of posterior pituitary extracts. J Physiol 1937; 89: 81–95.
Yalow RS, Berson SA . Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest 1960; 39: 1157–1175.
McIntyre N, Holdsworth CD, Turner DS . Intestinal factors in the control of insulin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1965; 25: 1317–1324.
Bell GI, Santerre RF, Mullenbach GT . Hamster preproglucagon contains the sequence of glucagon and two related peptides. Nature 1983; 302: 716–718.
Nauck MA, Homberger E, Siegel EG, Allen RC, Eaton RP, Ebert R et al. Incretin effects of increasing glucose loads in man calculated from venous insulin and C-peptide responses. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1986; 63: 492–498.
Lindgren O, Carr RD, Holst JJ, Deacon CF, Ahren B . Dissociated incretin hormone response to protein versus fat ingestion in obese subjects. Diabetes Obes Metab 2011; 13: 863–865.
Bagger JI, Knop FK, Lund A, Vestergaard H, Holst JJ, Vilsboll T . Impaired regulation of the incretin effect in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011; 96: 737–745.
Mari A, Bagger JI, Ferrannini E, Holst JJ, Knop FK, Vilsboll T . Mechanisms of the incretin effect in subjects with normal glucose tolerance and patients with type 2 diabetes. PLoS One 2013; 8: e73154.
Nauck MA, Vardarli I, Deacon CF, Holst JJ, Meier JJ . Secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in type 2 diabetes: what is up, what is down? Diabetologia 2011; 54: 10–18.
Nauck M, Stockmann F, Ebert R, Creutzfeldt W . Reduced incretin effect in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes. Diabetologia 1986; 29: 46–52.
Hojberg PV, Vilsboll T, Rabol R, Knop FK, Bache M, Krarup T et al. Four weeks of near-normalisation of blood glucose improves the insulin response to glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2009; 52: 199–207.
Ma X, Hui H, Liu Z, He G, Hu J, Meng J et al. Poly-GLP-1, a novel long-lasting glucagon-like peptide-1 polymer, ameliorates hyperglycaemia by improving insulin sensitivity and increasing pancreatic beta-cell proliferation. Diabetes Obes Metab 2009; 11: 953–965.
Farilla L, Bulotta A, Hirshberg B, Li Calzi S, Khoury N, Noushmehr H et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 inhibits cell apoptosis and improves glucose responsiveness of freshly isolated human islets. Endocrinology 2003; 144: 5149–5158.
Wang Q, Brubaker PL . Glucagon-like peptide-1 treatment delays the onset of diabetes in 8 week-old db/db mice. Diabetologia 2002; 45: 1263–1273.
De Leon DD, Deng S, Madani R, Ahima RS, Drucker DJ, Stoffers DA . Role of endogenous glucagon-like peptide-1 in islet regeneration after partial pancreatectomy. Diabetes 2003; 52: 365–371.
Campbell JE, Drucker DJ . Pharmacology, physiology, and mechanisms of incretin hormone action. Cell Metab 2013; 17: 819–837.
Laferrère B . Effect of gastric bypass surgery on the incretins. Diabetes Metab 2009; 35: 513–517.
Van der Schueren BJ, Homel P, Alam M, Agenor K, Wang G, Reilly D et al. Magnitude and variability of the glucagon-like peptide-1 response in patients with type 2 diabetes up to 2 years following gastric bypass surgery. Diabetes Care 2012; 35: 42–46.
Laferrère B, Heshka S, Wang K, Khan Y, McGinty J, Teixeira J et al. Incretin levels and effect are markedly enhanced 1 month after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007; 30: 1709–1716.
Korner J, Bessler M, Inabnet W, Taveras C, Holst JJ . Exaggerated glucagon-like peptide-1 and blunted glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide secretion are associated with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass but not adjustable gastric banding. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2007; 3: 597–601.
Wu Q, Xiao Z, Cheng Z, Tian H . Changes of blood glucose and gastrointestinal hormones 4 months after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery in Chinese obese type 2 diabetes patients with lower body mass index. J Diabetes Invest 2013; 4: 214–221.
Kim MJ, Park HK, Byun DW, Suh KI, Hur KY . Incretin levels 1 month after laparoscopic single anastomosis gastric bypass surgery in non-morbid obese type 2 diabetes patients. Asian J Surg 2014; 37: 130–137.
Morinigo R, Moize V, Musri M, Lacy AM, Navarro S, Marin JL et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1, peptide YY, hunger, and satiety after gastric bypass surgery in morbidly obese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006; 91: 1735–1740.
Olivan B, Teixeira J, Bose M, Bawa B, Chang T, Summe H et al. Effect of weight loss by diet or gastric bypass surgery on peptide YY3-36 levels. Ann Surg 2009; 249: 948–953.
Laferrère B, Swerdlow N, Bawa B, Arias S, Bose M, Olivan B et al. Rise of oxyntomodulin in response to oral glucose after gastric bypass surgery in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010; 95: 4072–4076.
Horowitz M, Cook DJ, Collins PJ, Harding PE, Hooper MJ, Walsh JF et al. Measurement of gastric emptying after gastric bypass surgery using radionuclides. Br J Surg 1982; 69: 655–657.
Naslund I, Beckman KW . Gastric emptying rate after gastric bypass and gastroplasty. Scand J Gastroenterol 1987; 22: 193–201.
Wang G, Agenor K, Pizot J, Kotler DP, Harel Y, Van Der Schueren BJ et al. Accelerated gastric emptying but no carbohydrate malabsorption 1 year after gastric bypass surgery (GBP). Obes Surg 2012; 22: 1263–1267.
Pournaras DJ, Aasheim ET, Bueter M, Ahmed AR, Welbourn R, Olbers T et al. Effect of bypassing the proximal gut on gut hormones involved with glycemic control and weight loss. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2012; 8: 371–374.
McLaughlin T, Peck M, Holst J, Deacon C . Reversible hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia after gastric bypass: a consequence of altered nutrient delivery. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010; 95: 1851–1855.
Nguyen NQ, Debreceni TL, Bambrick JE, Chia B, Deane AM, Wittert G et al. Upregulation of intestinal glucose transporters after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass to prevent carbohydrate malabsorption. Obesity 2014; 22: 2164–2171.
Dirksen C, Bojsen-Moller KN, Jorgensen NB, Jacobsen SH, Kristiansen VB, Naver LS et al. Exaggerated release and preserved insulinotropic action of glucagon-like peptide-1 underlie insulin hypersecretion in glucose-tolerant individuals after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Diabetologia 2013; 56: 2679–2687.
Lindqvist A, Spegel P, Ekelund M, Garcia Vaz E, Pierzynowski S, Gomez MF et al. Gastric bypass improves beta-cell function and increases beta-cell mass in a porcine model. Diabetes 2014; 63: 1665–1671.
Bose M, Teixeira J, Olivan B, Bawa B, Arias S, Machineni S et al. Weight loss and incretin responsiveness improve glucose control independently after gastric bypass surgery. J Diabetes 2010; 2: 47–55.
Bunck MC, Corner A, Eliasson B, Heine RJ, Shaginian RM, Taskinen MR et al. Effects of exenatide on measures of beta-cell function after 3 years in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011; 34: 2041–2047.
Service GJ, Thompson GB, Service FJ, Andrews JC, Collazo-Clavell ML, Lloyd RV . Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia with nesidioblastosis after gastric-bypass surgery. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 249–254.
Panunzi S, De Gaetano A, Carnicelli A, Mingrone G . Predictors of remission of diabetes mellitus in severely obese individuals undergoing bariatric surgery: do bmi or procedure choice matter? a meta-analysis. Ann Surg 2014; 261: 459–467.
Shah M, Law JH, Micheletto F, Sathananthan M, Dalla Man C, Cobelli C et al. Contribution of endogenous glucagon-like peptide 1 to glucose metabolism after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Diabetes 2014; 63: 483–493.
Jimenez A, Casamitjana R, Viaplana-Masclans J, Lacy A, Vidal J . GLP-1 action and glucose tolerance in subjects with remission of type 2 diabetes after gastric bypass surgery. Diabetes Care 2013; 36: 2062–2069.
Salehi M, Gastaldelli A, D'Alessio DA . Blockade of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor corrects postprandial hypoglycemia after gastric bypass. Gastroenterology 2014; 146: 669–80 e2.
Vetter ML, Wadden TA, Teff KL, Khan Z, Carvajal R, Ritter S et al. GLP-1 plays a limited role in improved glycemia shortly after roux-en-y gastric bypass: a comparison to intensive lifestyle modification. Diabetes 2014; 64: 434–446.
Jorgensen NB, Dirksen C, Bojsen-Moller KN, Jacobsen SH, Worm D, Hansen DL et al. Exaggerated glucagon-like peptide 1 response is important for improved beta-cell function and glucose tolerance after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2013; 62: 3044–3052.
Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, Jensen MD, Pories W, Fahrbach K et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2004; 292: 1724–1737.
Buchwald H, Estok R, Fahrbach K, Banel D, Jensen MD, Pories WJ et al. Weight and type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med 2009; 122: 248–56 e5.
Schauer PR, Kashyap SR, Wolski K, Brethauer SA, Kirwan JP, Pothier CE et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy in obese patients with diabetes. N Engl J Med 2012; 366: 1567–1576.
Mingrone G, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A, Guidone C, Iaconelli A, Leccesi L et al. Bariatric surgery versus conventional medical therapy for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2012; 366: 1577–1585.
Puzziferri N, Roshek TB 3rd, Mayo HG, Gallagher R, Belle SH, Livingston EH . Long-term follow-up after bariatric surgery: a systematic review. JAMA 2014; 312: 934–942.
Sjostrom L, Peltonen M, Jacobson P, Ahlin S, Andersson-Assarsson J, Anveden A et al. Association of bariatric surgery with long-term remission of type 2 diabetes and with microvascular and macrovascular complications. JAMA 2014; 311: 2297–2304.
Ye J, Hao Z, Mumphrey MB, Townsend RL, Patterson LM, Stylopoulos N et al. GLP-1 receptor signaling is not required for reduced body weight after RYGB in rodents. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Compar Physiol 2014; 306: R352–R362.
Jimenez A, Mari A, Casamitjana R, Lacy A, Ferrannini E, Vidal J . GLP-1 and glucose tolerance after sleeve gastrectomy in morbidly obese subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2014; 63: 3372–3377.
Chambers AP, Smith EP, Begg DP, Grayson BE, Sisley S, Greer T et al. Regulation of gastric emptying rate and its role in nutrient-induced GLP-1 secretion in rats after vertical sleeve gastrectomy. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2014; 306: E424–E432.
Madsbad S, Holst JJ . GLP-1 as a mediator in the remission of type 2 diabetes after gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy surgery. Diabetes 2014; 63: 3172–3174.
Wilson-Perez HE, Chambers AP, Ryan KK, Li B, Sandoval DA, Stoffers D et al. Vertical sleeve gastrectomy is effective in two genetic mouse models of glucagon-like Peptide 1 receptor deficiency. Diabetes 2013; 62: 2380–2385.
Dutia R, Brakoniecki K, Bunker P, Paultre F, Homel P, Carpentier AC et al. Limited recovery of beta-cell function after gastric bypass despite clinical diabetes remission. Diabetes 2014; 63: 1214–1223.
Guldstrand M, Ahren B, Adamson U . Improved beta-cell function after standardized weight reduction in severely obese subjects. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2003; 284: E557–E565.
Villareal DT, Banks MR, Patterson BW, Polonsky KS, Klein S . Weight loss therapy improves pancreatic endocrine function in obese older adults. Obesity 2008; 16: 1349–1354.
Campos GM, Rabl C, Peeva S, Ciovica R, Rao M, Schwarz JM et al. Improvement in peripheral glucose uptake after gastric bypass surgery is observed only after substantial weight loss has occurred and correlates with the magnitude of weight lost. J Gastrointest Surg 2010; 14: 15–23.
Bradley D, Conte C, Mittendorfer B, Eagon JC, Varela JE, Fabbrini E et al. Gastric bypass and banding equally improve insulin sensitivity and beta cell function. J Clin Invest 2012; 122: 4667–4674.
Sirinek KR, O'Dorisio TM, Hill D, McFee AS . Hyperinsulinism, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, and the enteroinsular axis in morbidly obese patients before and after gastric bypass. Surgery 1986; 100: 781–787.
Dutia R, Brakoniecki K, Wang G, Mogul S, Agenor K, McGinty J, Belsley SJ, Rosen D, Laferrère B . Greater improvement in β-cell function after gastric bypass is independent of weight loss. Diabetes 2013; 62 (Suppl 1): A1–828; 1825.
Sarson DL, Besterman HS, Bloom SR . Radioimmunoassay of gastric inhibitory polypeptide and its release in morbid obesity and after jejuno-ileal bypass [proceedings]. J Endocrinol 1979; 81: 155P–156P.
Sarson DL, Scopinaro N, Bloom SR . Gut hormone changes after jejunoileal (JIB) or biliopancreatic (BPB) bypass surgery for morbid obesity. Int J Obes 1981; 5: 471–480.
Halverson JD, Kramer J, Cave A, Permutt A, Santiago J . Altered glucose tolerance, insulin response, and insulin sensitivity after massive weight reduction subsequent to gastric bypass. Surgery 1982; 92: 235–240.
Naslund E, Backman L, Holst JJ, Theodorsson E, Hellstrom PM . Importance of small bowel peptides for the improved glucose metabolism 20 years after jejunoileal bypass for obesity. Obes Surg 1998; 8: 253–260.
Verdich C, Flint A, Gutzwiller JP, Naslund E, Beglinger C, Hellstrom PM et al. A meta-analysis of the effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 (7-36) amide on ad libitum energy intake in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 4382–4389.
Valverde I, Puente J, Martin-Duce A, Molina L, Lozano O, Sancho V et al. Changes in glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) secretion after biliopancreatic diversion or vertical banded gastroplasty in obese subjects. Obes Surg 2005; 15: 387–397.
Korner J, Bessler M, Cirilo LJ, Conwell IM, Daud A, Restuccia NL et al. Effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery on fasting and postprandial concentrations of plasma ghrelin, peptide YY, and insulin. J Clin Edocrinol Metab 2005; 90: 359–365.
Borg CM, le Roux CW, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR, Patel AG, Aylwin SJ . Progressive rise in gut hormone levels after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass suggests gut adaptation and explains altered satiety. Br J Surg 2006; 93: 210–215.
Jorgensen NB, Jacobsen SH, Dirksen C, Bojsen-Moller KN, Naver L, Hvolris L et al. Acute and long-term effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on glucose metabolism in subjects with Type 2 diabetes and normal glucose tolerance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2012; 303: E122–E131.
Jacobsen SH, Olesen SC, Dirksen C, Jorgensen NB, Bojsen-Moller KN, Kielgast U et al. Changes in gastrointestinal hormone responses, insulin sensitivity, and beta-cell function within 2 weeks after gastric bypass in non-diabetic subjects. Obes Surg 2012; 22: 1084–1096.
Romero F, Nicolau J, Flores L, Casamitjana R, Ibarzabal A, Lacy A et al. Comparable early changes in gastrointestinal hormones after sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-En-Y gastric bypass surgery for morbidly obese type 2 diabetic subjects. Surg Endosc 2012; 26: 2231–2239.
Mallipedhi A, Prior SL, Barry JD, Caplin S, Baxter JN, Stephens JW . Temporal changes in glucose homeostasis and incretin hormone response at 1 and 6 months after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2014; 10: 860–869.
Plourde CE, Grenier-Larouche T, Caron-Dorval D, Biron S, Marceau S, Lebel S et al. Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch improves insulin sensitivity and secretion through caloric restriction. Obesity 2014; 22: 1838–1846.
Acknowledgements
Some of the work discussed here was funded by grants from the American Diabetes Association CR-7-05 CR-18, National Institutes of Health (R01-DK067561, P30-DK26687, P30-DK063608), the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, through Grant Number UL1 TR000040. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH. Publication of this article was sponsored by the Université Laval’s Research Chair in Obesity in an effort to inform the public on the causes, consequences, treatments, and prevention of obesity. BL is the recipient of one Investigator-initiated grant from Merck. However, data referred to in this review are not related to this source of funding. BL has received grant support from the National Institutes of Health and the American Heart Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laferrère, B. Bariatric surgery and obesity: influence on the incretins. Int J Obes Supp 6 (Suppl 1), S32–S36 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijosup.2016.8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijosup.2016.8
This article is cited by
-
Changes of serum retinol-binding protein 4 associated with improved insulin resistance after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy in Chinese obese patients
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome (2020)
-
Rapid changes in neuroendocrine regulation may contribute to reversal of type 2 diabetes after gastric bypass surgery
Endocrine (2020)
-
Efficacy of High-Dose Liraglutide as an Adjunct for Weight Loss in Patients with Prior Bariatric Surgery
Obesity Surgery (2018)
-
Preserving Duodenal-Jejunal (Foregut) Transit Does Not Impair Glucose Tolerance and Diabetes Remission Following Gastric Bypass in Type 2 Diabetes Sprague-Dawley Rat Model
Obesity Surgery (2018)