Abstract
Alkali production by oral bacteria is believed to have a major impact on oral microbial ecology and to be inibitory to the initiation and progression of dental caries. A substantial body of evidence is beginning to accumulate that indicates the modulation of the alkalinogenic potential of dental biofilms may be a promising strategy for caries control. This brief review highlights recent progress toward understanding molecular genetic and physiologic aspects of important alkali-generating pathways in oral bacteria, and the role of alkali production in the ecology of dental biofilms in health and disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Dental biofilms, the microbial communities that colonize the surfaces of the teeth, exist in a dynamic equilibrium with host defenses and are generally compatible with the integrity of the tissues they colonize.1,2,3,4 A strong correlation is evident between the compositional and metabolic changes of the dental biofilms and the transition from oral health to disease states, including dental caries and periodontal disease.2,5 In the case of caries, frequent acidification of dental biofilms favors the emergence of an acidogenic and aciduric microflora, including mutans streptococci and Lactobacillus spp., which ferment dietary carbohydrates rapidly and lower the pH to values that accelerate tooth demineralization.1,2,3,6,7 As might be predicted, the increase in the proportions of aciduric organisms appears to occur at the expense of species that are less aciduric and often associated with dental health.8,9,10 Importantly, many of the organisms that are associated with dental health are able to use arginine or urea to generate ammonia via the arginine deiminase system or urease enzymes, respectively.1 Alkali production by these bacteria can positively affect the balance between remineralization and demineralization of the tooth and may also help to prevent the emergence of a cariogenic microflora.11,12,13,14
A substantial body of evidence suggests that the modulation of the alkali-generating potential of dental plaque may be a promising strategy for caries prevention. In light of the emerging recognition of the inverse correlation between alkali generation and caries, additional research efforts have been focused on the molecular biology, physiology, ecological impact and clinical relevance of alkali production in dental biofilms. The aim of this review is to highlight some of the more recent advances in these areas and immediate research needs.
Primary sources of alkali generation in dental biofilms
The two primary routes for alkali generation in dental plaque are the hydrolysis of urea by urease enzymes and the metabolism of arginine via the arginine deiminase system (ADS).15,16,17,18 Urea is provided continuously in salivary secretions and gingival exudates at concentrations roughly equivalent to those in serum, which range from about 3 to10 mmol·L−1 in healthy humans. Urea is rapidly converted to ammonia and CO2 by bacterial ureases (Figure 1), which are produced by a small subset of oral bacteria that includes Streptococcus salivarius, Actinomyces naeslundii and oral haemophili.19,20,21,22 Arginine is abundant in salivary secretions as polypeptides, and free arginine concentrations in ductal saliva average around 50 µmol·L−1.18 Arginine in the oral cavity is catabolized primarily by the ADS to release ornithine, ammonia and CO2 (Figure 1). Unlike urea breakdown by urease enzymes, arginine catabolism by the ADS provides bacteria with adenosine triphosphate (ATP).15 ADS-positive bacteria are abundant members of the normal oral flora that colonizes the teeth and soft tissues and include Streptococcus sanguinis, Streptococcus gordonii, Streptococcus parasanguis and Streptococcus mitis. Certain Lactobacillus and Actinomyces species, other oral streptococci and some oral spirochetes have been also identified as arginolytic.15,23,24,25
Agmatine catabolism may also have a significant effect on oral biofilm ecology, albeit not in the way that arginine or urea metabolism does.26 Agmatine can be produced in dental biofilms from arginine by bacterial arginine decarboxylase enzymes, but it also occurs naturally in foods, such as rice, milk and beer.27,28 Agmatine has been measured at concentrations of 0.75 µmol in dental plaque and 0.2 µmol in saliva when the samples were normalized to protein concentration (e.g. 0.75 µmol per mg of protein in plaque).29 The primary route for agmatine utilization is through the agmatine deiminase system (AgDS), which is highly similar to the ADS, with end products being putrescine, ammonia, CO2 and ATP (Figure 1). A survey of bacterial genomes and/or functional studies revealed that the AgDS is present in multiple oral bacteria, including Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus sobrinus, Streptococcus downeii, Streptococcus rattus, Streptococcus uberis, Streptococcus mitis and Streptococcus cricetus, as well Lactobacillus salivarius and Lactobacillus brevis.29 Notably, some of these species are strongly associated with dental caries and express the AgDS at relatively high levels. Only S. sanguinis and S. salivarius, which are associated with dental health, can also generate ammonia via the ADS or urease, respectively, in addition to the AgDS.29 These oral bacteria were reported to be highly capable of generating ammonia through the ADS or urease, but had much lower capacities for agmatine utilization. Therefore, the AgDS may not play as important role in the physiology of these oral commensals as it does in cariogenic streptococci. In fact, it has been postulated that the AgDS, unlike the ADS or urease, does not produce sufficient quantities of alkali to impact the pH of oral biofilm. Rather, the AgDS may actually enhance the acid tolerance of certain cariogenic organisms through ATP generation and raising of the cytoplasmic pH, which could enhance the ability of the bacteria to continue to catabolize carbohydrates at low pH values.26
It should also be noted that malate metabolism through malolactic fermentation (MLF) has recently been identified as another pathway to reduce the extent of acidification of dental biofilms, including S. mutans. Through MLF, L-malate can be catabolized to L-lactate and CO2 by the malolactic enzyme30,31 (Figure 1). Although the MLF does not produce ammonia, it has been proposed to contribute to cytoplasmic alkalinization, which has been postulated to support the generation of ATP by means of the F1F0-ATPase acting in the synthetic mode.30,31
Genetics and regulation of alkali generation
Urease
The genetics, biogenesis, biochemistry and effects on the host of bacterial ureases have been reviewed elsewhere,32,33 while a previous review covered many of the specifics of oral bacterial ureolysis.15 Briefly, urease is a nickel-containing oligomeric enzyme and the biogenesis of a functional urease requires at least seven gene products that are usually encoded in operons. The urease apoenzyme is composed of α, β and γ-subunits encoded by the ureC-A and -B genes. The subunits are assembled into an (αβγ)3 oligomeric complex with six-nickel ions coordinated at the active site. Four additional genes, ureDEFG, encode a chaperone complex that facilitates the incorporation of nickel and CO2 at the active site.34,35 The expression of oral bacterial ureases is often regulated by multiple inputs.36,37,38,39 Commonly, the presence of urea or limitation for a nitrogen source can induce urease gene transcription. In some bacteria, urease expression is repressed at neutral pH values, but under acidic conditions the urease genes become activated. Urease gene expression can also be sensitive to carbohydrate availability and rate of growth.36,37,38
Arginine metabolism
The ADS is widely distributed among prokaryotes, and the primary structures of the enzymes in the system have been conserved during evolution. The genes encoding the ADS are commonly arranged in an operon (For example, see Figure 2), although the gene order varies among species.40,41,42,43,44 The arcA gene encodes arginine deiminase, which hydrolyzes arginine to generate citrulline and ammonia. The arcB gene encodes a catabolic ornithine carbamyltransferase, which converts citrulline to ornithine and carbamoylphosphate, and arcC encodes the catabolic carbamate kinase that transfers a phosphate group from carbamylphosphate to ADP to generate ATP, CO2 and ammonia. Many organisms also harbor an arginine/ornithine antiporter (ArcD) that is encoded in the same operon, and arginine aminopeptidases and transcriptional regulators are often encoded in ADS gene clusters.41,44 Of note, the oral commensal S. gordonii was identified to be the only ADS-positive bacterium containing a queA homologue associated with the ADS gene cluster. QueA is a predicted S-adenosylmethionine:tRNA ribosyltransferase-isomerase responsible for queosine modification of tRNAs45 and queA is cotranscribed with the gene for the ADS transcriptional regulator. It has been postulated that the association of QueA with the ADS is indicative of a link between translational efficiency and arginine catabolism.
The regulation of the ADS genes has been studied extensively in certain oral streptococci and in a variety of non-oral species.41,42,43,46 In all cases examined so far, the ADS is subject to regulation by multiple environmental stimuli, although the modes and mechanisms of control vary between species. ADS expression in most bacteria, including oral streptococci, is induced by arginine and low pH. Similarly, the operon is sensitive to carbon catabolite repression (CCR) and downregulated in response to elevated oxygen levels, although the sensitivities to CCR and oxygen vary among species.47,48 Interestingly, interspecies interactions, including coaggregation of S. gordonii with A. naeslundii, substantially enhanced ADS activity in S. gordonii, possibly by activating arginine biosythesis and ADS expression.49
In S. gordonii, it was determined that ArcR is involved in the induction of the ADS genes by arginine and that CCR of the operon occurs primarily through CcpA (Figure 2).41,47 An Fnr-like protein and the two-component system VicRK are required for the induction of the ADS in S. gordonii under anaerobic conditions (Figure 2).47 Other two-component systems including CiaRH, ComDE and VicRK were found to be involved in the induction of the ADS in S. gordonii under acidic conditions (Figure 2).50,51 QueA was also found to have a negative effect on arc gene transcription, possibly by impacting the translational efficiency of ADS genes or ADS regulatory genes (Figure 2).45
AgDS
The AgDS does not appear to be as widely distributed in microbes as the ADS. Besides the oral species identified, only a few non-oral species, including Enterococcus faecalis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacillus cereus, Lactobacillus hilgardii and Helicobacter pylori have been reported to be AgDS-positive.52,53,54,55 Like the ADS genes, the AgDS genes are typically encoded in an operon consisting of aguBDAC26 (Figure 3). Free agmatine can enter the cell via an agmatine-putrescine antiporter (AguD) and is hydrolyzed to N-carbamoylputrescine and ammonia by the agmatine deiminase enzyme encoded by aguA. The N-carbamoylputrescine is then metabolized by the putrescine carbamoyltransferase, encoded by aguB, to yield putrescine and carbamoylphosphate. Finally, carbamate kinase, the product of the aguC gene, transfers a phosphate group from carbamoylphosphate to ADP to generate ATP, CO2 and NH3. The putrescine generated can be exchanged for agmatine via the antiporter.26 The aguR gene, which is located upstream of, and in the opposite orientation to, the agu operon in S. mutans encodes a transcriptional activator of the agu genes.56,57
In oral streptococci, AgD activity is generally lower than arginine deiminase or urease activity,26 although there is some variation among AgDS-positive species. Comparable levels of AgD activity were detected in S. mutans and S. rattus, but over 50-fold lower activity was observed in S. cricetus and S. sobrinus.29 In S. mutans, AgDS activity is growth-phase dependent, as well as inducible by agmatine and certain environmental stresses, including low pH and heat shock (Figure 3).26,56,57 Expression of the AgDS genes in S. mutans was also sensitive to CCR and influenced by CcpA and a putative CcpB orthologue (Figure 3).26 The AgDS is also inducible by low pH and agmatine through a predicted interaction between AguR and AguD. In particular, it has been proposed that agmatine stimulates AguR binding to its target upstream of the agu operon, and that acidic conditions favor a configuration of AguR that enhances binding to its target.57 In the absence of exogenous agmatine, the interaction of AguR with AguD may prevent an interation of AguR with its substate and/or its target.57 Multiple two-component systems, including CiaRH, ComDE and VicRK, were disclosed to be involved in the induction of the AgDS genes by low pH, and CiaRH was also shown to contribute to optimal expression of the AgDS under thermal stress (Figure 3).58
Contribution of alkali generation to bacterial physiology and biofilm ecology
As reviewed previously, oral organisms harvest significant benefits from alkali generation in the form of protection against acid damage and enhancement to cell growth.15 Dental biofilms are complex ecosystems with hundreds of metabolically and physiologically diverse species, and there is believed to be considerable competition for nutrients. The ability of oral species to metabolize urea, arginine or agmatine at low pH could impart an advantage to these organisms through alkalinization of the cytoplasm by ammonia. The generation of ATP by the ADS would also enhance acid tolerance by providing energy for proton extrusion, growth or maintenance.26,41,59,60,61,62,63
There is reason to believe that the contributions of the ADS, urease and AgDS to oral biofilm pH homeostasis and ecology may be quite different. For example, in some oral commensals, such as S. salivarius and S. gordonii, urease and the ADS, respectively, cleary can provide the bacteria with protection from environmental acidification.19,47 At the same time, other less-aciduric species in the biofilm community benefit from arginine or urea breakdown because sufficient ammonia is sufficient to stabilize the pH of the local environment.19,47 However, the caries pathogens S. mutans and S. sobrinus have no urease or ADS, but carry an AgDS that is expressed in vitro at a lower level than the ADS or urease is in oral commensals.26,29 Further, agmatine, which arises primarily from the decarboxylation of arginine, is present at concentrations much lower than that of arginine in the oral cavity.18 Consequently, ammonia generation from agmatine in dental biofilms probably does not cause significant alkalinization of the environment. However, it could enhance the ability of S. mutans to continue to engage in glycolysis at low pH values, thus enhancing acid production. Similarly, MLF may not have much of a beneficial effect on biofilm pH, and like the AgDS, the benefits may be restricted to enhancing the growth and metabolism of the species that possess them.
Observations on the relationship of alkali generation to caries status
Evidence continues to accumulate from in vitro studies and clinical observations that caries risk is associated with reduced alkali-generating capacity of the oral microbiome.11,17,18,64,65,66,67,68 For example, indirect evidence that the oral metabolism of urea may enhance caries resistance was obtained from a study with chronic renal failure patients, who rarely develop caries even with carbohydrate-rich diet, but who also produce some 10- to 50-fold greater salivary urea levels than healthy subjects.67,69 In another study, higher resting pH values in the dental plaque of caries-free (CF) individuals compared with those of caries-active (CA) individuals was noted, and the increased pH was shown to be correlated with elevated ammonia released in plaque.17 Elevated levels of free arginine in saliva were revealed to be strongly correlated with caries resistance.18 Noticeably, a potent inhibitory effect on caries development was observed in rats that were infected with a genetically-engineered strain of S. mutans expressing the urease genes of S. salivarius.16,68 Specifically, rats colonized by the S. mutans strain expressing high levels of urease had fewer caries lesions and lower caries severity scores than those of control animals.
Investigators have now begun exploring whether there are clinical correlations between oral alkali-generating capacity and caries susceptibility. In studies with young adult subjects, higher urease and ADS activity levels were detected in pooled supragingival plaque and whole saliva of CF individuals compared to those of CA individuals.64,66 More recently, a positive correlation between oral arginine metabolism and dental health was also observed in children70 when supragingival plaque was collected from specific tooth sites. Ammonia generation via plaque urease activity has also been correlated with reduced risk71 for dental caries in a longitudinal study with children. A few recent studies have begun to explore the effects of including arginine in confections of oral health care products. Acevedo et al.72,73 demonstrated in randomize clinical trials that toothpaste67 and sugarless mints68 containing arginine bicarbonate can have potent anti-caries effects. A very recent report showed that addition of arginine-bicarbonate to mouth rinse at concentrations as low as 2% can effectively raise the plaque pH above the critical pH for enamel dissolution following a sucrose challenge.74
One of the major challenges facing caries researchers today is to understand the microbiological and molecualr basis for the differences in alkali-generating potential in the dental biofilms of CA versus CF individuals. Although a number of studies have shown positive correlations of arginolytic species, e.g. S. sanguinis, with health and a decrease in the proportions of these species in caries, analysis of the oral microbiome has not revealed consistent changes in cultivable, non-cultivable or cultivated arginolytic taxa in CF and CA subjects.75 Likewise, real-time PCR quantification showed no differences in the percentage of certain known arginolytic organisms in dental plaque of CF versus CA groups.64 Thus, there may be reasons that CA subjects have higher ADS activity than CF subject other than simple decreases in the proportions of ADS-positive bacteria in carious tooth sites. For example, there may be additional arginolytic species beyond those previously identified that effect the bulk of arginolysis, although this seems unlikely as the microbiome data have been carefully analyzed. Alternatively, the oral environment of the host could influence the arginolytic capacity of the oral bacteria by affecting the expression of the genes or the activity of the enzymes involved in alkali production. Finally, there may be high- and low-producing strains of known ADS-positive species that are abundant in dental plaque but cannot be differentiated on the basis of 16S sequence, and health may be associated with colonization by high-producing strains. These high-producing strains may have constitutionally high expression or express comparatively high activity in response to pH, oxygen, carbohydrate and substrate availability versus the low-producing strains.25,76
Epilogue
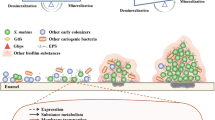
Alkali generation is widespread among oral species and is important in the physiology, ecology and pathogenicity of dental biofilms. A substantial body of evidence from microbiological, genetic, biochemical analyses and clinical studies has accumulated to confirm that the modulation of the alkalinogenic potential of dental biofilms is a promising strategy for caries control. One of the strengths of alkali production as a strategy for control of caries is that it attacks the problem in two very important ways (Figure 4). First, it directly increases the pH of dental plaque, which tips the balance in favor of remineralization and away from demineralization. Secondly, alkali generation favors the persistence of health-associated bacteria while discouraging the outgrowth of those cariogenic bacteria that depend on low pH to gain an ecological advantage, e.g. S. mutans.
The role of alkali generation in caries prevention. Dental biofilms in a healthy host displays a balance in pH and microflora conducive to a favorable demineralization/remineralization dynamic. With repeated acidification and exposure to other stresses, a shift in the composition and biochemical activities of the microflora creates conditions where demineralization is favored over remineralization, allowing for the initiation and/or progression of a caries lesion. Alkali generation by oral biofilm bacteria directly impacts plaque pH while preventing the emergence of a cariogenic microflora.
Despite recent progress in this area, there remain major gaps in our knowledge on the microbiological and ecological basis for differences in the alkalinogenic potential of dental plaque of different populations. In addition, we currently have a poor understanding of the otogeny of the alkalinogenic microflora. Likewise, additional clinical studies are needed: (i) to confirm that the supplementation of arginine to plaque bacteria is in fact effective against caries in adults and children; (ii) to ensure that arginine does not diminish the impact of fluoride in the oral cavity; and (iii) to optimize the formulations for caries control. Other areas worthy of investigation include exploring probiotic applications to enhance oral arginolysis and prevent the development of caries lesions. Collectively, this information will facilitate the rationale design of strategies that rely on alkali production for caries risk assessment and interventions.
References
Bradshaw DJ, Marsh PD . Analysis of pH-driven disruption of oral microbial communities in vitro. Caries Res 1998; 32( 6): 456–462.
Burne RA . Oral streptococci ... products of their environment. J Dent Res 1998; 77( 3): 445–452.
Burne RA, Ahn SJ, Wen ZT et al. Opportunities for disrupting cariogenic biofilms. Adv Dent Res 2009; 21( 1): 17–20.
Marsh PD . Microbial ecology of dental plaque and its significance in health and disease. Adv Dent Res 1994; 8( 2): 263–271.
van Houte J, Lopman J, Kent R . The predominant cultivable flora of sound and carious human root surfaces. J Dent Res 1994; 73( 11): 1727–1734.
Bowden GH . Possibilities for modifying the caries attack by altering the oral microflora. J Can Dent Assoc 1984; 50( 2): 169–172.
van Ruyven FO, Lingstrom P, van Houte J et al</author>. Relationship among mutans streptococci, ‘low-pH’ bacteria, and lodophilic polysaccharide-producing bacteria in dental plaque and early enamel caries in humans. J Dent Res 2000; 79( 2): 778–784.
Aas JA, Griffen AL, Dardis SR et al. Bacteria of dental caries in primary and permanent teeth in children and young adults. J Clin Microbiol 2008; 46( 4): 1407–1417.
Becker MR, Paster BJ, Leys EJ et al. Molecular analysis of bacterial species associated with childhood caries. J Clin Microbiol 2002; 40( 3): 1001–1009.
Corby PM, Lyons-Weiler J, Bretz WA et al. Microbial risk indicators of early childhood caries. J Clin Microbiol 2005; 43( 11): 5753–5759.
Dawes C, Dibdin GH . Salivary concentrations of urea released from a chewing gum containing urea and how these affect the urea content of gel-stabilized plaques and their pH after exposure to sucrose. Caries Res 2001; 35( 5): 344–353.
Dibdin GH, Dawes CA . mathematical model of the influence of salivary urea on the pH of fasted dental plaque and on the changes occurring during a cariogenic challenge. Caries Res 1998; 32( 1): 70–74.
Sissons CH, Hancock EM, Cutress TW . The source of variation in ureolysis in artificial plaques cultured from human salivary bacteria. Arch Oral Biol 1988; 33( 10): 721–726.
Kleinberg I . Effect of urea concentration on human plaque pH levels in situ. Arch Oral Biol 1967; 12( 12): 1475–1484.
Burne RA, Marquis RE . Alkali production by oral bacteria and protection against dental caries. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2000; 193( 1): 1–6.
Clancy KA, Pearson S, Bowen WH et al. Characterization of recombinant, ureolytic Streptococcus mutans demonstrates an inverse relationship between dental plaque ureolytic capacity and cariogenicity. Infect Immun 2000; 68( 5): 2621–2629.
Margolis HC, Duckworth JH, Moreno EC . Composition and buffer capacity of pooled starved plaque fluid from caries-free and caries-susceptible individuals. J Dent Res 1988; 67( 12): 1476–1482.
van Wuyckhuyse BC, Perinpanayagam HE, Bevacqua D et al. Association of free arginine and lysine concentrations in human parotid saliva with caries experience. J Dent Res 1995; 74( 2): 686–690.
Chen YY, Weaver CA, Burne RA . Dual functions of Streptococcus salivarius urease. J Bacteriol 2000; 182( 16): 4667–4669.
Liu Y, Hu T, Zhang J et al. Characterization of the Actinomyces naeslundii ureolysis and its role in bacterial aciduricity and capacity to modulate pH homeostasis. Microbiol Res 2006; 161( 4): 304–310.
Morou-Bermudez E, Burne RA . Analysis of urease expression in Actinomyces naeslundii WVU45. Infect Immun 2000; 68( 12): 6670–6676.
Liu Y, Hu T, Jiang D et al. Analysis of urease gene expression by Actinomyces naeslundii in biofilm. J Dent Res 2006; 85( B): 315.
Marquis RE, Bender GR, Murray DR et al. Arginine deiminase system and bacterial adaptation to acid environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 1987; 53( 1): 198–200.
Rogers AH . Utilization of nitrogenous compounds by oral bacteria. Aust Dent J 1990; 35( 5): 468–471.
Liu Y, Nascimento MM, Schulte R et al. Characterization of the arginolytic microflora of human dental biofilms J Dent Res 2012; 91( A): 1262.
Griswold AR, Chen YY, Burne RA . Analysis of an agmatine deiminase gene cluster in Streptococcus mutans UA159. J Bacteriol 2004; 186( 6): 1902–1904.
Bardocz S . The role of dietary polyamines. Eur J Clin Nutr 1993; 47( 10): 683–690.
Sakakibara Y, Yanagisawa H . Agmatine deiminase from cucumber seedlings is a mono-specific enzyme: purification and characteristics. Protein Expr Purif 2003; 30( 1): 88–93.
Griswold AR, Nascimento MM, Burne RA . Distribution, regulation and role of the agmatine deiminase system in mutans streptococci. Oral Microbiol Immunol 2009; 24( 1): 79–82.
Sheng J, Baldeck JD, Nguyen PT et al. Alkali production associated with malolactic fermentation by oral streptococci and protection against acid, oxidative, or starvation damage. Can J Microbiol 2010; 56( 7): 539–547.
Sheng J, Marquis RE . Malolactic fermentation by Streptococcus mutans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2007; 272( 2): 196–201.
Burne RA, Marquis RE . Alkali production by oral bacteria and protection against dental caries. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2000; 193( 1): 1–6.
Liu Y, Hu T, Zhou XD . The relationship ureolysis and ecological balance of dental plaque. Intel J Stomatol 2003; 30( 3): 201–202, 205.
Park IS, Carr MB, Hausinger RP . In vitro activation of urease apoprotein and role of UreD as a chaperone required for nickel metallocenter assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994; 91( 8): 3233–3237.
Park IS, Hausinger RP . Requirement of carbon dioxide for in vitro assembly of the urease nickel metallocenter. Science 1995; 267( 5201): 1156–1158.
Liu Y, Hu T, Jiang D et al. Regulation of urease gene of Actinomyces naeslundii in biofilms in response to environmental factors. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2008; 278( 2): 157–163.
Liy Y, Dan J, Tao H et al. Regulation of urease expression of Actinomyces naeslundii in biofilms in response to pH and carbohydrate. Oral Microbiol Immunol 2008; 23( 4): 315–319.
Chen YY, Weaver CA, Mendelsohn DR et al. Transcriptional regulation of the Streptococcus salivarius 57.I urease operon. J Bacteriol 1998; 180( 21): 5769–5675.
Liu Y, Hu T, Zhang JY et al. The primary research on relevant factors influencing urease activity of Actinomyces naeslundii. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2007; 38( 4): 675–677.
Barcelona-Andres B, Marina A, Rubio V . Gene structure, organization, expression, and potential regulatory mechanisms of arginine catabolism in Enterococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol 2002; 184( 4): 6289–6300.
Dong Y, Chen YY, Snyder JA et al. Isolation and molecular analysis of the gene cluster for the arginine deiminase system from Streptococcus gordonii DL1. Appl Environ Microbiol 2002; 68( 11): 5549–5553.
Maghnouj A, de Sousa Cabral TF, Stalon V et al. The arcABDC gene cluster, encoding the arginine deiminase pathway of Bacillus licheniformis, and its activation by the arginine repressor argR. J Bacteriol 1998; 180( 24): 6468–6475.
Vander Wauven C, Pierard A, Kley-Raymann M et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants affected in anaerobic growth on arginine: evidence for a four-gene cluster encoding the arginine deiminase pathway. J Bacteriol 1984; 160( 3): 928–934.
Zuniga M, Champomier-Verges M, Zagorec M et al. Structural and functional analysis of the gene cluster encoding the enzymes of the arginine deiminase pathway of Lactobacillus sake. J Bacteriol 1998; 180( 16): 4154–4159.
Liu Y, Dong Y, Chen YY et al. Environmental and growth phase regulation of the Streptococcus gordonii arginine deiminase genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 2008; 74( 16): 5023–5030.
Lu CD, Winteler H, Abdelal A et al. The ArgR regulatory protein, a helper to the anaerobic regulator ANR during transcriptional activation of the arcD promoter in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 1991; 181( 8): 2459–2464.
Dong Y, Chen YY, Burne RA . Control of expression of the arginine deiminase operon of Streptococcus gordonii by CcpA and Flp. J Bacteriol 2004; 186( 8): 2511–2514.
Liu Y, Dong Y, Chen YY et al. Arginine deiminase gene regulation in Streptococcus gordonii. J Dent Res 2008; 87( B): 714.
Jakubovics NS, Gill SR, Iobst SE et al. Regulation of gene expression in a mixed-genus community: stabilized arginine biosynthesis in Streptococcus gordonii by coaggregation with Actinomyces naeslundii. J Bacteriol 2008; 190( 10): 3646–3657.
Liu Y, Burne RA . Multiple two-component systems modulate alkali generation in Streptococcus gordonii in response to environmental stresses. J Bacteriol 2009; 191( 23): 7353–7362.
Liu Y, Burne RA . The major autolysin of Streptococcus gordonii is subject to complex regulation and modulates stress tolerance, biofilm formation, and extracellular-DNA release. J Bacteriol 2011; 193( 11): 2826–2837.
Simon JP, Stalon V . Enzymes of agmatine degradation and the control of their synthesis in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol 1982; 152( 2): 676–681.
Driessen AJ, Smid EJ, Konings WN . Transport of diamines by Enterococcus faecalis is mediated by an agmatine-putrescine antiporter. J Bacteriol 1988; 170( 10): 4522–4527.
Nakada Y, Jiang Y, Nishijyo T et al. Molecular characterization and regulation of the aguBA operon, responsible for agmatine utilization in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J Bacteriol 2001; 183( 22): 6517–6524.
Arena ME, Fiocco D, Manca de Nadra MC et al. Characterization of a Lactobacillus plantarum strain able to produce tyramine and partial cloning of a putative tyrosine decarboxylase gene. Curr Microbiol 2007; 55( 3): 205–210.
Griswold AR, Jameson-Lee M, Burne RA . Regulation and physiologic significance of the agmatine deiminase system of Streptococcus mutans UA159. J Bacteriol 2006; 188( 3): 834–841.
Liu Y, Zeng L, Burne RA . AguR is required for induction of the Streptococcus mutans agmatine deiminase system by low pH and agmatine. Appl Environ Microbiol 2009; 75( 9): 2629–2637.
Liu Y, Burne RA . Multiple two-component systems of Streptococcus mutans regulate agmatine deiminase gene expression and stress tolerance. J Bacteriol 2009; 191( 23): 7363–7366.
Liu YL, Hu T, Zhang JY et al. A preliminary study of the modulation of Actinomyces naeslundii urease to the pH balance of dental biofilm. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue 2005; 14( 6): 605–607.
Liu Y, Hu T, Zhou X . The effect of ureolysis on the proliferation and acid-resistance of Actinomyces naeslundii. J Pract Stomatol 2006; 22( 2): 145–147.
Chen YY, Clancy KA, Burne RA . Streptococcus salivarius urease: genetic and biochemical characterization and expression in a dental plaque streptococcus. Infect Immun 1996; 64( 2): 585–592.
Morou-Bermudez E, Burne RA . Genetic and physiologic characterization of urease of Actinomyces naeslundii. Infect Immun 1999; 67( 2): 504–512.
Burne RA, Liu Y, Zeng L . Acid tolerance strategies of commensal and pathogenic oral streptococci. Proceedings of Society for General Microbiology Autumn 2010 Meeting; 6–9 September 2010; University of Nottingham: Nottingham, UK.
Nascimento MM, Gordan VV, Garvan CW et al. Correlations of oral bacterial arginine and urea catabolism with caries experience. Oral Microbiol Immunol 2009; 24( 2): 89–95.
Peterson S, Woodhead J, Crall J . Caries resistance in children with chronic renal failure: Plaque pH, salivary pH, and salivary composition. Pediatr Res 1985; 19( 8): 796–799.
Shu M, Morou-Bermudez E, Suárez-Pérez E et al. The relationship between dental caries status and dental plaque urease activity. Oral Microbiol Immunol 2007; 22( 1): 61–66.
Epstein SR, Mandel I, Scopp IW . Salivary composition and calculus formation in patients undergoing hemodialysis. J Periodontol 1980; 51( 6): 336–338.
Clancy A, Burne RA . Construction and characterization of a recombinant ureolytic Streptococcus mutans and its use to demonstrate the relationship of urease activity to pH modulating capacity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 1997; 151( 2): 205–211.
Peterson S, Woodhead J, Crall J . Caries resistance in children with chronic renal failure: plaque pH, salivary pH, and salivary composition. Pediatr Res 1985; 19( 8): 796–799.
Nascimento M, Liu Y, Kalra R et al. Arginine metabolism may confer caries resistance in children. J Dent Res 2012; 91( A): 714.
Morou-Bermudez E, Elias-Boneta A, Billings RJ et al. Urease activity in dental plaque and saliva of children during a three-year study period and its relationship with other caries risk factors. Arch Oral Biol 2011; 56( 11): 1282–1289.
Acevedo AM, Machado C, Rivera LE et al. The inhibitory effect of an arginine bicarbonate/calcium carbonate CaviStat-containing dentifrice on the development of dental caries in Venezuelan school children. J Clin Dent 2005; 16( 3): 63–70.
Acevedo AM, Montero M, Rojas-Sanchez F et al. Clinical evaluation of the ability of CaviStat in a mint confection to inhibit the development of dental caries in children. J Clin Dent 2008; 19( 1): 1–8.
Wang X, Peng D, Gan Y . Effects of urea and arginine-bicarbonate solutions on plaque pH. Proceedings of International Association of Dental Research Annual Meeting 2012; 20–23 June 2012. International Association of Dental Research: Iguacu FallBrazil.
Dewhirst FE, Chen T, Izard J et al. The human oral microbiome. J Bacteriol 2010; 192( 19): 5002–5017.
Burne R, Zeng L, Ahn SJ et al. Progress dissecting the oral microbiome in caries and health. Adv Dent Res 2012; 24( 2): 77–80.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research Grant DE10362.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, YL., Nascimento, M. & Burne, R. Progress toward understanding the contribution of alkali generation in dental biofilms to inhibition of dental caries. Int J Oral Sci 4, 135–140 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijos.2012.54
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijos.2012.54
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The oral microbiome in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular disease
Nature Reviews Cardiology (2023)
-
Functional changes in the oral microbiome after use of fluoride and arginine containing dentifrices: a metagenomic and metatranscriptomic study
Microbiome (2022)
-
Interspecies competition in oral biofilms mediated by Streptococcus gordonii extracellular deoxyribonuclease SsnA
npj Biofilms and Microbiomes (2022)
-
Oral and vaginal microbiota in selected field mice of the genus Apodemus: a wild population study
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Micro-PAD card for measuring total ammonia nitrogen in saliva
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2020)