Abstract
Background/Objectives:
Approximately 17% of obese Americans are free of the cardiometabolic risk factors, but few studies have compared responses to weight change in metabolically healthy obese (MHO) and metabolically healthy normal weight (MHNW) adults. We compared the impact of weight loss, weight maintenance and weight gain on cardiometabolic risk factors in the MHO and the MHNW.
Subjects/Methods:
Data were from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Multiple observations on 2710 participants were included, yielding 4541 observations of sequential 3-year intervals. Metabolically healthy was defined as absence of all components of metabolic syndrome excluding waist circumference. Mixed effects models were used to compare changes in each of five cardiometabolic risk factors within weight change categories (<−3% for weight loss, ±3% for weight maintenance and >3% for weight gain).
Results:
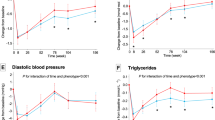
Weight loss was associated with comparable small changes or no changes in cardiometabolic risk factors in MHO and MHNW individuals. Weight gain was associated with larger increases in systolic (8.6 vs 6.2 mm Hg) and diastolic (3.9 vs 2.5 mm Hg) blood pressure, triglycerides (21.9 vs 15.8 mg/dl) and glucose (4.9 vs 1.9 mg/dl) in MHO individuals compared with MHNW individuals. Weight maintenance was associated with larger increases in triglycerides (10.0 vs 6.4 mg/dl) and glucose (1.7 vs 0.9 mg/dl) in MHO compared with MHNW individuals. MHO weight losers had more favorable changes in the five cardiometabolic risk factors compared to MHO weight maintainers (P<0.02) or gainers (P<0.0001).
Conclusions:
This work showed differences between MHNW and MHO adults and supports recommendations for weight loss in the MHO in order to avoid increases in risk factors associated with weight maintenance and weight gain.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jensen MD, Ryan DH, Apovian CM, Ard JD, Comuzzie AG, Donato KA et al2013 AHA/ACC/TOS Guideline for the Management of Overweight and Obesity in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. Circulation 2014; 129 (25 Suppl 2): S102–S138.
Wildman RP, Muntner P, Reynolds K, McGinn AP, Rajpathak S, Wylie-Rosett J et al. The obese without cardiometabolic risk factor clustering and the normal weight with cardiometabolic risk factor clustering: prevalence and correlates of 2 phenotypes among the US population (NHANES 1999-2004). Arch Intern Med 2008; 168: 1617–1624.
Karelis AD . To be obese—does it matter if you are metabolically healthy? Nat Rev Endocrinol 2011; 7: 699–700.
Aucott L, Poobalan A, Smith WC, Avenell A, Jung R, Broom J et al. Weight loss in obese diabetic and non-diabetic individuals and long-term diabetes outcomes—a systematic review. Diabetes Obes Metab 2004; 6: 85–94.
Aucott L, Poobalan A, Smith WC, Avenell A, Jung R, Broom J . Effects of weight loss in overweight/obese individuals and long-term hypertension outcomes: a systematic review. Hypertension 2005; 45: 1035–1041.
Kantartzis K, Machann J, Schick F, Rittig K, Machicao F, Fritsche A et al. Effects of a lifestyle intervention in metabolically benign and malign obesity. Diabetologia 2011; 54: 864–868.
Janiszewski PM, Ross R . Effects of weight loss among metabolically healthy obese men and women. Diabetes Care 2010; 33: 1957–1959.
Shin MJ, Hyun YJ, Kim OY, Kim JY, Jang Y, Lee JH . Weight loss effect on inflammation and LDL oxidation in metabolically healthy but obese (MHO) individuals: low inflammation and LDL oxidation in MHO women. Int J Obes (Lond) 2006; 30: 1529–1534.
Karelis AD, Messier V, Brochu M, Rabasa-Lhoret R . Metabolically healthy but obese women: effect of an energy-restricted diet. Diabetologia 2008; 51: 1752–1754.
McLaughlin T, Abbasi F, Lamendola C, Liang L, Reaven G, Schaaf P et al. Differentiation between obesity and insulin resistance in the association with C-reactive protein. Circulation 2002; 106: 2908–2912.
Sesti G, Folli F, Perego L, Hribal ML, Pontiroli AE . Effects of weight loss in metabolically healthy obese subjects after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding and hypocaloric diet. PLoS One 2011; 6: e17737.
Ruiz JR, Ortega FB, Labayen I . A weight loss diet intervention has a similar beneficial effect on both metabolically abnormal obese and metabolically healthy but obese premenopausal women. Ann Nutr Metab 2013; 62: 223–230.
Dalzill C, Nigam A, Juneau M, Guilbeault V, Latour E, Mauriege P et al. Intensive lifestyle intervention improves cardiometabolic and exercise parameters in metabolically healthy obese and metabolically unhealthy obese individuals. Can J Cardiol 2014; 30: 434–440.
The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study: design and objectives. Am J Epidemiol 1989; 129: 687–702.
Nagele U, Hagele EO, Sauer G, Wiedemann E, Lehmann P, Wahlefeld AW et al. Reagent for the enzymatic determination of serum total triglycerides with improved lipolytic efficiency. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 1984; 22: 165–174.
Warnick GR, Benderson J, Albers JJ . Dextran sulfate-Mg2+ precipitation procedure for quantitation of high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol. Clin Chem 1982; 28: 1379–1388.
Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report on a WHO Consultation on Obesity. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser 2000; 894: i-xii, 1–253.
Stevens J, Truesdale KP, McClain JE, Cai J . The definition of weight maintenance. Int J Obes (Lond) 2006; 30: 391–399.
Grundy SM, Brewer HB Jr, Cleeman JI, Smith SC Jr, Lenfant C et al. Definition of metabolic syndrome: Report of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/American Heart Association conference on scientific issues related to definition. Circulation 2004; 109: 433–438.
Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. 10-year follow-up of diabetes incidence and weight loss in the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study. Lancet 2009; 374: 1677–1686.
Lindstrom J, Ilanne-Parikka P, Peltonen M, Aunola S, Eriksson JG, Hemio K et al. Sustained reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes by lifestyle intervention: follow-up of the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study. Lancet 2006; 368: 1673–1679.
Look AHEAD Research Group. Long-term effects of a lifestyle intervention on weight and cardiovascular risk factors in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: four-year results of the Look AHEAD trial. Arch Intern Med 2010; 170: 1566–1575.
Sjostrom CD, Lystig T, Lindroos AK . Impact of weight change, secular trends and ageing on cardiovascular risk factors: 10-year experiences from the SOS study. Int J Obes (Lond) 2011; 35: 1413–1420.
Norman JE, Bild D, Lewis CE, Liu K, West DS . The impact of weight change on cardiovascular disease risk factors in young black and white adults: the CARDIA study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2003; 27: 369–376.
Truesdale KP, Stevens J, Lewis CE, Schreiner PJ, Loria CM, Cai J . Changes in risk factors for cardiovascular disease by baseline weight status in young adults who maintain or gain weight over 15 years: the CARDIA study. Int J Obes (Lond) 2006; 30: 1397–1407.
Truesdale KP, Stevens J, Cai J . Nine-year changes in cardiovascular disease risk factors with weight maintenance in the atherosclerosis risk in communities cohort. Am J Epidemiol 2007; 165: 890–900.
Wildman RP, Kaplan R, Manson JE, Rajkovic A, Connelly SA, Mackey RH et al. Body size phenotypes and inflammation in the Women's Health Initiative Observational Study. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2011; 19: 1482–1491.
Chang Y, Ryu S, Suh BS, Yun KE, Kim CW, Cho SI . Impact of BMI on the incidence of metabolic abnormalities in metabolically healthy men. Int J Obes (Lond) 2012; 36: 1187–1194.
Bobbioni-Harsch E, Pataky Z, Makoundou V, Laville M, Disse E, Anderwald C et al. From metabolic normality to cardiometabolic risk factors in subjects with obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2012; 20: 2063–2069.
Bo S, Musso G, Gambino R, Villois P, Gentile L, Durazzo M et al. Prognostic implications for insulin-sensitive and insulin-resistant normal-weight and obese individuals from a population-based cohort. Am J Clin Nutr 2012; 96: 962–969.
Hwang LC, Bai CH, Sun CA, Chen CJ . Prevalence of metabolically healthy obesity and its impacts on incidences of hypertension, diabetes and the metabolic syndrome in Taiwan. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2012; 21: 227–233.
Lee SK, Kim SH, Cho GY, Baik I, Lim HE, Park CG et al. Obesity phenotype and incident hypertension: a prospective community-based cohort study. J Hypertens 2013; 31: 145–151.
Bradshaw PT, Monda KL, Stevens J . Metabolic syndrome in healthy obese, overweight, and normal weight individuals: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2013; 21: 203–209.
Bell JA, Kivimaki M, Hamer M . Metabolically healthy obesity and risk of incident type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Obes Rev 2014; 15: 504–515.
Fan J, Song Y, Chen Y, Hui R, Zhang W . Combined effect of obesity and cardio-metabolic abnormality on the risk of cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Int J Cardiol 2013; 168: 4761–4768.
Kramer CK, Zinman B, Retnakaran R . Are metabolically healthy overweight and obesity benign conditions? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 2013; 159: 758–769.
Soriguer F, Gutierrez-Repiso C, Rubio-Martin E, Garcia-Fuentes E, Almaraz MC, Colomo N et al. Metabolically healthy but obese, a matter of time? Findings from the prospective Pizarra study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013; 98: 2318–2325.
Redmond N, Baer HJ, Hicks LS . Health behaviors and racial disparity in blood pressure control in the national health and nutrition examination survey. Hypertension 2011; 57: 383–389.
Acknowledgements
The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study is carried out as a collaborative study supported by National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute contracts (HHSN268201100005C, HHSN268201100006C, HHSN268201100007C, HHSN268201100008C, HHSN268201100009C, HHSN268201100010C, HHSN268201100011C and HHSN268201100012C). We thank the staff and participants of the ARIC study for their important contributions. This study was not supported by funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on International Journal of Obesity website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, Z., Truesdale, K., Bradshaw, P. et al. Three-year weight change and cardiometabolic risk factors in obese and normal weight adults who are metabolically healthy: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Int J Obes 39, 1203–1208 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.56
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.56
This article is cited by
-
Obesity, kidney dysfunction and hypertension: mechanistic links
Nature Reviews Nephrology (2019)
-
Long-term metabolic risk for the metabolically healthy overweight/obese phenotype
International Journal of Obesity (2018)
-
Fatty liver as a risk factor for progression from metabolically healthy to metabolically abnormal in non-overweight individuals
Endocrine (2017)